The primary hazards of hydraulic machines are high-pressure fluid injection injuries, mechanical failures leading to crushing or impact, and secondary risks like burns, electrical shock, and slips from leaked fluid. These dangers stem from the immense amount of energy stored within the pressurized hydraulic system.
The core danger of any hydraulic system is its incredible power density. The same force that allows a machine to lift tons is what makes a pinhole leak or component failure so catastrophic. Understanding and respecting this stored energy is the foundation of hydraulic safety.

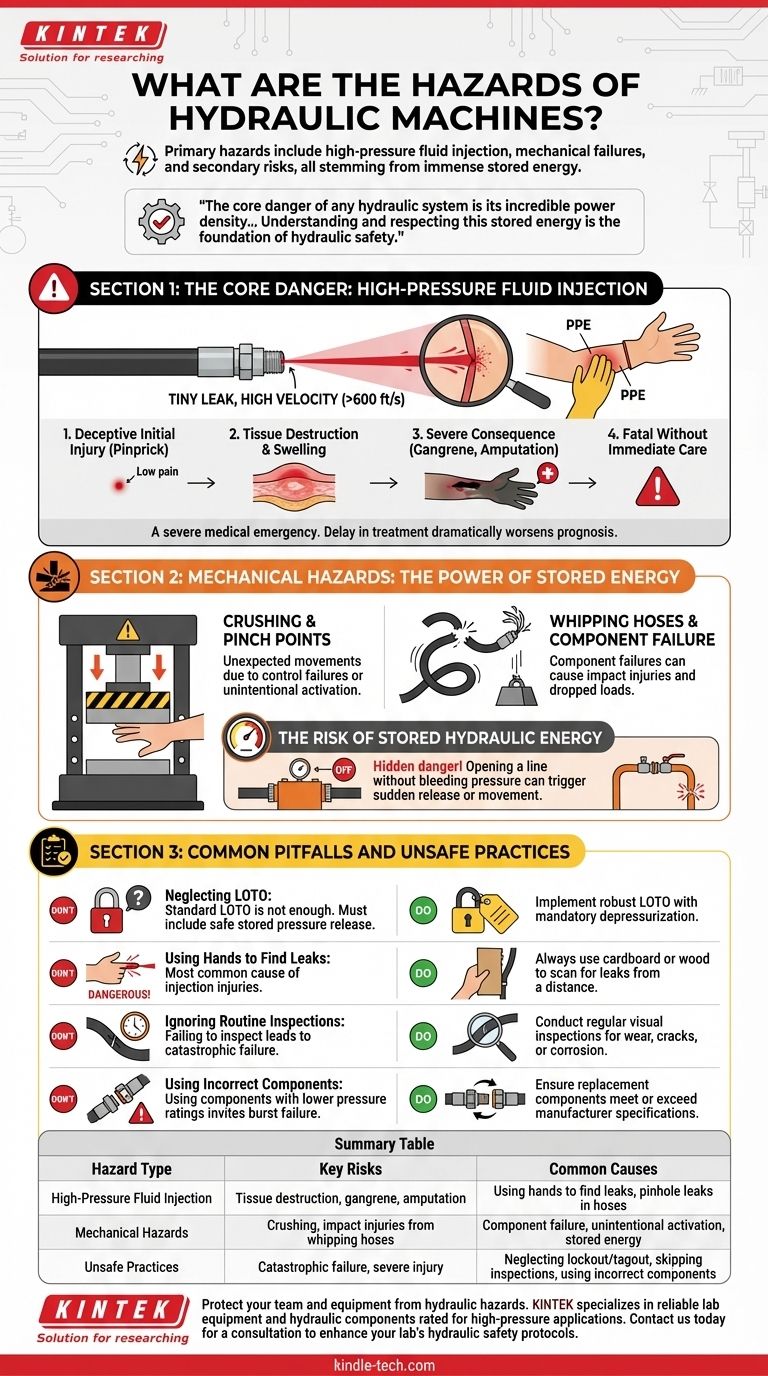
The Core Danger: High-Pressure Fluid Injection
The most unique and severe hazard associated with hydraulics is fluid injection. This occurs when a high-pressure stream of fluid penetrates the skin, and it is a severe medical emergency.
What is a Fluid Injection Injury?
A hydraulic system can operate at pressures exceeding 2,000 PSI. A tiny, almost invisible leak in a hose can create a fluid jet traveling at over 600 feet per second.
This high-velocity stream can easily pierce skin and personal protective equipment (PPE), injecting hydraulic fluid deep into the tissue.
The Devastating Consequences
The initial entry wound may look like a simple pinprick, showing little to no pain. However, the injected fluid quickly begins to destroy tissue, leading to severe swelling, gangrene, and often, amputation of the affected limb.
Without immediate and specialized medical intervention, a fluid injection injury can be fatal.
Why It's Deceptively Dangerous
The harmless appearance of the initial injury is its most treacherous aspect. Workers may be tempted to ignore it, believing it's just a small cut. This delay in treatment dramatically worsens the prognosis.
Mechanical Hazards: The Power of Stored Energy
Beyond fluid injection, the mechanical force generated by hydraulic systems presents significant crushing and impact hazards.
Crushing and Pinch Points
Hydraulic actuators, booms, and clamps move with incredible force. An unexpected movement can easily trap or crush a person, causing life-threatening injuries. These movements can be caused by control failures or unintentional activation.
Failure of Mechanical Components
When a hydraulic hose or fitting fails under pressure, it can result in two critical hazards. The hose can whip around violently, causing severe impact injuries, while the component it was powering (like a heavy lift) can suddenly fall.
The Risk of Stored Hydraulic Energy
A hydraulic system can retain high pressure even when turned off. This stored energy is a hidden danger. If a maintenance worker opens a line without first properly bleeding the pressure, they can trigger a sudden release of fluid or unexpected machine movement.
Common Pitfalls and Unsafe Practices
Most hydraulic incidents are not caused by spontaneous failure but by predictable and preventable human error. Understanding these common mistakes is crucial for prevention.
Neglecting Lockout/Tagout (LOTO)
A standard Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) procedure is not enough for hydraulics. The procedure must explicitly include steps to safely release all stored hydraulic pressure before any maintenance work begins.
Using Hands to Find Leaks
The single most common cause of fluid injection injuries is a worker using their hand or finger to locate a suspected leak. This practice is extremely dangerous and must be prohibited. Always use a piece of cardboard or wood to scan for leaks from a safe distance.
Ignoring Routine Inspections
Hydraulic hoses and fittings degrade over time due to pressure cycles, abrasion, and environmental exposure. Failing to conduct regular visual inspections for wear, cracks, or corrosion is a direct path to catastrophic failure.
Using Incorrect Components
Every hose and fitting has a specific pressure rating. Using a component with a pressure rating lower than the system's operating pressure is a critical error that invites a burst failure.
A Proactive Approach to Hydraulic Safety
Managing hydraulic hazards requires a safety-first mindset that addresses the system's inherent power. Your approach should be tailored to your specific role and responsibilities.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Prioritize comprehensive training on injection injuries and enforce the absolute rule of never using hands to find leaks.
- If your primary focus is maintenance and repair: Implement and strictly enforce a robust LOTO procedure that includes a mandatory depressurization step for all stored energy.
- If your primary focus is system reliability and prevention: Establish a rigorous and documented schedule for inspecting all hoses and fittings and ensure replacement components always meet or exceed manufacturer specifications.
Understanding that hydraulic energy must be actively controlled, even when a machine is off, is the first step toward mastering this powerful technology safely.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Type | Key Risks | Common Causes |
|---|---|---|
| High-Pressure Fluid Injection | Tissue destruction, gangrene, amputation | Using hands to find leaks, pinhole leaks in hoses |
| Mechanical Hazards | Crushing, impact injuries from whipping hoses | Component failure, unintentional activation, stored energy |
| Unsafe Practices | Catastrophic failure, severe injury | Neglecting lockout/tagout, skipping inspections, using incorrect components |
Protect your team and equipment from hydraulic hazards. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables, including hydraulic system components rated for high-pressure applications. Our experts can help you select the right parts to ensure safety and system integrity. Contact us today for a consultation to enhance your lab's hydraulic safety protocols.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis



















