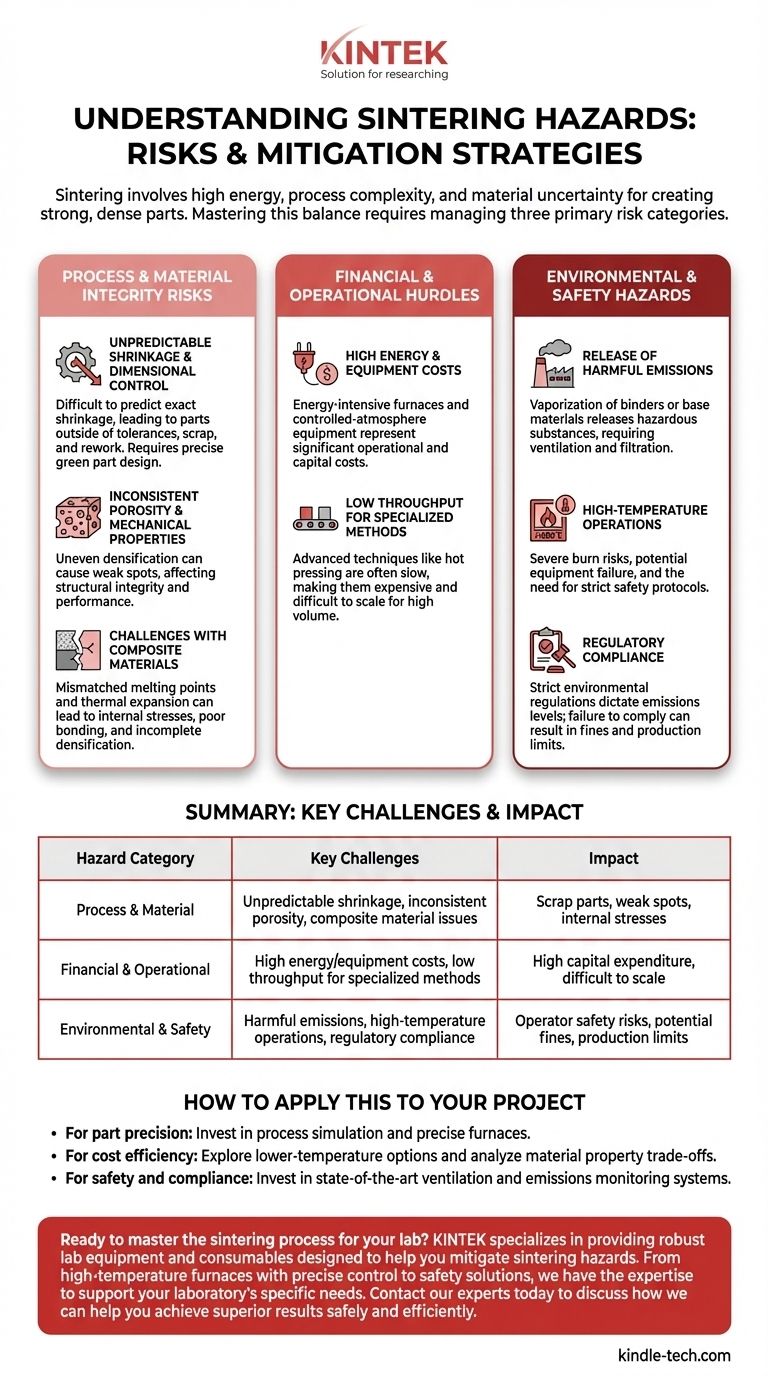
The hazards of sintering fall into three primary categories: process-related risks that affect the final part's quality, financial risks tied to high energy and equipment costs, and environmental or safety risks stemming from high-temperature operations. Successfully implementing sintering requires a clear understanding of how to manage the challenges within each of these domains.
The central challenge of sintering is not merely avoiding danger, but mastering a delicate balance. You are trading high energy costs, process complexity, and material uncertainty for the unique ability to create strong, dense parts with superior properties that are often unattainable through other methods.

Process and Material Integrity Risks
The most immediate hazards in sintering relate to achieving the desired outcome. The process fundamentally alters the material's structure, and controlling this transformation is a significant engineering challenge.
Unpredictable Shrinkage and Dimensional Control
During sintering, the gaps between material particles close as they fuse, causing the entire part to shrink. While this densification is the goal, predicting the exact amount of shrinkage is difficult.
Unexpected variations can lead to parts that are outside of dimensional tolerances, resulting in scrap and rework. This factor must be meticulously modeled and accounted for in the initial "green part" design.
Inconsistent Porosity and Mechanical Properties
Sintering is used to reduce porosity, which in turn increases strength and density. However, achieving perfectly uniform porosity is challenging.
If densification is uneven, it can leave behind weak spots or internal voids that compromise the part's structural integrity. Controlling the final porosity is critical for applications where mechanical performance is non-negotiable.
Challenges with Composite Materials
When sintering parts made from multiple materials (composites), the process becomes far more complex. Different materials have different melting points, sintering temperatures, and rates of thermal expansion.
This mismatch can lead to internal stresses, poor bonding between the materials, or incomplete densification of one component. It requires highly specialized knowledge and precise control over the heating cycle.
Financial and Operational Hurdles
Beyond the material science, sintering presents significant economic and logistical challenges that can impact a project's viability.
High Energy and Equipment Costs
Sintering is an energy-intensive process. The furnaces required to reach and maintain the necessary high temperatures consume a substantial amount of power, leading to high operational costs.
Furthermore, the initial investment in high-temperature furnaces and controlled-atmosphere equipment can be considerable, representing a significant capital expenditure.
Low Throughput for Specialized Methods
While all sintering has operational costs, certain advanced methods like hot pressing exacerbate the issue. These techniques offer superior material properties but are often slow and process parts one at a time or in small batches.
This low productivity makes them expensive and difficult to scale for high-volume manufacturing, limiting their use to high-value, specialized components.
Environmental and Safety Hazards
The high temperatures and materials involved in sintering introduce direct risks to personnel and the environment.
Release of Harmful Emissions
Heating powdered materials can cause the release of harmful substances. This can include the vaporization of binders or lubricants used to form the green part, or even elements from the base material itself.
These emissions can be hazardous to operators and require robust ventilation, filtration, and atmospheric control systems.
High-Temperature Operations
Operating equipment at temperatures often exceeding 1000°C (1832°F) presents an inherent safety risk. This includes the danger of severe burns to personnel, the potential for catastrophic equipment failure, and the need for strict, well-enforced safety protocols.
Regulatory Compliance
Due to the potential for harmful emissions, sintering operations are often subject to strict environmental regulations. These governmental norms dictate acceptable emission levels and can require expensive monitoring and abatement equipment.
Failure to comply can result in fines and may even force a reduction in production rates, directly impacting operational output.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your approach to mitigating these hazards depends entirely on your primary goal for the component you are producing.
- If your primary focus is part precision: You must invest heavily in process simulation to accurately predict shrinkage and use advanced furnaces with precise temperature control.
- If your primary focus is cost efficiency: Explore lower-temperature sintering options or faster cycle times, and carefully analyze the trade-off in final material properties.
- If your primary focus is safety and compliance: Your first investment should be in state-of-the-art ventilation, atmospheric control, and continuous emissions monitoring systems.
By understanding these hazards not as roadblocks but as engineering variables to be controlled, you can effectively leverage the power of the sintering process.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Category | Key Challenges | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Process & Material | Unpredictable shrinkage, inconsistent porosity, composite material issues | Scrap parts, weak spots, internal stresses |
| Financial & Operational | High energy/equipment costs, low throughput for specialized methods | High capital expenditure, difficult to scale |
| Environmental & Safety | Harmful emissions, high-temperature operations, regulatory compliance | Operator safety risks, potential fines, production limits |
Ready to master the sintering process for your lab? KINTEK specializes in providing robust lab equipment and consumables designed to help you mitigate sintering hazards. From high-temperature furnaces with precise control to safety solutions for emissions management, we have the expertise to support your laboratory's specific needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior results safely and efficiently.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What are the parameters for spark plasma sintering? Master Speed, Pressure & Temperature Control
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology
- What are the steps in spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication



















