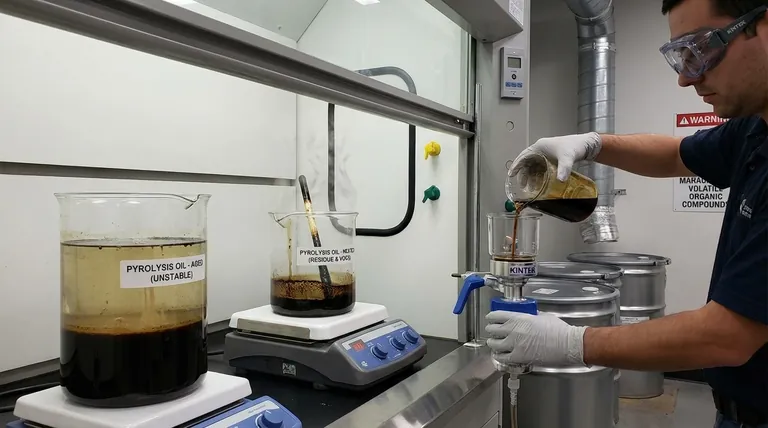
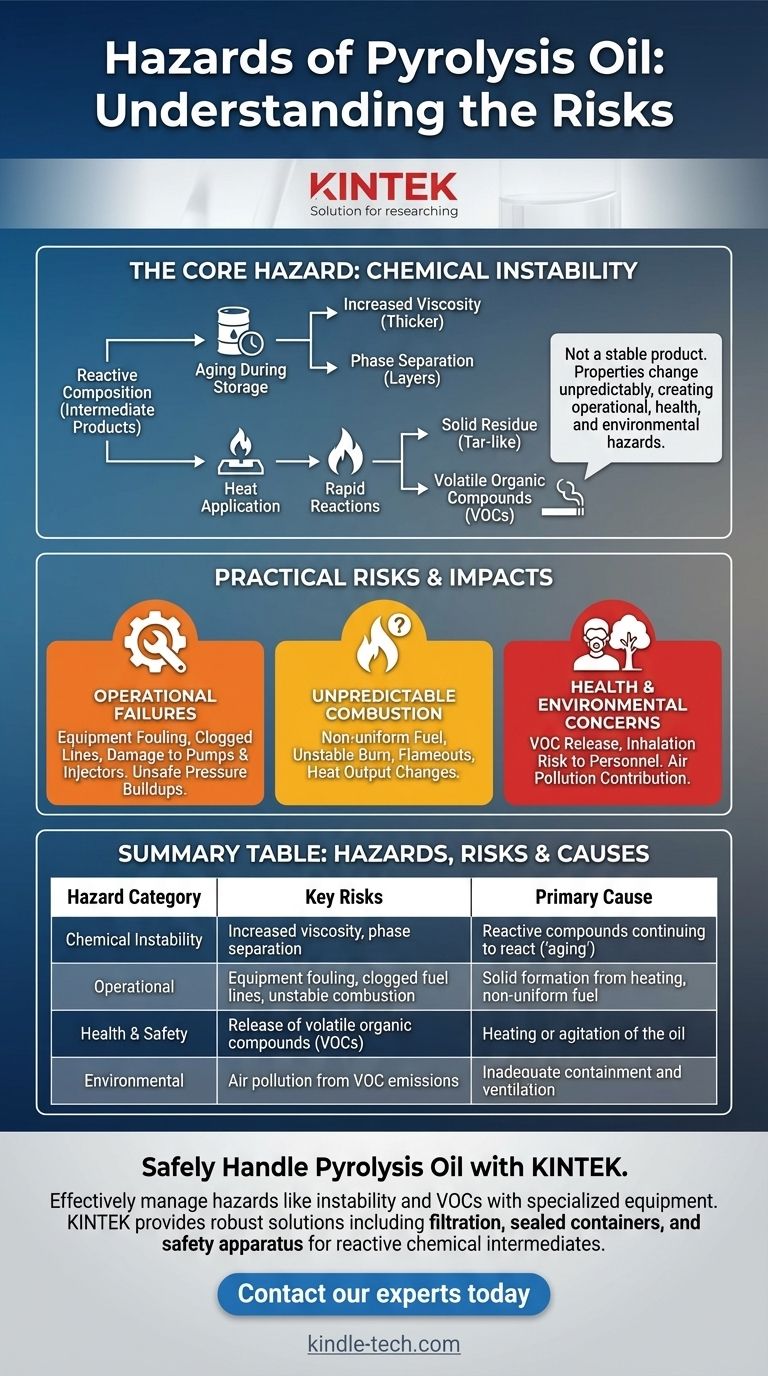
The primary hazards of pyrolysis oil stem from its inherent chemical instability and its composition of reactive compounds. This instability means the oil changes over time, increasing in viscosity and potentially separating into different phases, which creates significant risks during storage and use. Furthermore, heating the oil can trigger rapid reactions that produce hazardous volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and solid residues.
The core challenge with pyrolysis oil is that it is not a finished, stable product like conventional fuel oil. It should be treated as a reactive chemical intermediate whose properties can change unpredictably, creating operational, health, and environmental hazards.

The Core Hazard: Chemical Instability
Pyrolysis oil is fundamentally different from refined petroleum fuels. It is a crude mixture of oxygenated organic compounds left over from the thermal decomposition of a feedstock, and these compounds are not done reacting.
A Reactive Composition
The oil is composed of intermediate products from thermal decomposition. These molecules are inherently unstable and will continue to react with each other over time in a process often called "aging."
The Problem of Aging
During storage, these slow condensation reactions cause the oil's properties to change. Its viscosity gradually increases, making it thicker and more difficult to pump. The oil can also undergo phase separation, where it separates into layers with different chemical properties and energy content.
The Danger of Heat
Applying heat significantly accelerates these reactions. Heating pyrolysis oil to 100°C or more can cause it to rapidly polymerize, forming a solid, tar-like residue. This process also releases a significant amount of volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Understanding the Practical Risks
This underlying chemical instability creates tangible hazards for anyone storing, transporting, or using pyrolysis oil.
Equipment Fouling and Failure
The gradual increase in viscosity and the rapid formation of solids when heated can clog fuel lines, foul heat exchangers, and damage pumps and injectors. This not only leads to operational failure but can also create unsafe pressure buildups in closed systems.
Unpredictable Combustion
Because the oil can separate into phases, the fuel being fed into a burner or engine may not be uniform. This can lead to unstable combustion, flameouts, or unexpected changes in heat output, which are significant risks in any industrial heating application.
Health and Environmental Concerns
The release of VOCs, especially during heating or handling, poses a direct inhalation risk to personnel. These compounds can also contribute to air pollution if not properly contained and managed.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The most common mistake is treating pyrolysis oil like a standard fuel oil, which overlooks the critical hazards associated with its reactive nature.
Assuming Long-Term Stability
Unlike diesel or bunker fuel, pyrolysis oil cannot be stored for long periods without consequences. Assuming it will maintain its initial properties is a direct path to the operational problems of fouling and phase separation.
Inadequate Material and Process Design
Systems designed for stable fuels may not be adequate for pyrolysis oil. The potential for solid formation requires different filtration strategies and heating protocols to prevent rapid degradation of the oil and fouling of the equipment.
Overlooking Ventilation Requirements
The risk of VOC release means that standard ventilation may not be sufficient. Enclosed spaces where pyrolysis oil is heated or agitated require robust air handling systems to protect worker health.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Managing the hazards of pyrolysis oil requires aligning your strategy with your specific application.
- If your primary focus is safe storage: You must use sealed containers, minimize exposure to heat and air, and plan for a limited shelf life to avoid issues from increased viscosity and separation.
- If your primary focus is use as a fuel: You must filter the oil effectively and control its heating process carefully to prevent the formation of solids that can damage your combustion equipment.
- If your primary focus is personnel safety: You must implement strict handling procedures and ensure adequate ventilation to manage exposure to volatile organic compounds.
Ultimately, safely handling pyrolysis oil depends on recognizing it as a dynamic chemical mixture rather than a simple, stable fuel.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Category | Key Risks | Primary Cause |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Instability | Increased viscosity, phase separation | Reactive compounds continuing to react ('aging') |
| Operational | Equipment fouling, clogged fuel lines, unstable combustion | Solid formation from heating, non-uniform fuel |
| Health & Safety | Release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) | Heating or agitation of the oil |
| Environmental | Air pollution from VOC emissions | Inadequate containment and ventilation |
Safely handle pyrolysis oil with the right equipment from KINTEK.
Effectively managing the hazards of pyrolysis oil—from chemical instability to VOC release—requires specialized lab equipment and consumables. KINTEK specializes in providing robust solutions for laboratory needs, including filtration systems, sealed containers, and safety apparatus designed for reactive chemical intermediates.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our products can help you mitigate risks, protect your personnel, and ensure operational safety in your pyrolysis oil applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Thin-Layer Spectral Electrolysis Electrochemical Cell
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success







