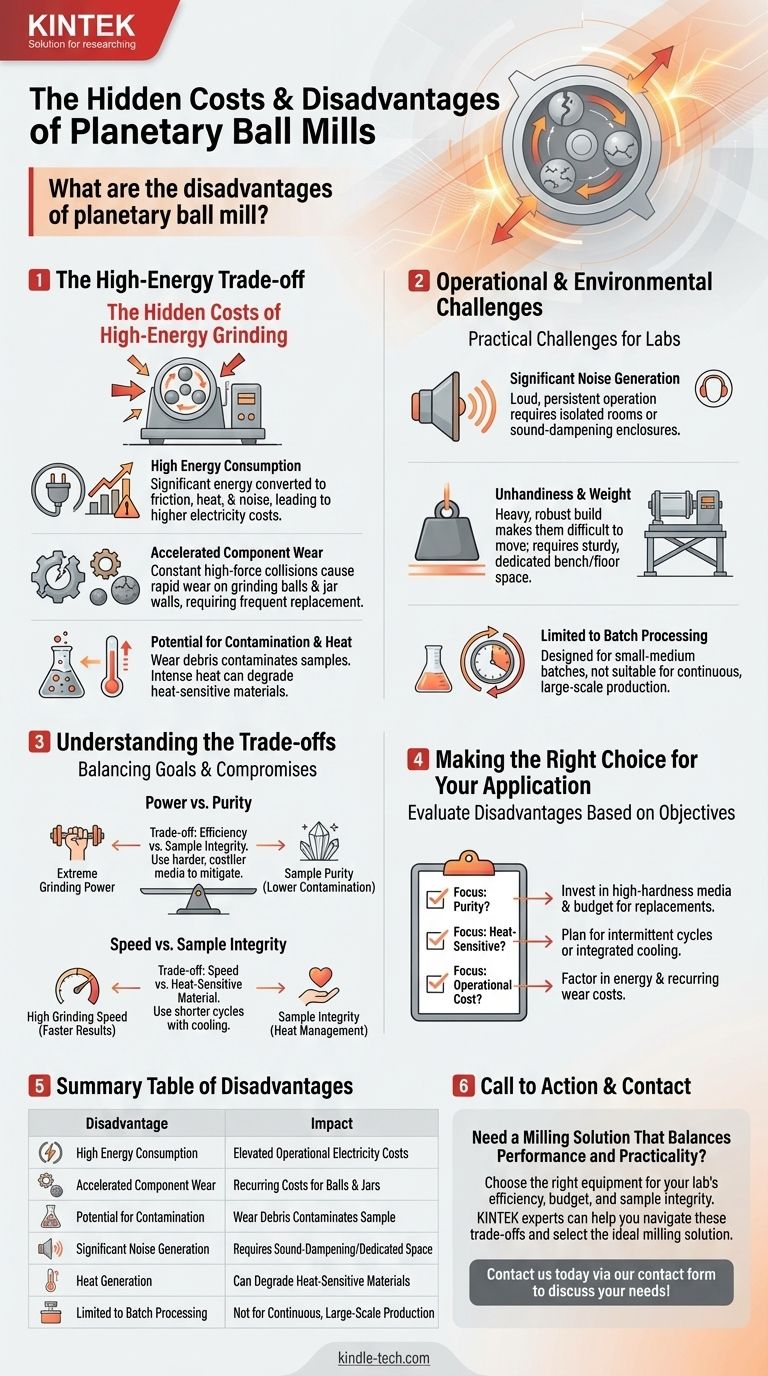
While highly effective, the primary disadvantages of a planetary ball mill are its high energy consumption, significant operational noise, and the considerable wear and tear it imposes on its grinding media and jars. These factors stem directly from the high-energy impact and friction forces that make the machine so powerful for particle size reduction.
Planetary ball mills are unparalleled for grinding difficult materials to a fine powder at the lab scale. However, their core mechanism introduces unavoidable trade-offs in energy cost, noise pollution, and material contamination that must be carefully evaluated before acquisition.

The Hidden Costs of High-Energy Grinding
The power of a planetary ball mill comes from the intense forces generated as grinding jars rotate opposite to a main "sun wheel." This high-energy environment is the source of its main operational drawbacks.
High Energy Consumption
A significant portion of the electrical energy supplied to the mill is not used for grinding. Instead, it is converted into friction, heat, and noise.
This high specific energy consumption translates directly into higher operational electricity costs compared to lower-intensity milling methods.
Accelerated Component Wear
The constant, high-force collisions cause rapid wear on the grinding balls and the inner walls of the grinding jars.
This wear is a major recurring cost, as these components are consumables that must be replaced. The rate of wear depends on the hardness of the material being milled and the material of the grinding media itself.
Potential for Contamination and Heat
Wear doesn't just represent a cost; it also introduces contamination into your sample. Material from the balls and jar walls will be incorporated into your final powder.
Furthermore, the intense friction generates significant heat. This can be detrimental to heat-sensitive materials, potentially causing melting, chemical degradation, or unwanted phase changes.
Operational and Environmental Challenges
Beyond the direct costs, operating a planetary ball mill presents several practical challenges for a lab or production environment.
Significant Noise Generation
The repeated high-speed impacts of the grinding balls create a loud and persistent noise during operation.
This often requires the mill to be placed in a dedicated, isolated room or within a sound-dampening enclosure to comply with workplace safety standards and prevent disruption.
Unhandiness and Weight
Planetary ball mills are typically heavy and robustly built to withstand the intense internal forces. Their large weight and bulk make them difficult to move.
They require a sturdy, dedicated bench or floor space capable of supporting the machine and absorbing vibrations during operation.
Limited to Batch Processing
These mills are designed for processing discrete, small-to-medium-sized batches of material. They are not suited for continuous, large-scale production.
This limits their throughput and makes them primarily a tool for research, development, and quality control rather than bulk manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing to use a planetary ball mill means accepting a series of compromises. The key is to align these trade-offs with your specific goals.
Power vs. Purity
The extreme grinding power that achieves fine particle sizes is the same force that causes component wear. This creates an inherent trade-off between grinding efficiency and sample purity. Using harder grinding media (e.g., zirconia) can mitigate this, but at a higher initial cost.
Speed vs. Sample Integrity
The speed of grinding directly correlates with heat generation. For heat-sensitive compounds, running the mill at maximum intensity for long periods is not viable. You must trade processing speed for sample integrity by using shorter cycles with cooling periods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Evaluate the disadvantages of a planetary ball mill in the context of your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maintaining sample purity: You must invest in high-hardness grinding media (like silicon carbide or zirconia) and budget for their eventual replacement to minimize contamination.
- If your primary focus is processing heat-sensitive materials: You must plan for intermittent grinding cycles or select a model with integrated cooling capabilities to prevent sample degradation.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational cost: You must carefully factor in the high energy consumption and the recurring expense of replacing grinding balls and jars over the machine's lifetime.
Understanding these inherent limitations allows you to properly budget for the true cost of achieving superior particle size reduction.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Impact |
|---|---|
| High Energy Consumption | Leads to elevated operational electricity costs. |
| Accelerated Component Wear | Results in recurring costs for grinding balls and jars. |
| Potential for Contamination | Wear debris from media/jars can contaminate the sample. |
| Significant Noise Generation | Requires sound-dampening measures or dedicated space. |
| Heat Generation | Can degrade heat-sensitive materials during milling. |
| Limited to Batch Processing | Not suitable for continuous, large-scale production. |
Need a Milling Solution That Balances Performance and Practicality?
While planetary ball mills are powerful, their disadvantages in energy use, noise, and contamination are critical to consider. Choosing the right equipment is essential for your lab's efficiency, budget, and sample integrity.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you navigate these trade-offs and select the ideal milling solution for your specific materials and application requirements, ensuring you achieve your particle size reduction goals without compromising on cost or quality.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss your needs and find the right equipment for your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type Milling Machine
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in the synthesis of Li2S–P2S5 sulfide solid-state electrolytes?
- What role does a high-energy planetary ball mill play in Mo-La2O3 alloying? Achieve Superior Microstructure Control
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in Al-LLZ lithium garnet preparation? Optimize Solid-State Electrolyte Synthesis
- What is the primary function of a planetary ball mill for LLZTO targets? Achieving High-Energy Pulverization
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in SHS? Optimize Powder Activation for Superior Alloy Synthesis



















