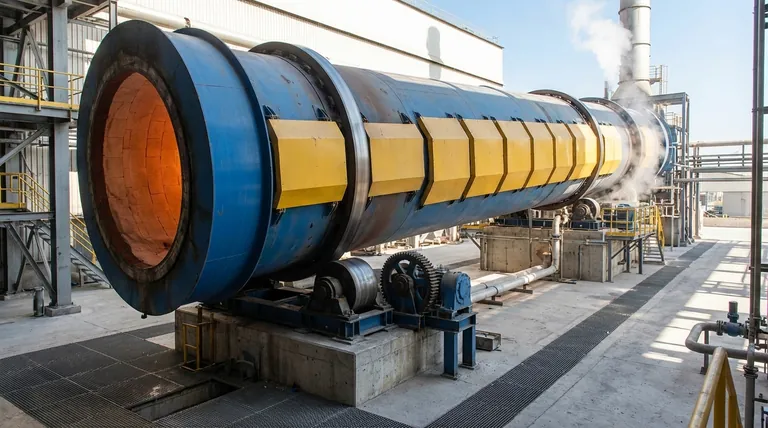
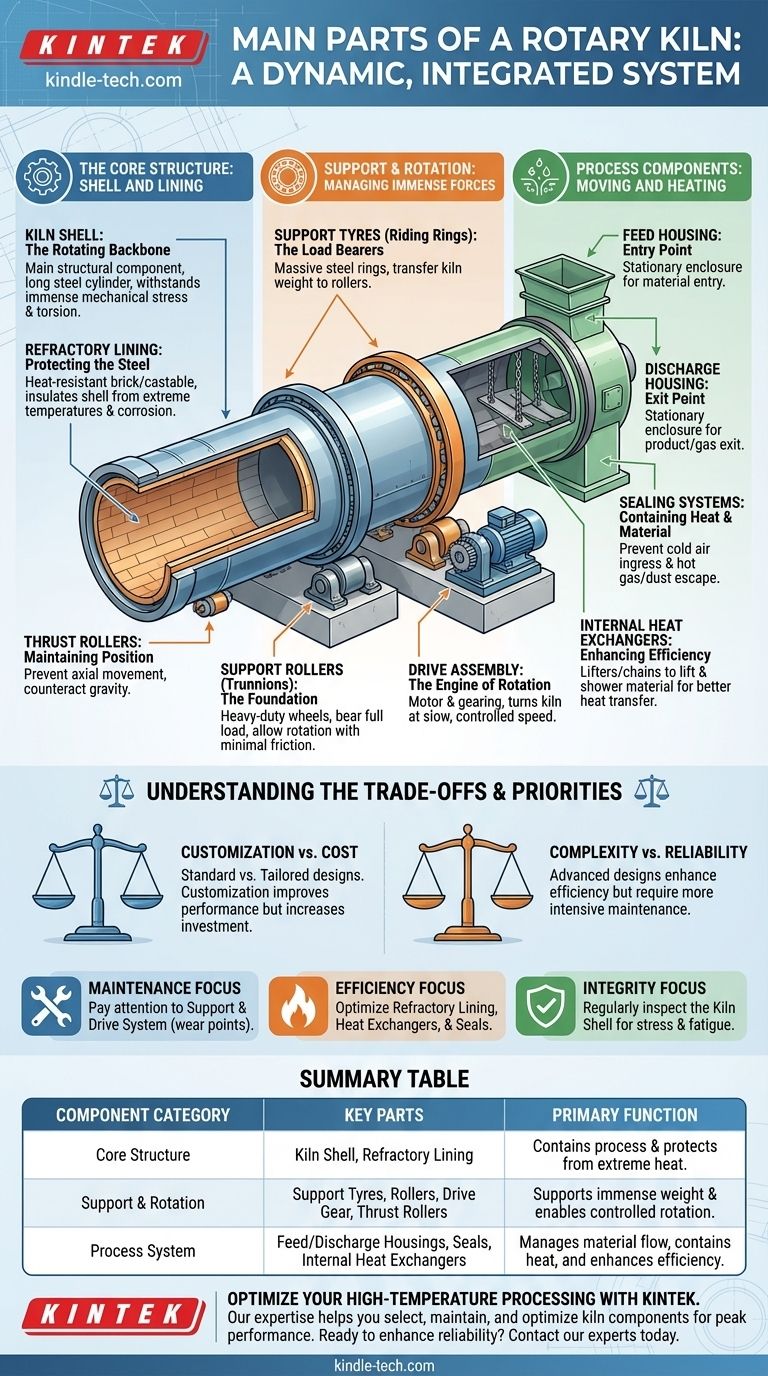
At its core, a rotary kiln is a complex system built around a few primary components. The main parts are the kiln shell, the internal refractory lining, the support tyres and rollers that allow it to rotate, and a drive gear that provides the rotational force. These elements work together within a larger system that includes feed and discharge housings.
A rotary kiln is not merely a collection of parts, but a dynamic, integrated system designed for a single purpose: to process materials at extreme temperatures. Each component is a precise engineering solution to the immense challenges of heat, load, and motion.

The Core Structure: Shell and Lining
The foundation of any rotary kiln is its massive cylindrical body and the protective layer within it. These two components contain the entire process.
The Kiln Shell: The Rotating Backbone
The kiln shell is the main structural component, a long steel cylinder typically tilted at a slight angle. It must withstand enormous mechanical stress, including torsion from the drive system and flexing from its own immense weight. The conical tapering at its ends helps manage material flow.
The Refractory Lining: Protecting the Steel
Inside the shell is a refractory lining, a heat-resistant brick or castable material. Its critical function is to insulate the steel shell from the extreme internal process temperatures and to protect it from chemical corrosion and physical abrasion from the material being processed.
The Support and Rotation System: Managing Immense Forces
Supporting and rotating a structure weighing hundreds or thousands of tons requires a robust and precisely engineered mechanical system.
Support Tyres (Riding Rings): The Load Bearers
Support tyres, also known as riding rings, are massive steel rings attached to the outside of the kiln shell. These rings transfer the entire weight of the kiln and its contents to the support rollers.
Support Rollers (Trunnions): The Foundation
The support tyres ride on sets of heavy-duty support rollers, or trunnion wheels. These rollers are mounted on a solid foundation and bear the full load of the kiln, allowing the massive cylinder to rotate with minimal friction.
The Drive Assembly: The Engine of Rotation
The drive assembly is the motor and gearing system that turns the kiln at a slow, controlled speed. Common types include gear drives, which use a large ring gear mounted on the shell, as well as chain, friction, or direct drive systems.
Thrust Rollers: Maintaining Position
Because the kiln is installed on an incline, gravity constantly pulls it downhill. Thrust rollers are positioned to push against the side of the support tyres, preventing this axial movement and keeping the kiln in its correct position.
The Process Components: Moving and Heating Material
These components manage how material enters, moves through, and exits the kiln, directly impacting process efficiency.
Feed and Discharge Housings: The Entry and Exit Points
At either end of the rotating shell are stationary feed and discharge housings (or breeching). These enclosures provide the connection points for material to enter the kiln and for the final product and hot gases to exit.
Sealing Systems: Containing Heat and Material
Effective seals are installed between the rotating shell and the stationary housings. Their purpose is crucial: to prevent cold air from leaking into the kiln (which hurts efficiency) and to stop hot gas and material dust from escaping into the environment.
Internal Heat Exchangers: Enhancing Efficiency
Many kilns contain internal heat exchangers, such as lifters or chains. As the kiln rotates, these devices lift and shower the material through the hot gas stream, dramatically improving heat transfer and reducing fuel consumption.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting and maintaining kiln components involves balancing competing priorities. An ideal system for one process may be inefficient for another.
Customization vs. Cost
Standard kiln components form the basic design, but most applications require customization. Adjusting the shell diameter, refractory type, or drive system to match a specific material’s needs can significantly improve performance but also increases the initial investment.
Mechanical Complexity vs. Reliability
A rotary kiln is a high-wear environment. The components of the support and rotation system—rollers, tyres, gears, and seals—are under constant mechanical stress. While complex designs can enhance efficiency, they often require more intensive maintenance schedules to ensure long-term reliability.
How to Think About Kiln Components
Your operational priorities will determine which components demand the most attention.
- If your primary focus is on maintenance and reliability: Pay closest attention to the support and drive system, as the tyres, rollers, and drive gear are the primary points of mechanical wear.
- If your primary focus is on process efficiency: The refractory lining, internal heat exchangers, and sealing systems are your key levers for controlling heat loss and optimizing fuel consumption.
- If your primary focus is on structural integrity: The kiln shell itself is the most critical element, requiring regular inspection for signs of stress, fatigue, or distortion.
Understanding how these components function as a unified system is the key to mastering rotary kiln operation and design.
Summary Table:
| Component Category | Key Parts | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Core Structure | Kiln Shell, Refractory Lining | Contains the process & protects from extreme heat |
| Support & Rotation | Support Tyres, Rollers, Drive Gear, Thrust Rollers | Supports immense weight & enables controlled rotation |
| Process System | Feed/Discharge Housings, Seals, Internal Heat Exchangers | Manages material flow, contains heat, and enhances efficiency |
Optimize Your High-Temperature Processing with KINTEK
Understanding the intricate system of a rotary kiln is the first step toward maximizing your operational efficiency and product quality. Whether your priority is maximizing reliability, improving process efficiency, or ensuring structural integrity, the right equipment and support are critical.
KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables, including robust systems designed for demanding thermal processing applications. Our expertise can help you select, maintain, and optimize the key components of your kiln system for peak performance.
Ready to enhance your kiln's performance and reliability? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can bring value to your laboratory or production process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing



















