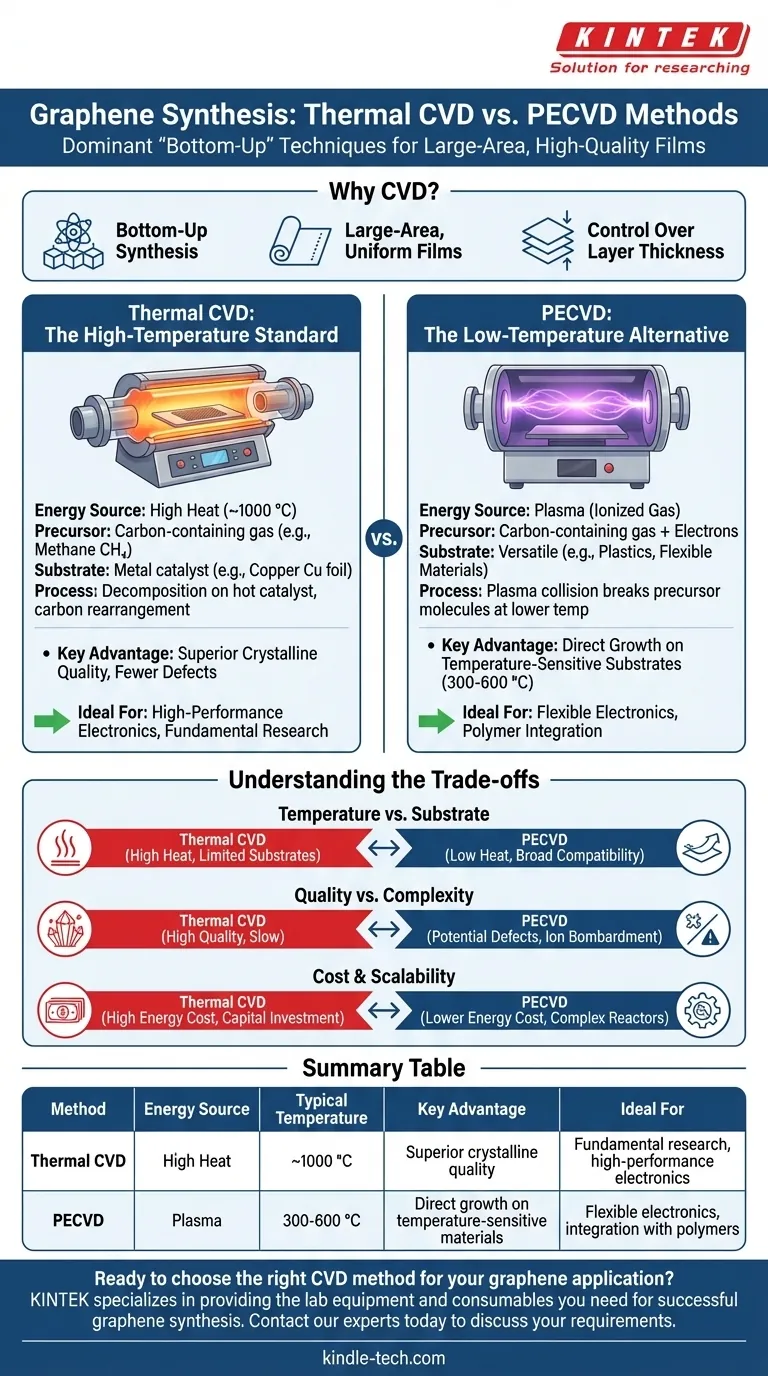
The primary methods for synthesizing graphene via chemical vapor deposition (CVD) are Thermal CVD and Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD). Thermal CVD relies on high temperatures (around 1000 °C) to decompose a carbon-containing gas on a metal catalyst, while PECVD uses an energy-rich plasma to achieve this decomposition at significantly lower temperatures. Both approaches are considered "bottom-up" methods, building the graphene lattice atom by atom to create large, high-quality films.
While CVD has become the dominant technique for producing large-area graphene suitable for commercial applications, the choice between its methods involves a critical trade-off. Thermal CVD sets the standard for quality, but its high heat limits substrate options, whereas PECVD enables deposition on sensitive materials at the potential cost of crystalline perfection.

Why CVD Leads Graphene Production
Chemical vapor deposition is not just one method among many; it is the most promising technique for moving graphene from the laboratory to industrial applications. Its advantages stem from the fundamental way it constructs the material.
The Advantage of "Bottom-Up" Synthesis
Unlike "top-down" methods like exfoliation, which carve graphene from bulk graphite, CVD builds the graphene sheet from individual carbon atoms. This process allows for a high degree of control over the final structure.
By carefully managing gas flow, temperature, and pressure, it's possible to produce highly crystalline, uniform graphene with minimal defects.
Enabling Large-Area, Uniform Films
The single greatest advantage of CVD is its ability to produce continuous, single- or few-layer graphene films over large areas, particularly on metal foils. This scalability is essential for applications in electronics, transparent conductive films, and sensors, where wafer-scale production is a requirement.
Control Over Layer Thickness
The CVD process enables precise control over the number of graphene layers. By tuning the reaction time and precursor concentration, technicians can reliably produce single-layer, bi-layer, or few-layer graphene, tailoring the material's electronic and optical properties for a specific device.
A Breakdown of Core CVD Methods
While the goal is the same, the two main CVD techniques use different energy sources to drive the chemical reaction, leading to distinct process characteristics.
Thermal CVD: The High-Temperature Standard
This is the most common and well-established CVD method for high-quality graphene. A substrate, typically a copper (Cu) foil, is heated to approximately 1000 °C inside a vacuum chamber.
A carbon precursor gas, most often methane (CH₄), is then introduced. At this high temperature, the methane molecules decompose on the hot copper surface, and the resulting carbon atoms arrange themselves into the hexagonal lattice of graphene.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD): The Low-Temperature Alternative
PECVD uses an electric field to generate a plasma, an ionized gas containing high-energy electrons. These electrons collide with the precursor gas molecules, breaking them apart at much lower temperatures than required for thermal decomposition.
This allows graphene deposition to occur at temperatures as low as 300-600 °C, making it possible to grow graphene directly on substrates that cannot withstand the intense heat of Thermal CVD.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a CVD method is an engineering decision based on balancing competing priorities of quality, substrate compatibility, and process complexity.
Temperature vs. Substrate Compatibility
The high temperature of Thermal CVD restricts its use to thermally stable substrates like copper, nickel, or silicon carbide. This often necessitates a complex and potentially damaging transfer process to move the graphene to a final target like a polymer or glass.
PECVD's lower operating temperature dramatically broadens the range of compatible substrates, allowing direct growth on plastics, flexible electronics, and other temperature-sensitive materials.
Quality vs. Process Complexity
Thermal CVD is renowned for producing graphene with superior crystalline quality and electronic properties. The slow, controlled growth on a catalytic surface results in larger crystal domains and fewer defects.
The high-energy environment of PECVD can sometimes introduce structural defects or impurities into the graphene lattice due to ion bombardment. While techniques are improving, achieving the same pristine quality as Thermal CVD remains a challenge.
Cost and Scalability
Both CVD methods require significant capital investment in vacuum and gas handling equipment. Thermal CVD incurs high ongoing energy costs due to the extreme temperatures. PECVD may have lower energy costs but can involve more complex reactor designs.
Selecting the Right CVD Method for Your Goal
Your application's specific requirements should dictate your choice of synthesis method. There is no single "best" approach; there is only the most appropriate tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research or maximum electronic quality: Thermal CVD on a copper catalyst is the established gold standard for producing the most pristine, defect-free graphene.
- If your primary focus is integrating graphene onto temperature-sensitive substrates: Plasma-Enhanced CVD is the necessary choice due to its lower processing temperatures, enabling direct deposition on materials like polymers.
- If your primary focus is industrial-scale production: The decision will depend on balancing the higher energy cost of Thermal CVD against the potential quality variations and substrate flexibility of PECVD.
Ultimately, the choice between thermal and plasma-enhanced CVD is a strategic decision guided by your specific material and application requirements.
Summary Table:
| Method | Energy Source | Typical Temperature | Key Advantage | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal CVD | High Heat | ~1000 °C | Superior crystalline quality | Fundamental research, high-performance electronics |
| PECVD | Plasma | 300-600 °C | Direct growth on temperature-sensitive materials | Flexible electronics, integration with polymers |
Ready to choose the right CVD method for your graphene application?
KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables you need for successful graphene synthesis. Whether you are optimizing a Thermal CVD process for maximum quality or exploring the versatility of PECVD, our expertise and products support your research and development goals.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can help you achieve superior results in your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition



















