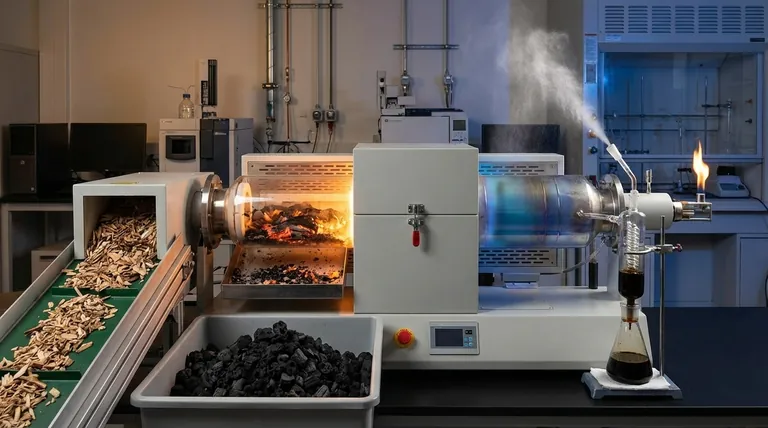
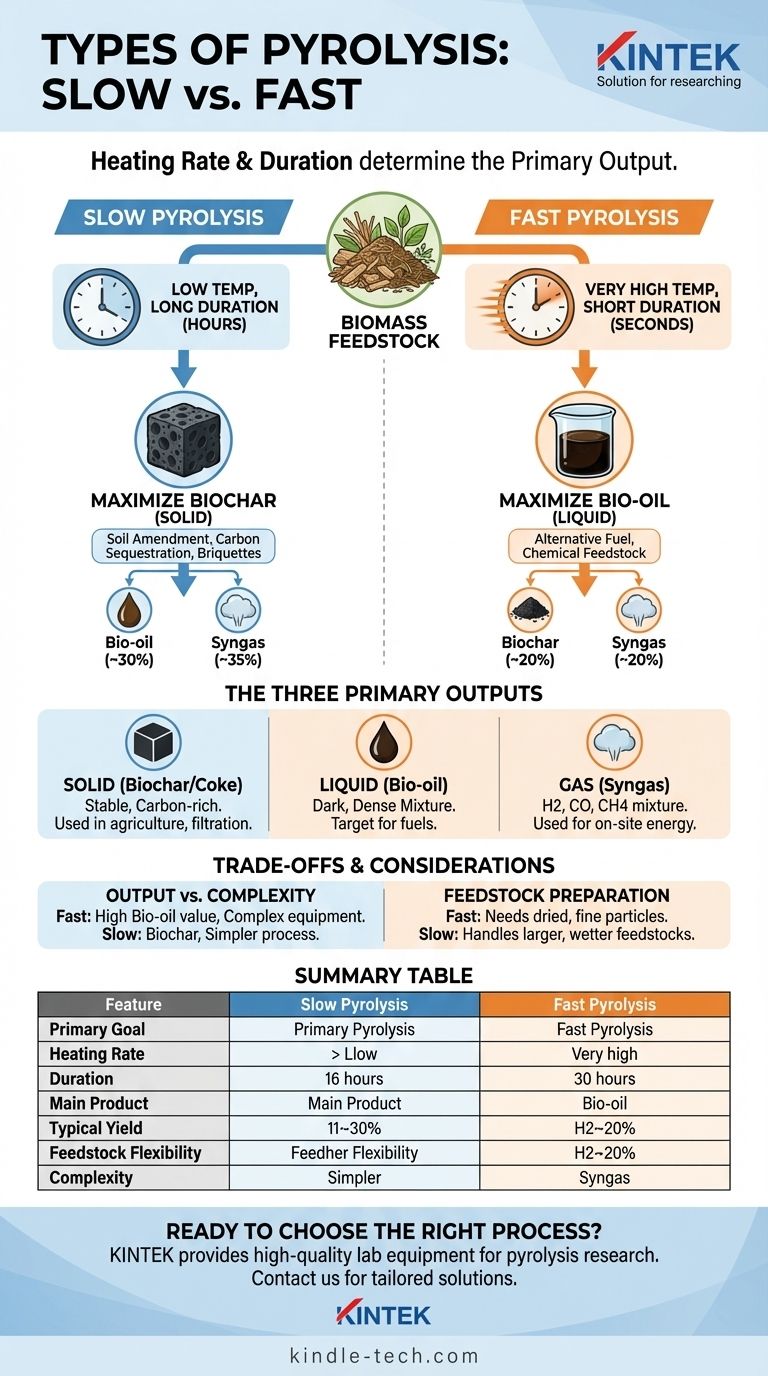
The primary types of pyrolysis are categorized by their heating rate and duration: slow and fast pyrolysis. These two methods are fundamentally different in their approach and the products they are designed to create. Slow pyrolysis is a long process, taking several hours, used to maximize the output of solid biochar, while fast pyrolysis is completed in seconds to maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil.
The "type" of pyrolysis you choose is not just a technical detail; it is a strategic decision that directly controls the final output. The core trade-off is between producing a solid for soil amendment and carbon sequestration (biochar from slow pyrolysis) or a liquid fuel source (bio-oil from fast pyrolysis).

The Core Distinction: Process Speed and Temperature
The fundamental difference between pyrolysis types lies in the rate at which biomass is heated and the time it is exposed to that heat. This determines which chemical reactions dominate and, therefore, which products are formed.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Biochar
Slow pyrolysis involves heating feedstock at a low temperature over a long period, often several hours. This process is optimized to produce the maximum amount of solid residue.
The classic example of slow pyrolysis is the traditional method of making charcoal from wood. Its primary product is biochar, a stable, carbon-rich solid.
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing Bio-Oil
Fast pyrolysis uses a very high heating rate and a short reaction time, typically less than two seconds. This process rapidly breaks down organic materials before they can form solid char.
This method is the most common for industrial applications aiming to create liquid fuels. It typically yields around 60% bio-oil, 20% biochar, and 20% syngas.
Understanding the Three Primary Outputs
Regardless of the process speed, pyrolysis breaks down feedstock into three distinct product streams: a solid, a liquid, and a gas. The ratio of these products is what each pyrolysis type controls.
The Solid Product: Biochar or Coke
This is the stable, carbon-rich solid material left after the volatile components have been driven off.
It is commonly used in agriculture as a soil amendment, for producing energy briquettes, or as a sorbent for filtration.
The Liquid Product: Bio-Oil
Bio-oil is a dark, dense liquid mixture of hundreds of organic compounds. It is the primary target of fast pyrolysis.
This liquid can be used as an alternative industrial fuel or further refined into transportation fuels like biodiesel and other valuable chemicals.
The Gaseous Product: Syngas
This non-condensable gas mixture contains components like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane.
In most modern pyrolysis plants, the syngas is captured and burned on-site to provide the heat needed to run the process, making the system more energy-efficient.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a pyrolysis method involves balancing operational complexity against the desired output. Each approach comes with distinct advantages and challenges.
Output vs. Complexity
Fast pyrolysis yields valuable liquid bio-oil but requires more sophisticated equipment and precise control over temperature and feedstock particle size.
Slow pyrolysis is a simpler, more robust, and more forgiving process, but its primary output, biochar, often has a lower market value than liquid fuel.
Feedstock Preparation
Fast pyrolysis demands that the input material be dried and ground into fine particles. This ensures the rapid heat transfer necessary for the reaction to work correctly.
Slow pyrolysis can handle larger, more varied, and wetter feedstocks, reducing the need for extensive pre-processing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal pyrolysis method is defined entirely by your end goal. By understanding what you want to produce, you can select the appropriate process.
- If your primary focus is on soil amendment and carbon sequestration: Slow pyrolysis is the direct path to producing stable, high-quality biochar.
- If your primary focus is on producing liquid fuels or chemical feedstocks: Fast pyrolysis is the necessary choice to maximize the yield of bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction with energy recovery: Either method is effective, as the syngas can be used to power the system and the outputs (char and oil) are dense, valuable commodities.
Understanding these types transforms pyrolysis from a single process into a versatile tool for converting diverse feedstocks into specific, valuable resources.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Slow Pyrolysis | Fast Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Maximize biochar production | Maximize bio-oil production |
| Heating Rate | Low | Very High |
| Process Duration | Hours | Seconds |
| Main Product | Biochar (solid) | Bio-oil (liquid) |
| Typical Yield | ~35% Biochar, ~30% Bio-oil, ~35% Syngas | ~20% Biochar, ~60% Bio-oil, ~20% Syngas |
| Feedstock Flexibility | Handles larger, wetter, more varied feedstocks | Requires dried, finely ground feedstocks |
| Complexity | Simpler, more robust process | Requires sophisticated equipment & precise control |
Ready to choose the right pyrolysis process for your lab or production needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're focusing on biochar for soil amendment or bio-oil for fuel production, our expertise and reliable equipment can help you achieve precise and efficient results.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's pyrolysis projects with tailored solutions and expert guidance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision
- At what temperature does wood pyrolysis begin? Control the Process for Biochar, Bio-Oil, or Syngas
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data



















