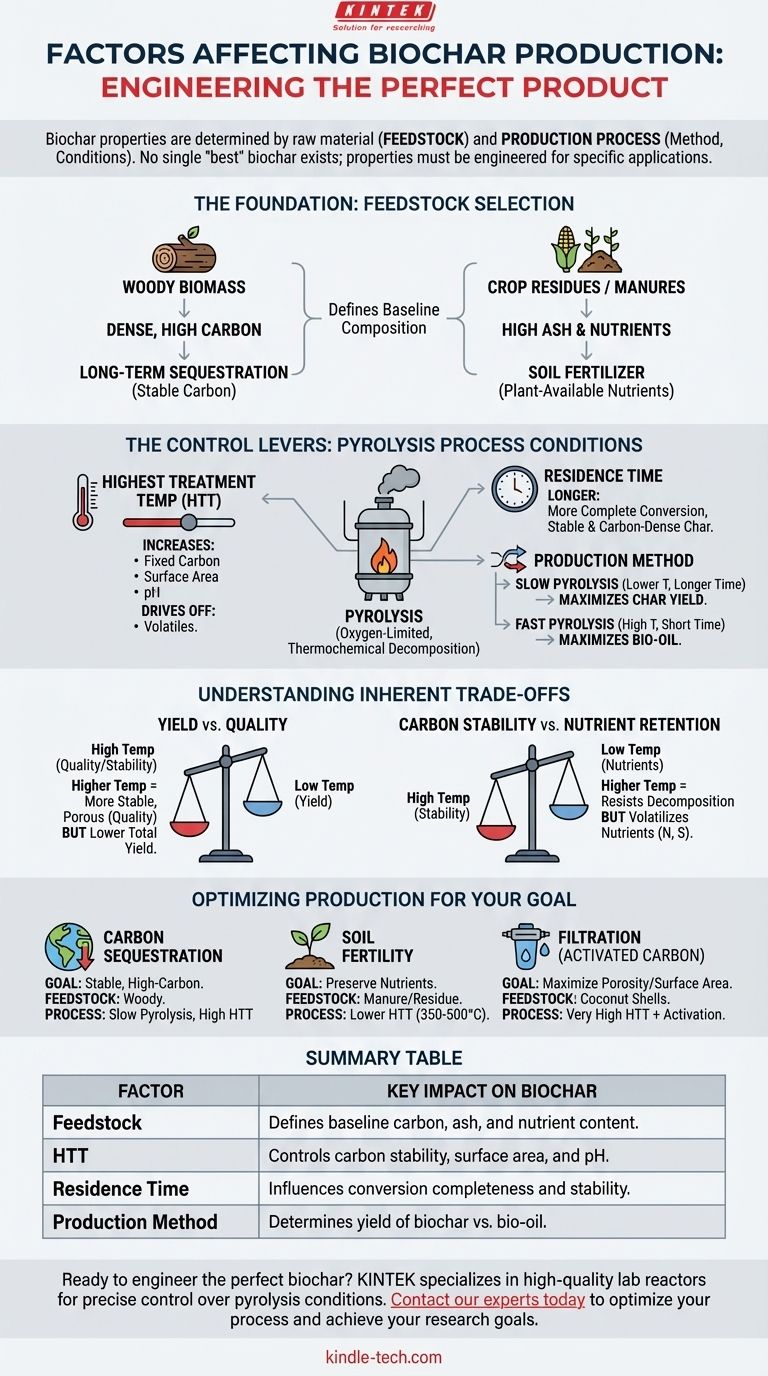
The final properties of biochar are determined by a combination of the raw material used and the specific production process employed. The three primary factors you can control are the initial biomass feedstock, the production method (such as slow or fast pyrolysis), and the precise process conditions, most notably the highest treatment temperature and the duration of the process, known as residence time.
The central challenge in biochar production is its variability. To overcome this, you must understand that there is no single "best" biochar. Instead, the key is to intentionally manipulate the production factors to engineer a final product with the specific physical and chemical properties required for your intended application.

The Foundation: Feedstock Selection
The type of biomass used is the starting point that defines the potential characteristics of your biochar. Different feedstocks have fundamentally different chemical compositions, which carry through to the final product.
The Role of Feedstock Type
The choice between woody biomass, crop residues, or manures will create biochars with vastly different properties. A feedstock's initial structure, moisture content, and elemental composition (like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus) set the baseline.
Impact on Biochar Properties
For example, a dense, woody feedstock will generally produce a more stable, high-carbon biochar that is excellent for long-term carbon sequestration. In contrast, a feedstock like manure will result in a biochar with a higher ash and nutrient content, making it better suited for use as a soil fertilizer.
The Control Levers: Pyrolysis Process Conditions
Pyrolysis is the thermochemical decomposition of biomass in an oxygen-limited environment. The specific conditions under which you conduct this process give you precise control over the final outcome.
Highest Treatment Temperature (HTT)
Temperature is arguably the single most influential process parameter. As the highest treatment temperature (HTT) increases, it drives off more volatile compounds, resulting in a biochar with a higher percentage of fixed carbon, greater surface area, and higher pH.
Residence Time
Residence time refers to how long the biomass is held at the highest treatment temperature. A longer residence time ensures a more complete conversion process, leading to a more stable and carbon-dense char. Short residence times may leave some organic compounds unconverted.
Production Method
The overall technique, such as slow pyrolysis versus fast pyrolysis, also dictates the outcome. Slow pyrolysis, which involves lower temperatures over longer periods, typically maximizes char yield. Fast pyrolysis uses high temperatures and very short residence times to maximize the production of liquid bio-oil, yielding less biochar.
Understanding the Inherent Trade-offs
Controlling biochar production is a game of balancing competing properties. Optimizing for one characteristic often means compromising on another.
Yield vs. Quality
One of the most common trade-offs is between yield and quality. Higher production temperatures create a more porous and stable biochar (high quality for sequestration), but they also burn off more of the initial biomass, resulting in a lower total yield.
Carbon Stability vs. Nutrient Retention
Higher temperatures create highly stable carbon structures that resist decomposition for centuries. However, these same high temperatures can volatilize and drive off valuable nutrients like nitrogen and sulfur, making the biochar less effective as a direct fertilizer.
Optimizing Production for Your Goal
To produce effective biochar, you must first define your primary objective. Your goal determines the ideal combination of feedstock and process conditions.
- If your primary focus is long-term carbon sequestration: Use a woody feedstock and a slow pyrolysis process with a high treatment temperature (e.g., >550°C) to create a stable, high-carbon biochar.
- If your primary focus is improving soil fertility: Use a nutrient-rich feedstock like manure or crop residue and a lower-temperature pyrolysis process (e.g., 350-500°C) to preserve plant-available nutrients.
- If your primary focus is creating activated carbon for filtration: Use a feedstock that produces a high surface area (like coconut shells) and a very high temperature process, often followed by an activation step, to maximize porosity.
By deliberately controlling these factors, you can move from producing a variable byproduct to engineering a high-performance material tailored to a specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Impact on Biochar |
|---|---|
| Feedstock | Defines baseline carbon, ash, and nutrient content. |
| Highest Treatment Temperature (HTT) | Controls carbon stability, surface area, and pH. |
| Residence Time | Influences conversion completeness and stability. |
| Production Method (e.g., Slow Pyrolysis) | Determines yield of biochar vs. bio-oil. |
Ready to engineer the perfect biochar for your specific needs? The right lab equipment is crucial for precise control over pyrolysis temperature, residence time, and process conditions. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab reactors and pyrolysis systems that empower researchers to consistently produce biochar tailored for carbon sequestration, soil enhancement, or filtration applications. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your biochar production process and help you achieve your research or sustainability goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- How to regenerate activated carbon? Master the 3-Stage Thermal Process for Cost Savings
- What temperature is needed for porcelain? A Guide to Cone 6 and Cone 10 Firing
- How do you carbonize charcoal? Master the 3-Step Pyrolysis Process for High-Purity Carbon
- What is the temperature for activated carbon regeneration? Key Ranges from 220°C to 900°C



















