In principle, any organic material can be subjected to pyrolysis. The most common and commercially viable feedstocks include carbon-rich waste streams like biomass, plastics, and rubber. These materials are chosen for their ability to thermally decompose in a low-oxygen environment into valuable outputs like synthetic oil, gas, and solid char.
The suitability of a material for pyrolysis is not a simple yes or no question. It depends entirely on its chemical composition—specifically, its organic carbon content—and its physical properties, such as moisture and the presence of contaminants.

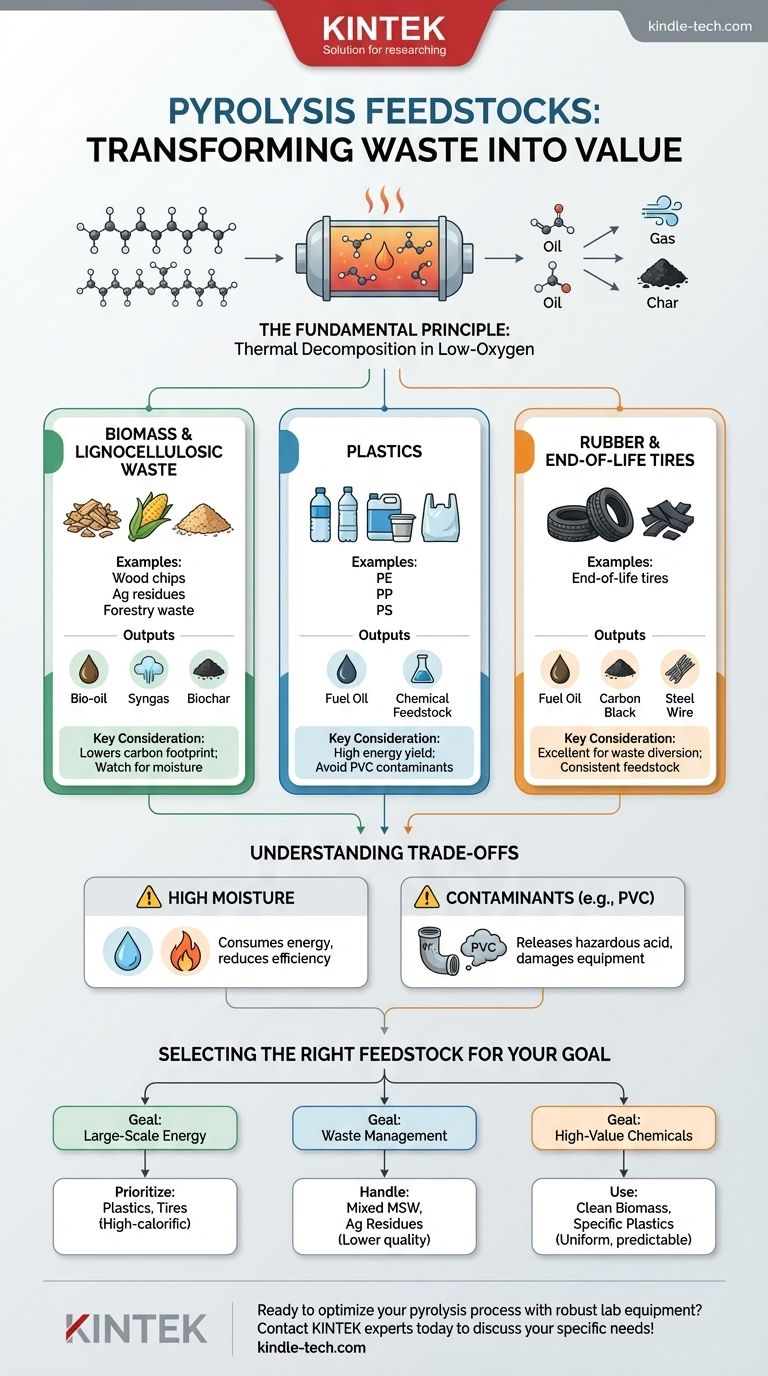
The Fundamental Principle: What Makes a Material Suitable?
Pyrolysis is a process of thermal decomposition. To understand what materials work, you must first understand this core mechanism.
It Must Be Organic
Pyrolysis works by breaking the chemical bonds within large, carbon-based molecules using heat. Materials like wood, plastic, and crops are made of these long organic chains.
Inorganic materials such as metal, glass, or rock do not have this chemical structure and will not decompose in the same way. They will simply get hot.
It Must Decompose Without Oxygen
This is the key difference between pyrolysis and combustion (burning). By heating the material in a near-total absence of oxygen, you prevent it from igniting.
Instead of burning into ash and smoke, the organic molecules crack and reform into smaller, valuable hydrocarbon molecules that make up pyrolysis oil (bio-oil), syngas, and a solid residue called biochar.
It Must Contain Key Compounds
For biomass, the crucial components are lignocellulose, a complex polymer found in the cell walls of plants.
For plastics and rubber, the key components are polymers, which are long, repeating chains of hydrocarbons. These long chains are ideal for being broken down into the shorter chains that constitute fuel and chemical products.
Key Categories of Pyrolysis Feedstock
While the theoretical list is long, a few categories dominate commercial and research applications due to their availability and favorable chemical makeup.
Biomass and Lignocellulosic Waste
This is the broadest and most traditional category. It includes any material derived from plants or animals.
Examples include wood chips, sawdust, agricultural residues (like corn stover and rice husks), forestry waste, and even manure.
Plastics
Pyrolysis offers a powerful solution for non-recyclable plastic waste. The process effectively converts the stored energy in plastics back into a liquid fuel or chemical feedstock.
Commonly used plastics include Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP), and Polystyrene (PS).
Rubber and End-of-Life Tires
Waste tires are an enormous environmental problem, and pyrolysis is one of the most effective methods for recycling them.
The process recovers carbon black (a valuable industrial filler), steel wire, and a tire-derived fuel oil.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Impurities
Not all organic materials are equally good for pyrolysis. The quality and composition of the feedstock directly impact the efficiency of the process and the value of the products.
The Problem of High Moisture
Water in the feedstock must be boiled off before the material's temperature can rise to pyrolysis levels. This consumes a significant amount of energy.
Feedstocks with high moisture content (like green wood or food waste) can make the process inefficient or even energy-negative without a pre-drying step.
The Impact of Contaminants
Certain elements can contaminate the output products or create hazardous emissions. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), for example, releases corrosive hydrochloric acid when heated, which can damage equipment and is an environmental hazard.
Inert materials like dirt, sand, and metal mixed with the feedstock do not contribute to the output and can increase operational costs and wear on machinery.
Feedstock Inconsistency
Using a mixed, inconsistent feedstock (like unsorted municipal solid waste) will produce variable and less predictable yields of oil, gas, and char.
For applications requiring a consistent, high-quality output (like chemical production), a clean and homogenous feedstock is essential.
Selecting the Right Feedstock for Your Goal
The "best" material depends entirely on your primary objective. Choosing the right feedstock is the first step toward designing a successful and economical pyrolysis system.
- If your primary focus is large-scale energy production: Prioritize high-calorific feedstocks like plastics and tires, as they yield the most energy-dense bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is waste management and landfill diversion: Be prepared to handle mixed, lower-quality streams like municipal solid waste or agricultural residues, accepting lower efficiency for the environmental benefit.
- If your primary focus is producing high-value chemicals or biochar: Use clean, uniform, and well-characterized feedstocks like specific plastic types or woody biomass to ensure a predictable and pure product.
Ultimately, a deep understanding of your feedstock's properties is the foundation of any successful pyrolysis operation.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Key Examples | Primary Outputs | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biomass | Wood chips, agricultural residues | Bio-oil, Syngas, Biochar | Lowers carbon footprint; watch for moisture content. |
| Plastics | Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP) | Fuel Oil, Chemical Feedstock | High energy yield; must avoid PVC contaminants. |
| Rubber/Tires | End-of-life tires | Fuel Oil, Carbon Black, Steel | Excellent for waste diversion; consistent feedstock. |
Ready to select the ideal feedstock for your pyrolysis project?
KINTEK specializes in providing robust lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and analysis. Our solutions help you accurately characterize materials like biomass and plastics to optimize your process for maximum yield and efficiency.
Let's turn your waste streams into valuable resources together. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas



















