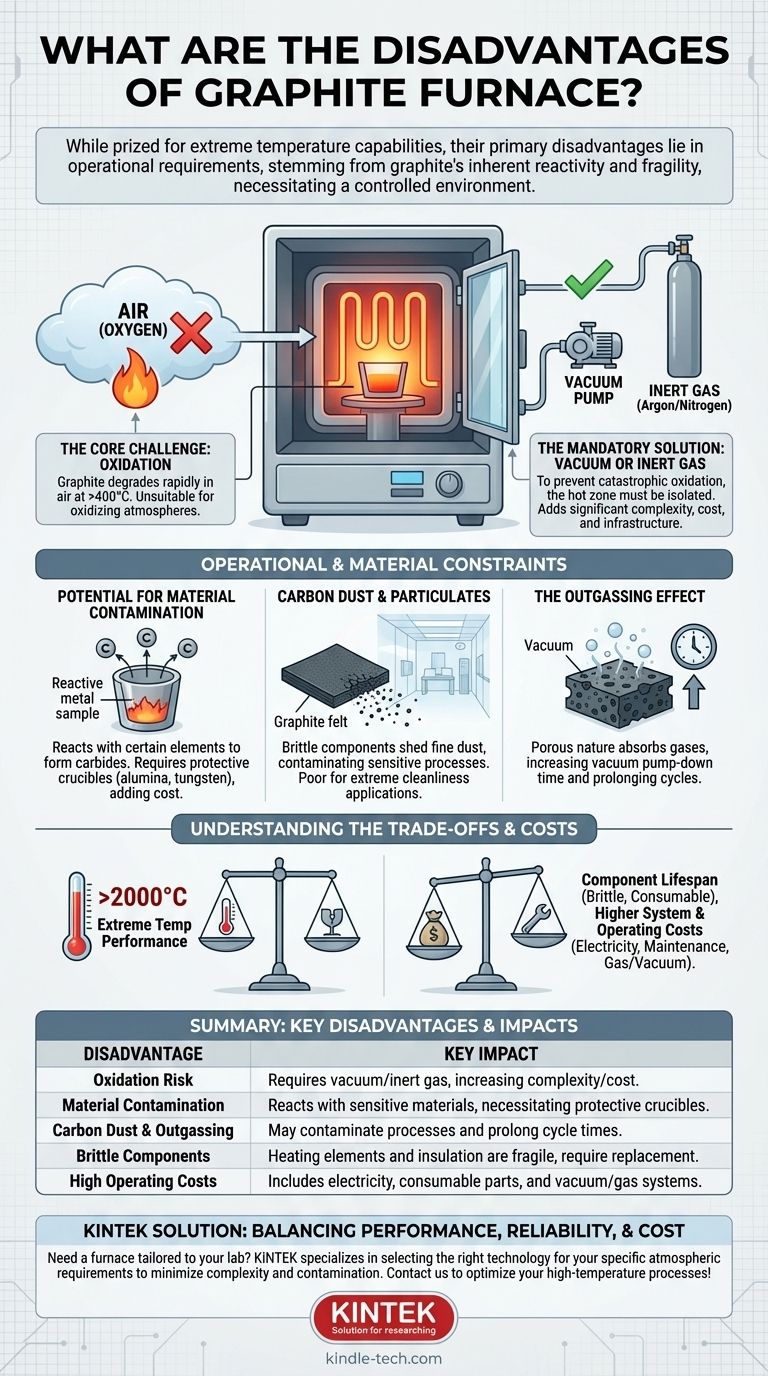
While prized for their extreme temperature capabilities, the primary disadvantages of graphite furnaces are not in their performance but in their operational requirements. The core drawbacks stem from graphite's inherent reactivity with oxygen at high temperatures, its potential for chemical interaction with certain materials, and the fragility of its components. These factors necessitate a controlled operating environment, which adds significant complexity and cost.
The exceptional high-temperature performance of a graphite furnace is fundamentally tied to a critical trade-off: it must operate within a protective vacuum or inert gas atmosphere. This requirement is the source of its main disadvantages, introducing challenges in material compatibility, contamination control, and operational cost.
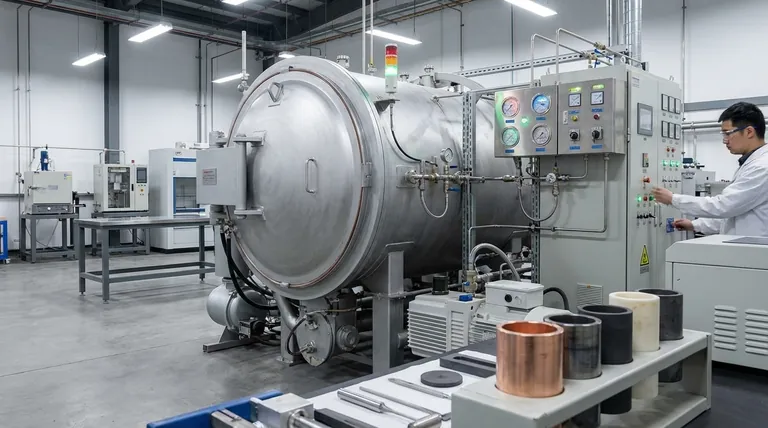

The Core Challenge: Graphite's Chemical Instability
The defining limitation of any graphite furnace is the chemical nature of carbon itself. This property dictates how the furnace must be designed and operated.
The Problem of Oxidation
Graphite reacts readily with oxygen at elevated temperatures, beginning as low as 400-500°C. In practice, this means it will rapidly degrade and essentially "burn away" if heated in the presence of air.
This single fact makes a graphite furnace completely unsuitable for any high-temperature process conducted in an oxidizing atmosphere.
The Mandatory Solution: Vacuum or Inert Gas
To prevent catastrophic oxidation, the furnace's hot zone must be isolated from air. This is achieved in two ways:
- Vacuum: The chamber is evacuated using a system of pumps to remove the air.
- Inert Gas: The chamber is filled with a non-reactive gas, such as argon or nitrogen, to displace the air.
This requirement adds significant complexity, including the need for a sealed vacuum chamber, robust pumping systems, gas delivery infrastructure, and precise atmospheric controls.
Operational and Material Constraints
Beyond the need for a controlled atmosphere, using a graphite furnace introduces several other practical limitations.
Potential for Material Contamination
At very high temperatures, graphite can react with certain elements to form carbides. This can be a problem when processing reactive metals (e.g., titanium, zirconium, tungsten), as the sample can become contaminated with carbon, or the furnace components can be damaged.
To prevent this, samples must often be placed in protective crucibles made of inert materials like alumina, molybdenum, or tungsten, adding another layer of complexity and cost.
Carbon Dust and Particulates
Graphite components, especially felt insulation, can be brittle and shed fine carbon dust over time. This dust can contaminate sensitive processes or high-purity materials, making graphite furnaces a poor choice for applications demanding extreme cleanliness, such as semiconductor manufacturing.
The Outgassing Effect
The porous nature of graphite allows it to absorb significant amounts of air and moisture when the chamber is open. Upon heating under vacuum, these trapped gases are slowly released in a process called outgassing.
This phenomenon can dramatically increase the time it takes to reach the desired vacuum level, extending the overall process cycle time.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Costs
The decision to use a graphite furnace involves balancing its unique capabilities against its inherent costs and fragility.
Component Lifespan and Brittleness
Graphite heating elements and shielding are brittle and susceptible to damage from mechanical shock or improper handling. They are considered consumable parts.
Furthermore, repeated thermal cycling (heating and cooling) induces stress that can lead to cracking and eventual failure, necessitating periodic and often costly replacement.
Higher System and Operating Costs
While the graphite material itself can be cost-effective, the total cost of ownership is high. The initial investment must include the furnace chamber plus the essential vacuum and/or inert gas control systems.
Ongoing operating costs include the electricity to reach high temperatures and the recurring expense of replacing the consumable graphite elements, shields, and insulation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if a graphite furnace is appropriate, you must weigh its performance against the demands of your specific process.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures (>2000 °C) for non-oxidizing materials: A graphite furnace is often the best or only choice, provided you can manage the required vacuum or inert atmosphere.
- If your process involves materials sensitive to carbon contamination: You must factor in the cost of high-purity furnace components and protective crucibles to act as a barrier.
- If your work involves heating materials in air or an oxidizing atmosphere: A graphite furnace is fundamentally unsuitable, and you should consider a furnace with metallic (e.g., Kanthal, Moly-D) or ceramic heating elements.
- If budget and operational simplicity are key for moderate-temperature work (<1800 °C): Other furnace technologies may offer a better balance of cost and performance without the stringent atmospheric controls of a graphite system.
Ultimately, the decision hinges on balancing the unparalleled high-temperature performance of graphite against the stringent environmental controls its chemistry demands.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Oxidation Risk | Requires vacuum or inert gas atmosphere, increasing system complexity and cost. |
| Material Contamination | Can react with sensitive materials, necessitating protective crucibles. |
| Carbon Dust & Outgassing | May contaminate processes and prolong cycle times. |
| Brittle Components | Heating elements and insulation are fragile and require periodic replacement. |
| High Operating Costs | Includes electricity, consumable parts, and maintenance of vacuum/gas systems. |
Need a high-temperature furnace solution tailored to your lab's specific requirements? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing laboratory equipment that balances performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Whether you're processing materials under vacuum, inert gas, or air, our experts can help you select the right furnace technology to avoid contamination, minimize operational complexity, and extend component lifespan.
Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment and consumables can optimize your high-temperature processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why graphite is used in furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment & Energy Efficiency
- What are the applications of graphite material? Leveraging Extreme Heat and Precision for Industrial Processes
- What is the temperature of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C
- What is the purpose of a graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme Temperatures for Advanced Materials
- What temperature can graphite withstand? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential



















