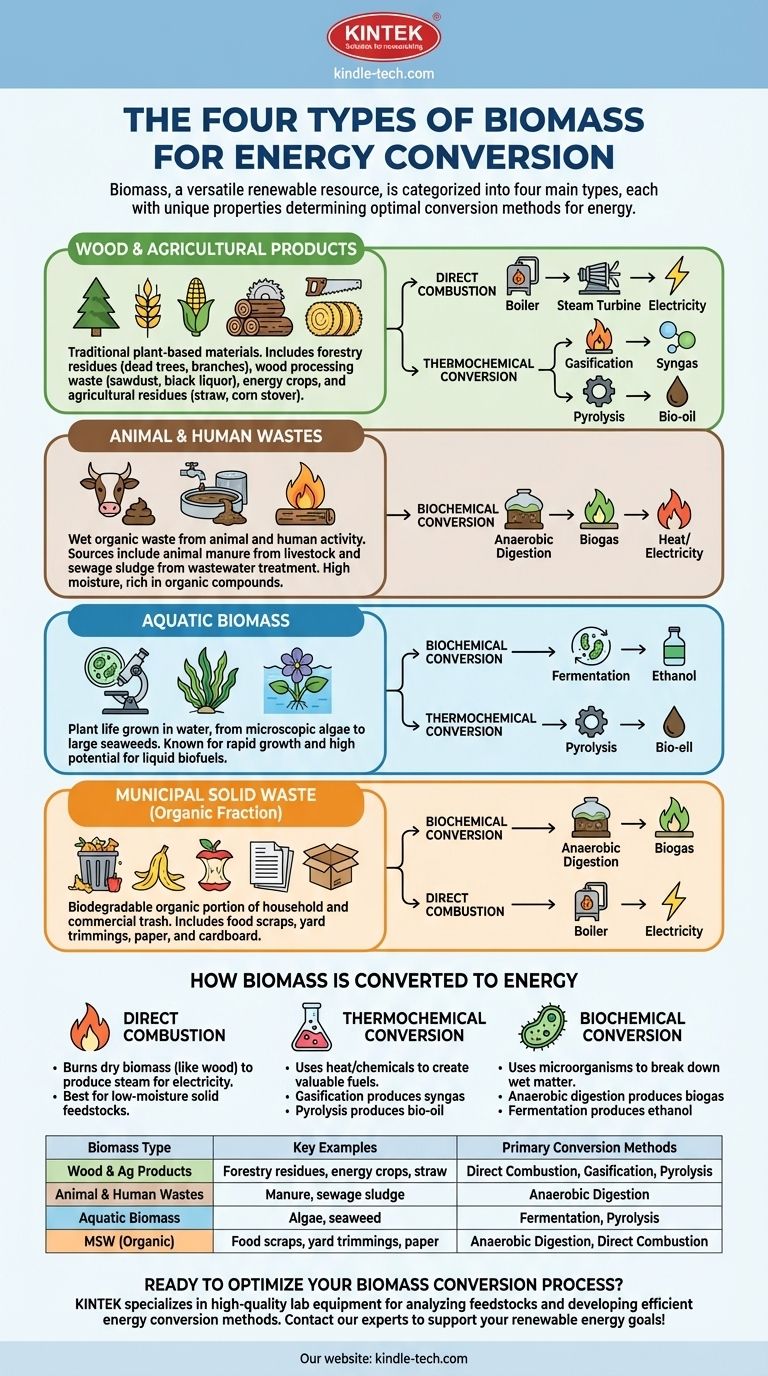
In energy production, biomass is broadly categorized into four primary types based on its origin. These sources are wood and agricultural products, animal and human wastes, aquatic biomass, and the organic portion of municipal solid waste. Each type possesses unique characteristics that determine the most effective methods for converting it into usable energy.
While the term "biomass" sounds singular, it represents a wide array of organic materials. Understanding the four main types is crucial because the source of the biomass dictates its composition, its availability, and the most efficient technology for its conversion.

A Closer Look at Biomass Sources
Biomass is simply organic matter that can be used as a fuel source. The key is understanding where this organic matter comes from, as each source has different properties.
Wood and Agricultural Products
This is the most traditional and widely used category of biomass. It includes all plant-based material grown on land.
Examples include forestry residues (such as dead trees, branches, and stumps), wood processing wastes (like sawdust and black liquor), and dedicated energy crops (fast-growing trees and grasses). It also includes agricultural crop residues like the straw and corn stover left after a harvest.
Animal and Human Wastes
This category consists of wet waste materials derived from animal and human activity. It is a potent source for a specific type of energy conversion.
The primary sources are animal manure from livestock farming and sewage sludge from wastewater treatment plants. These materials have high moisture content and are rich in organic compounds.
Aquatic Biomass
This group includes various forms of plant life grown in water, from microscopic organisms to larger plants.
The most notable examples are algae (microalgae and macroalgae, or seaweed) and other water plants like water hyacinth. Aquatic biomass is known for its rapid growth rates and high energy potential, particularly for producing liquid biofuels.
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW)
This category refers specifically to the biodegradable organic fraction of household and commercial trash. It represents a significant and readily available energy source in urban areas.
This includes food scraps, yard trimmings, paper, and cardboard. It is critical to distinguish this organic portion from non-biodegradable waste like plastics and metals.
How Biomass Is Converted to Energy
The type of biomass feedstock directly influences the optimal conversion pathway. The three main methods are direct combustion, thermochemical conversion, and biochemical conversion.
Direct Combustion
This is the simplest and most common method, especially for dry biomass like wood. The biomass is burned directly in a boiler to produce high-pressure steam.
As mentioned in common processes, this steam then drives a turbine connected to a generator to produce electricity. This method is well-suited for solid feedstocks with low moisture content.
Thermochemical Conversion
This process uses heat and chemical reactions to convert biomass into more valuable and versatile fuels. The two main methods are gasification and pyrolysis.
Gasification uses high temperatures with limited oxygen to convert biomass into a combustible gas mixture called "syngas." Pyrolysis involves heating biomass in the complete absence of oxygen to produce a liquid fuel known as bio-oil.
Biochemical Conversion
This pathway uses microorganisms to break down wet organic matter. It is ideal for feedstocks like animal wastes and sewage sludge.
Anaerobic digestion uses bacteria in an oxygen-free environment to decompose biomass, producing biogas (mostly methane) that can be burned for heat or electricity. Fermentation uses yeast to convert the sugars in biomass into ethanol.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While biomass is a valuable renewable resource, it is essential to understand its limitations and challenges to deploy it effectively.
Land and Water Use
Growing dedicated energy crops can create competition for land and water resources that might otherwise be used for food production. Sustainable forestry and using waste materials helps mitigate this concern.
Supply Chain Logistics
Biomass is often bulky, has a low energy density, and can be geographically dispersed. The cost and energy consumption associated with collecting, transporting, and storing biomass can be significant operational hurdles.
Conversion Efficiency and Emissions
The efficiency of converting biomass to energy varies widely depending on the feedstock and the technology used. While often considered "carbon neutral," emissions from transportation, processing, and land-use changes must be factored into its overall environmental impact.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a biomass strategy is not a one-size-fits-all decision. The optimal approach depends entirely on your available resources and primary objectives.
- If your primary focus is leveraging existing waste streams: Animal wastes and the organic portion of MSW are your best starting points, typically converted through anaerobic digestion to produce biogas.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, consistent power generation: Wood products and dedicated agricultural crops are the most established feedstocks, often used in direct combustion power plants.
- If your primary focus is developing advanced liquid biofuels: Aquatic biomass like algae and thermochemical conversion of agricultural residues represent the future, though the technology is still maturing.
Ultimately, a successful biomass strategy depends on matching local, sustainable resources with the most appropriate and efficient conversion technology.
Summary Table:
| Biomass Type | Key Examples | Primary Conversion Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Wood & Agricultural Products | Forestry residues, energy crops, straw | Direct Combustion, Gasification, Pyrolysis |
| Animal & Human Wastes | Manure, sewage sludge | Anaerobic Digestion |
| Aquatic Biomass | Algae, seaweed | Fermentation, Pyrolysis |
| Municipal Solid Waste (Organic Fraction) | Food scraps, yard trimmings, paper | Anaerobic Digestion, Direct Combustion |
Ready to optimize your biomass conversion process? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for analyzing biomass feedstocks and developing efficient energy conversion methods. Whether you're researching biofuels, testing material properties, or scaling up production, our solutions provide the precision and reliability you need. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your renewable energy goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions








