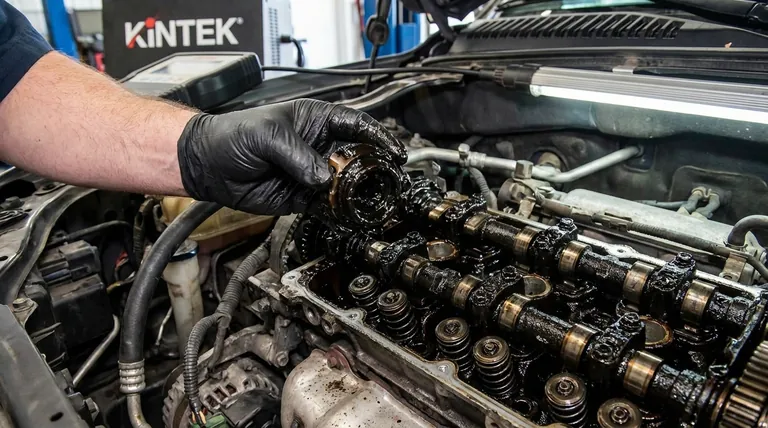
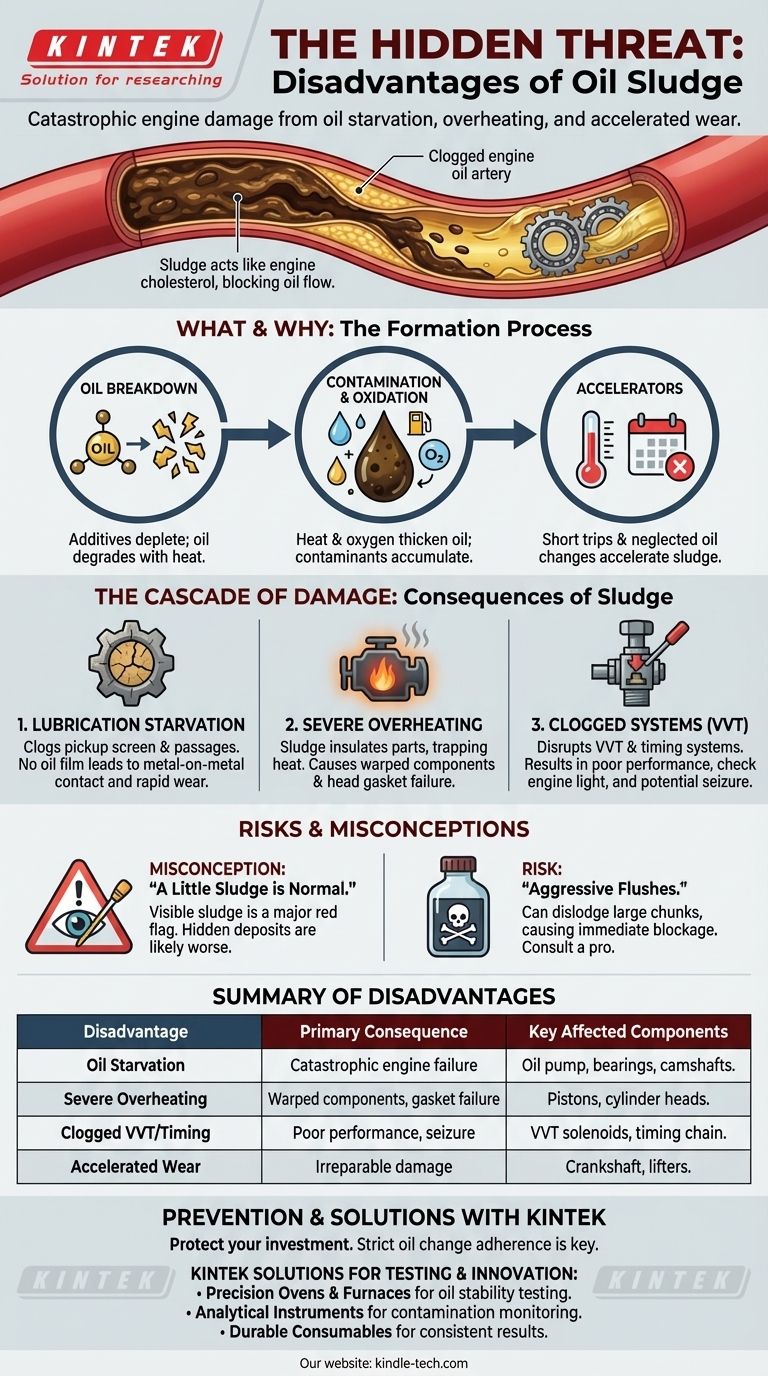
In simple terms, the primary disadvantages of oil sludge are catastrophic engine damage caused by oil starvation, overheating, and accelerated wear. This semi-solid buildup acts like cholesterol in your engine's arteries, blocking the flow of oil to critical components, which can quickly lead to complete engine failure.
Oil sludge is not merely "dirty oil." It is a thick, tar-like deposit that actively prevents your engine from lubricating and cooling itself, transforming a simple maintenance oversight into a direct cause of severe and often irreparable mechanical damage.

What Exactly is Oil Sludge and Why Does It Form?
To understand its disadvantages, you must first understand what sludge is. It’s a gel-like substance formed when motor oil breaks down and becomes contaminated. This process is not instantaneous but a gradual degradation accelerated by specific conditions.
The Breakdown of Oil and Additives
Modern motor oil contains a complex package of additives, including detergents and dispersants, designed to keep contaminants suspended so they can be removed by the oil filter. Over time and with exposure to heat, these additives become depleted and lose their effectiveness.
Contamination and Oxidation
As an engine runs, oil is exposed to intense heat, oxygen, and combustion byproducts like water vapor and unburnt fuel. This exposure causes the oil to oxidize, a process that thickens the oil and forms the building blocks of sludge.
The Impact of Driving Habits
Frequent short trips are particularly damaging. An engine that doesn't reach its full operating temperature for a sustained period fails to burn off condensation and fuel contaminants within the crankcase. This moisture mixes with the oil, creating a perfect environment for sludge formation.
Infrequent Oil Changes: The Primary Culprit
Ultimately, the most common cause of oil sludge is neglect. Exceeding the manufacturer's recommended oil change intervals guarantees that the oil's additives will be depleted, leaving the engine vulnerable to the accumulation of contaminants and oxidized oil.
The Cascade of Engine Damage Caused by Sludge
The presence of sludge initiates a chain reaction of failures. Each problem compounds the next, leading to a rapid decline in engine health.
Starving Components of Lubrication
This is the most critical disadvantage. Sludge is thick and clumpy, and it first accumulates in the oil pan. It can easily clog the oil pump pickup screen, preventing the pump from drawing in enough oil to circulate through the engine.
Even if some oil gets past the screen, sludge can block narrow oil passages and galleries that feed vital components like crankshaft bearings, camshafts, and lifters. Without this pressurized film of oil, metal-on-metal contact occurs, leading to rapid and destructive wear.
Causing Severe Overheating
Motor oil is responsible for up to 40% of an engine's cooling. It carries heat away from parts the coolant cannot reach, like the pistons and bearings.
Sludge is an excellent insulator. When it coats internal components, it traps heat. Combined with the reduced flow of oil, this causes localized and eventually widespread overheating, which can warp cylinder heads and cause head gasket failure.
Clogging VVT and Timing Systems
Modern engines rely on systems like Variable Valve Timing (VVT) to optimize performance and fuel economy. These systems are hydraulically operated by engine oil pressure.
Sludge can easily clog the tiny solenoids and passages that control these systems, causing them to malfunction. This often results in a check engine light, poor performance, rough idling, and failed emissions tests. In some cases, it can also affect the hydraulic tensioner for the timing chain, leading to catastrophic failure.
Understanding the Risks and Misconceptions
Addressing oil sludge is not always straightforward, and common beliefs about it can lead to bigger problems.
Misconception: "A Little Sludge is Normal"
Any visible sludge, especially thick deposits under the oil cap or on the dipstick, is a significant red flag. It indicates that the conditions for sludge formation exist and that unseen, more dangerous deposits are likely blocking critical areas deeper within the engine.
The Risk of Aggressive Engine Flushes
While chemical engine flushes can help clean a sludged engine, they are not without risk. An aggressive flush can dislodge a large piece of hardened sludge, which can then travel through the oiling system and completely block a critical passage, causing immediate engine seizure. A professional should always handle this process.
The High Cost of Ignoring the Problem
The cost of an oil change is negligible compared to the cost of fixing sludge-related damage. A new VVT solenoid can cost hundreds of dollars, while a full engine rebuild or replacement can cost thousands. Ignoring the signs of sludge is an expensive gamble.
How to Prevent and Address Oil Sludge
Your strategy depends entirely on the current health of your engine. Proactive prevention is always the most effective and least expensive path.
- If your primary focus is preventing sludge in a healthy engine: Strictly adhere to your vehicle manufacturer's oil change intervals using a high-quality oil and filter that meet specifications.
- If you are buying a used vehicle: Always check for sludge under the oil filler cap and demand to see comprehensive service records proving regular oil changes.
- If you suspect your engine already has sludge: Have the engine professionally diagnosed. Minor sludge might be managed by switching to a high-mileage oil with enhanced detergents and performing several short-interval oil changes.
- If you have confirmed significant sludge buildup: Do not ignore it. Consult a trusted mechanic to discuss the risks and potential benefits of a carefully performed professional engine cleaning procedure.
Proactive maintenance is the only guaranteed defense against the destructive and costly consequences of oil sludge.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Primary Consequence | Key Component Affected |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Starvation | Catastrophic engine failure due to lack of lubrication | Oil pump pickup screen, oil passages |
| Severe Overheating | Warped components, head gasket failure | Pistons, bearings |
| Clogged VVT/Timing Systems | Poor performance, rough idling, potential engine seizure | VVT solenoids, timing chain tensioners |
| Accelerated Wear | Metal-on-metal contact, leading to irreparable damage | Crankshaft bearings, camshafts, lifters |
Protect your engine and your investment with the right maintenance solutions.
At KINTEK, we understand that preventing issues like oil sludge starts with reliable equipment and precise processes. Whether you're developing new lubricants, testing materials under extreme heat, or ensuring product quality, our high-performance lab equipment is engineered for accuracy and durability.
Let KINTEK be your partner in innovation and maintenance:
- Precision Ovens & Furnaces: Simulate real-world operating temperatures to test oil stability and additive performance.
- Analytical Instruments: Accurately monitor contamination levels and oil degradation.
- Durable Consumables: Ensure consistent and reliable results in every test.
Don't let contamination and breakdowns slow you down. Contact our experts today to find the right laboratory solutions for your needs and keep your operations running smoothly.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Bottle Oil Fume Sampling Tube
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing








