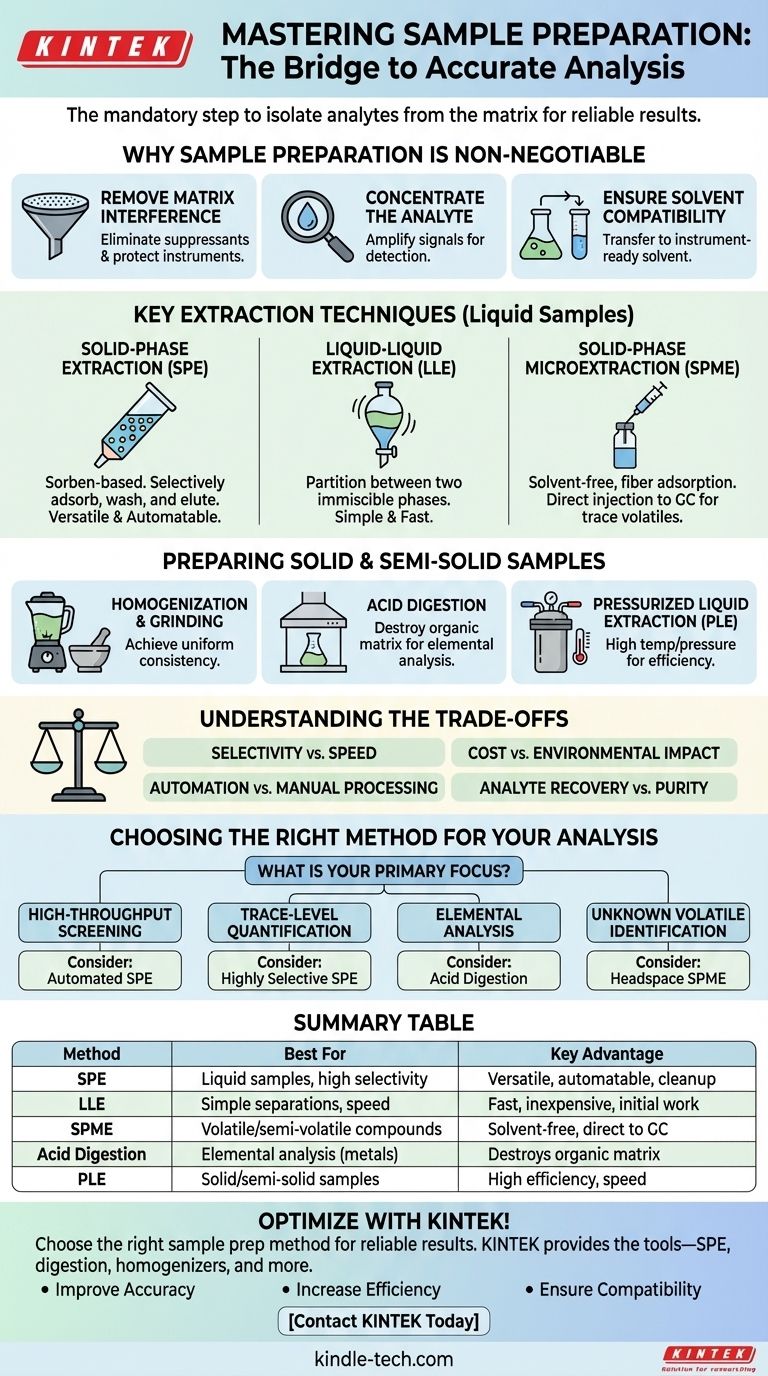
In analytical science, sample preparation is the mandatory bridge between collecting a raw sample and performing an instrumental analysis. It involves a series of steps to isolate the components of interest (analytes) from the rest of the material (the matrix). The primary methods include extraction techniques like solid-phase extraction (SPE), liquid-liquid extraction (LLE), and specialized approaches for solid materials like digestion and homogenization.
The choice of a sample preparation method is a strategic decision dictated by your starting material, your target analyte, and the requirements of your analytical instrument. The universal goal is to clean, concentrate, and transfer the analyte into a suitable solvent to ensure a reliable and accurate measurement.
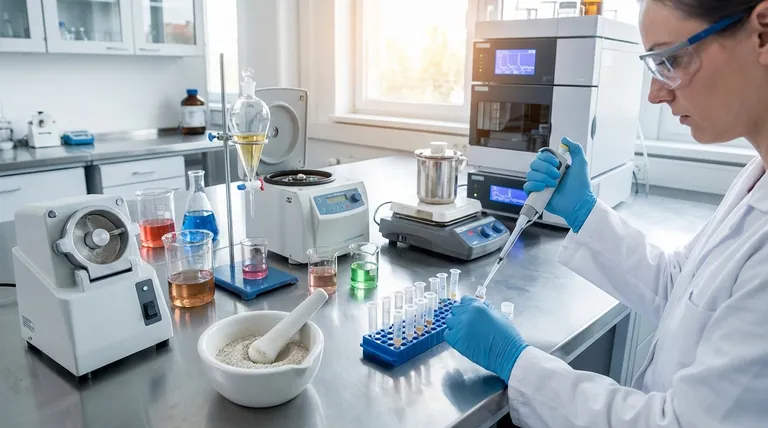

Why Sample Preparation is Non-Negotiable
Every analytical instrument has limitations. Sample preparation is designed to overcome these by conditioning the sample so the instrument can produce a clean, accurate signal.
Removing Matrix Interference
The matrix is everything in your sample that is not your analyte of interest. This can include proteins, salts, fats, pigments, and other complex biomolecules or environmental components.
These interfering substances can suppress the instrument's signal, create false positives, or physically damage sensitive equipment like a chromatography column. A good preparation method selectively removes this matrix.
Concentrating the Analyte
Often, the analyte is present at a very low concentration, sometimes below the instrument's limit of detection.
Most extraction techniques are designed to take a large volume of a sample and concentrate the target analyte into a much smaller final volume, amplifying its signal for measurement.
Ensuring Solvent Compatibility
The final sample must be dissolved in a solvent that is compatible with the analytical system. For example, a sample for gas chromatography must be volatile, while a sample for reverse-phase liquid chromatography typically needs to be in a water-miscible solvent.
Sample preparation often includes a solvent exchange step to transfer the purified analyte into the ideal final solvent.
Key Extraction Techniques
The most common methods involve partitioning the analyte between different physical phases to achieve separation.
Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE)
SPE is a workhorse technique that uses a solid adsorbent material (the sorbent), typically packed into a small cartridge. The liquid sample is passed through the cartridge.
Based on the chosen sorbent and solvents, the analyte can be made to stick to the sorbent while interferences are washed away. The clean analyte is then rinsed off (eluted) with a different solvent for collection. It is highly versatile and easy to automate.
Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE)
LLE is a classic method that separates compounds based on their relative solubilities in two immiscible liquids, typically water and an organic solvent.
The sample is shaken with the two liquids in a separatory funnel. The analyte partitions, or moves preferentially, into the liquid phase where it is more soluble, leaving many impurities behind. While simple, it often uses large volumes of organic solvents.
Solid-Phase Microextraction (SPME)
SPME is a modern, solvent-free evolution of SPE. It uses a small, coated fiber that is exposed directly to a liquid sample or to the vapor above it (headspace).
Analytes adsorb onto the fiber, which is then retracted and injected directly into an analytical instrument, usually a gas chromatograph. This method is excellent for concentrating volatile and semi-volatile organic compounds.
Preparing Solid and Semi-Solid Samples
When the starting material isn't a simple liquid, initial processing steps are required to liberate the analytes.
Homogenization and Grinding
Solid samples like tissue, food, or soil are heterogeneous. To analyze a representative portion, they must be homogenized into a uniform consistency using tools like blenders, bead beaters, or a mortar and pestle.
Digestion for Elemental Analysis
To measure the concentration of heavy metals (e.g., lead, mercury), the entire organic matrix must be destroyed. This is achieved through acid digestion, where the sample is heated with strong acids, leaving only the inorganic elements dissolved in a simple aqueous solution for analysis by techniques like ICP-MS.
Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE)
Also known as Accelerated Solvent Extraction (ASE), this technique uses common solvents at elevated temperatures and pressures to extract analytes from solid samples. The high pressure keeps the solvent liquid above its normal boiling point, dramatically increasing its extraction efficiency and speed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single method is perfect. The choice always involves balancing competing factors.
Selectivity vs. Speed
LLE is generally fast and simple but not very selective, meaning it may not provide a perfectly clean sample. SPE, particularly with specialized sorbents, offers far greater selectivity but requires more complex method development.
Cost and Environmental Impact
Traditional methods like LLE can be inexpensive per sample but generate significant volumes of hazardous solvent waste. Modern techniques like SPME are "greener" and use no solvent, but the initial cost of fibers and holders can be higher.
Automation vs. Manual Processing
Manual LLE is flexible but labor-intensive and prone to variability. SPE is easily automated, allowing for high throughput and excellent reproducibility, but this requires a significant capital investment in robotics.
Analyte Recovery vs. Purity
An aggressive cleanup method might result in a very pure final sample but may also lead to some loss of the target analyte. Your method must be optimized to provide a sample that is clean enough while maximizing the analyte recovery.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Analysis
Your choice should be guided by your analytical goal, your budget, and the nature of your sample.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput screening: Consider automated SPE systems or simpler "dilute-and-shoot" approaches if matrix effects can be managed.
- If your primary focus is trace-level quantification of a single analyte: A highly selective method like affinity-based SPE or a multi-step cleanup is likely required.
- If your primary focus is elemental analysis (metals) in a complex matrix: Acid digestion is the essential and non-negotiable first step.
- If your primary focus is identifying unknown volatile compounds in a food or fragrance: Headspace SPME is an ideal, solvent-free starting point.
Ultimately, the best sample preparation strategy is the one that most reliably and reproducibly delivers your analyte to the instrument in a clean, compatible, and concentrated form.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE) | Liquid samples, high selectivity | Versatile, easy to automate, excellent cleanup |
| Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE) | Simple separations, speed | Fast, inexpensive, good for initial separations |
| Solid-Phase Microextraction (SPME) | Volatile/semi-volatile compounds | Solvent-free, direct injection to GC, excellent for trace analysis |
| Acid Digestion | Elemental analysis (e.g., metals) | Destroys organic matrix, essential for ICP-MS |
| Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE) | Solid/semi-solid samples | High efficiency and speed with common solvents |
Optimize your lab's sample preparation workflow with KINTEK!
Choosing the right sample prep method is critical for achieving accurate, reliable results from your analytical instruments. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the tools you need for efficient and effective sample preparation—from SPE cartridges and digestion systems to homogenizers and extraction equipment.
We serve a wide range of laboratory needs, helping you:
- Improve Accuracy: Reduce matrix interference and concentrate analytes for clearer signals.
- Increase Efficiency: Leverage automated solutions for high-throughput processing.
- Ensure Compatibility: Prepare samples in solvents ideal for your specific analytical technique.
Let our expertise guide you to the optimal sample preparation strategy for your application. Contact us today to discuss your lab's specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What is the particle size for XRD analysis? Optimize Your Results with the Right Preparation
- What are the different types of laboratory mills? Choose the Right Grinder for Your Sample Material
- What is the function of a mortar and pestle in ZnS nanoparticle prep? Optimize Your Sample Refinement
- Why is an alumina mortar used for grinding dried Yttrium Oxide precursor materials? Ensure Maximum Purity and Quality
- Why is an agate mortar and pestle preferred for grinding MAX phase? Ensure Sample Purity & Zero Contamination



















