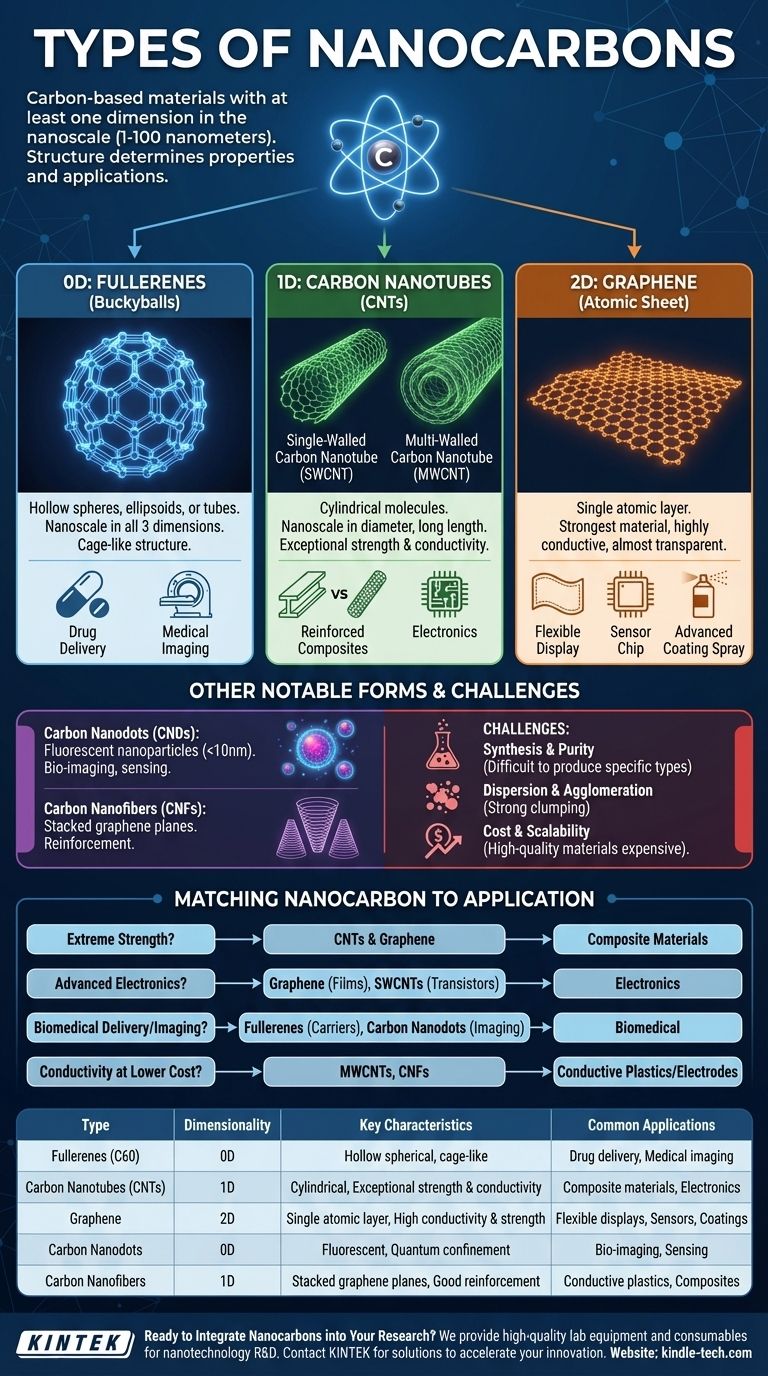
In essence, nanocarbons are materials built primarily from carbon atoms with at least one dimension in the nanoscale (1-100 nanometers). The main types are classified by their structure and dimensionality: zero-dimensional (0D) fullerenes, one-dimensional (1D) carbon nanotubes, and two-dimensional (2D) graphene, along with other variations like carbon nanodots and nanofibers. These structural differences give each type vastly different and often extraordinary properties.
The core takeaway is that the geometric arrangement of carbon atoms—whether they form a sphere, a tube, or a sheet—is the single most important factor determining a nanocarbon's properties and its potential applications. Understanding this "structure-property relationship" is the key to navigating this class of materials.

The Framework: Dimensionality of Nanocarbons
The most effective way to understand the family of nanocarbons is by their dimensionality. This refers to the number of dimensions that are not confined to the nanoscale.
0D: Fullerenes (The "Buckyball")
Fullerenes are molecules composed entirely of carbon, forming a hollow sphere, ellipsoid, or tube. The most famous is Buckminsterfullerene (C60), which has a soccer-ball structure of 60 carbon atoms.
As zero-dimensional materials, they are nanoscale in all three dimensions, behaving like individual particles or molecules. Their unique cage-like structure allows them to encapsulate other atoms or molecules, making them interesting for drug delivery and medical imaging applications.
1D: Carbon Nanotubes (The Rolled Sheet)
Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) are cylindrical molecules made of rolled-up sheets of graphene. They are one-dimensional because they are nanoscale in diameter but can be much longer, creating a tube or fiber-like structure.
There are two primary types:
- Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (SWCNTs): Consist of a single atomic layer of graphene rolled into a cylinder. Their electronic properties (metallic or semiconducting) depend on the angle of this roll.
- Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs): Comprise multiple concentric cylinders of graphene. They are typically easier and cheaper to produce but have more complex properties.
CNTs are renowned for their exceptional tensile strength (stronger than steel) and high electrical and thermal conductivity, making them ideal for reinforcing composites and for next-generation electronics.
2D: Graphene (The Atomic Sheet)
Graphene is a single, flat layer of carbon atoms arranged in a two-dimensional honeycomb lattice. It is the fundamental building block for other nanocarbons like CNTs and fullerenes.
As a two-dimensional material, it is only one atom thick but can extend indefinitely in the other two dimensions. Graphene is the strongest material ever tested, is highly conductive, and is almost completely transparent. These properties make it a candidate for flexible displays, ultra-efficient sensors, and advanced coatings.
Other Notable Forms
While the "big three" are fullerenes, CNTs, and graphene, other important structures exist.
Carbon Nanodots (CNDs) are small carbon nanoparticles, typically under 10 nm, that exhibit quantum confinement and fluorescence. This light-emitting property makes them excellent for bio-imaging and sensing.
Carbon Nanofibers (CNFs) are structurally distinct from CNTs, with graphene planes stacked in various ways (like cones or cups). They don't have the same perfect atomic structure as CNTs but are useful as reinforcement materials in composites.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Despite their remarkable properties, working with nanocarbons involves significant practical challenges that are critical to understand.
Synthesis and Purity
Producing a single, specific type of nanocarbon is extremely difficult. For example, synthesizing SWCNTs often results in a mix of metallic and semiconducting tubes, which must be separated for most electronic applications—a costly and complex process.
Dispersion and Agglomeration
Nanocarbons have a strong tendency to clump together due to powerful van der Waals forces. This makes it very difficult to disperse them evenly into a polymer, solvent, or other matrix, which is essential to realizing their strengthening or conductive properties.
Cost and Scalability
High-quality, high-purity nanocarbons—especially SWCNTs and large-area single-layer graphene—remain very expensive to produce at an industrial scale. This cost barrier is a primary reason they have not yet replaced conventional materials in many proposed applications.
Matching the Nanocarbon to the Application
Your choice depends entirely on the primary property you need to leverage for your project.
- If your primary focus is extreme mechanical strength: Carbon nanotubes (both SWCNTs and MWCNTs) and graphene are the leading candidates for creating ultra-strong, lightweight composite materials.
- If your primary focus is advanced electronics: Graphene is ideal for transparent conductive films, while specific semiconducting SWCNTs are being explored for next-generation transistors.
- If your primary focus is biomedical delivery or imaging: Fullerenes offer a cage-like structure for carrying drug molecules, and carbon nanodots provide excellent, non-toxic fluorescence for cellular imaging.
- If your primary focus is improving conductivity at a lower cost: Multi-walled carbon nanotubes and carbon nanofibers offer a good balance of performance and cost for applications like conductive plastics or battery electrodes.
Ultimately, navigating the world of nanocarbons requires a clear understanding that their geometry dictates their function.
Summary Table:
| Type | Dimensionality | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fullerenes (C60) | 0D | Hollow spherical molecules, cage-like structure | Drug delivery, medical imaging |
| Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) | 1D | Cylindrical tubes, exceptional strength & conductivity | Composite materials, electronics |
| Graphene | 2D | Single atomic layer, high conductivity & strength | Flexible displays, sensors, coatings |
| Carbon Nanodots | 0D | Fluorescent nanoparticles, quantum confinement | Bio-imaging, sensing |
| Carbon Nanofibers | 1D | Stacked graphene planes, good reinforcement | Conductive plastics, composites |
Ready to Integrate Nanocarbons into Your Research?
Understanding the different types of nanocarbons is the first step. The next is selecting the right materials and equipment for your specific application. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for nanotechnology research and development.
Whether you're working with carbon nanotubes for composite materials, graphene for electronics, or fullerenes for biomedical applications, we have the tools and expertise to support your work. Our products help researchers overcome common challenges like dispersion, purity, and scalability.
Let us help you unlock the potential of nanocarbons in your lab. Contact our experts today to discuss your project needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can accelerate your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of production of carbon nanotubes? From Lab Pioneers to Industrial Giants
- What is CVD lab grown diamond? A Real Diamond Grown in a Lab
- What are the methods of synthesis for carbon nanotubes? A Guide to Arc Discharge, Laser Ablation & CVD
- Can silicon be sputtered? A Guide to RF & DC Methods for Thin Film Deposition
- How is thin film used as coating material? A Guide to Enhancing Material Performance
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance
- What is the thickness of physical Vapour deposition? A Guide to Optimizing Your Coating Performance
- What are the disadvantages of ITO? Key Limitations for Flexible & Cost-Effective Electronics



















