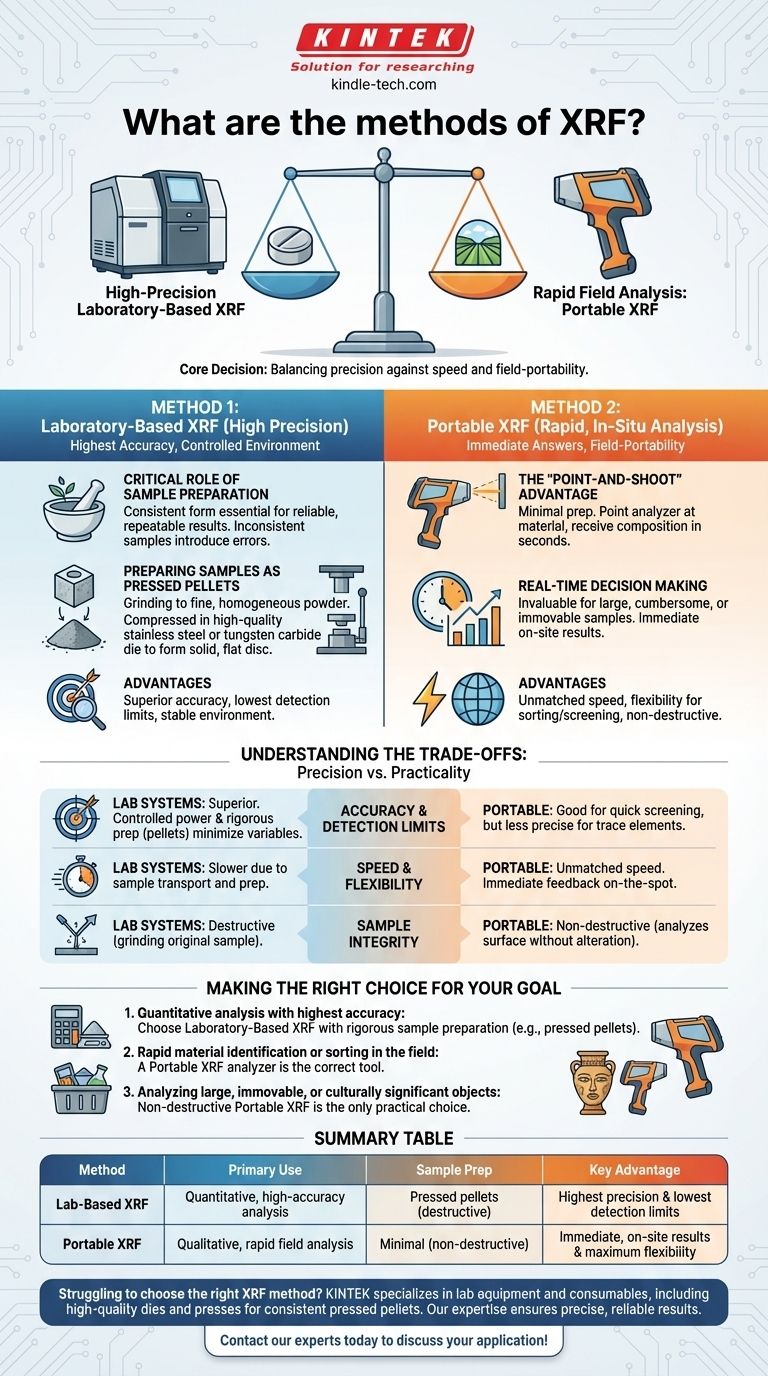
Fundamentally, X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) methods are defined by the type of instrument used and the way the sample is prepared for analysis. The two primary approaches are high-precision laboratory-based analysis, which often involves preparing samples as pressed pellets, and rapid field analysis using portable, handheld analyzers.
The core decision in choosing an XRF method is balancing the need for analytical precision against the demand for speed and field-portability. Laboratory methods provide the highest accuracy through controlled sample preparation, while portable methods offer immediate, on-the-spot answers.
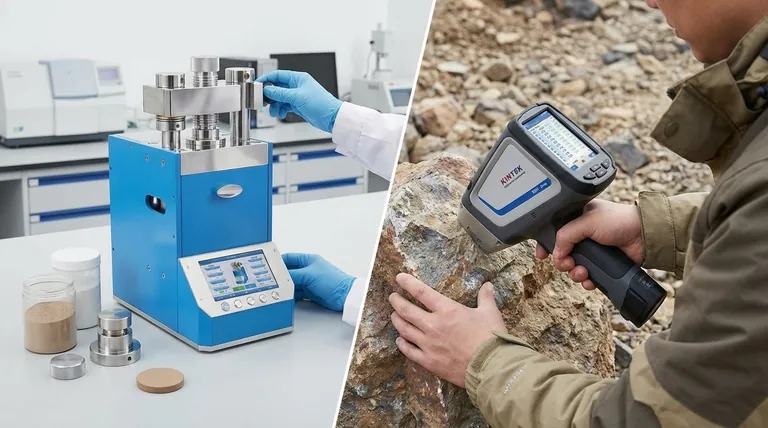

Two Core Approaches: Lab vs. Field
The most significant distinction in XRF methodology is where the analysis takes place. This determines the instrumentation, sample preparation requirements, and the quality of the results.
Method 1: Laboratory-Based XRF (High Precision)
This approach is used when the highest degree of accuracy and the lowest detection limits are required. Lab instruments are larger, more powerful, and operate in a controlled environment.
The Critical Role of Sample Preparation
For a lab-based XRF to produce reliable, repeatable results, the sample must be presented to the instrument in a consistent form. Inconsistent sample density, surface texture, or particle size can introduce significant errors.
Preparing Samples as Pressed Pellets
One of the most common and effective preparation techniques is creating a pressed pellet. This involves grinding a sample into a fine, homogeneous powder.
This powder is then placed into a high-quality die, often made of hardened 440C stainless steel, and compressed under high pressure to form a solid disc with a perfectly flat, smooth surface.
Using dies with a mirror finish ensures consistency between samples, which is crucial for repeatability. For analyses where iron contamination from a steel die is a concern, dies with tungsten carbide pressing faces are used instead.
Method 2: Portable XRF (Rapid, In-Situ Analysis)
Portable, or handheld, XRF analyzers bring the analysis directly to the sample. This is the method of choice for fieldwork where sending samples to a lab is impractical or too slow.
The "Point-and-Shoot" Advantage
This method is defined by its speed and minimal sample preparation. The user simply points the analyzer at the material and receives its elemental composition or alloy grade in seconds.
Portable analyzers are invaluable for testing large, cumbersome, or expensive samples that cannot be moved or destroyed. They provide real-time information that enables immediate decision-making in the field.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Precision vs. Practicality
Neither method is inherently superior; they are designed for different objectives. Understanding their trade-offs is key to selecting the right tool for the job.
Accuracy and Detection Limits
Laboratory systems offer superior accuracy. The controlled power, stable environment, and rigorous sample preparation (like pellet pressing) minimize variables and allow for the detection of elements at much lower concentrations.
Speed and Flexibility
Portable analyzers offer unmatched speed. They provide immediate feedback for sorting materials, screening sites, or identifying alloys on the spot, eliminating the logistical delays of lab analysis.
Sample Integrity
Portable XRF is non-destructive. It analyzes the surface of a material without altering it. In contrast, preparing a pressed pellet is a destructive method, as the original sample is ground into a powder.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate method, you must first define your primary analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis with the highest accuracy: Choose a laboratory-based XRF system with a rigorous sample preparation method like pressed pellets.
- If your primary focus is rapid material identification or sorting in the field: A portable XRF analyzer is the correct tool for immediate, on-site results.
- If your primary focus is analyzing large, immovable, or culturally significant objects: The non-destructive nature of portable XRF makes it the only practical choice.
Ultimately, the best XRF method is the one that aligns the need for analytical precision with the practical constraints of your sample and environment.
Summary Table:
| Method | Primary Use | Sample Prep | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lab-Based XRF | Quantitative, high-accuracy analysis | Pressed pellets (destructive) | Highest precision and lowest detection limits |
| Portable XRF | Qualitative, rapid field analysis | Minimal (non-destructive) | Immediate, on-site results and maximum flexibility |
Struggling to choose the right XRF method for your specific laboratory needs? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including the high-quality dies and presses essential for creating consistent pressed pellets for lab-based XRF analysis. Our expertise ensures you achieve the precise, reliable results your research demands. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and find the perfect solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press for XRF KBR FTIR Lab Applications
- XRF & KBR steel ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press utilized for electrolyte pelletizing? Unlock High Ionic Conductivity
- What is the use of manual hydraulic press? A Cost-Effective Tool for Lab Sample Preparation
- How do laboratory hydraulic presses facilitate biomass pelletization? Optimize Biofuel Density and Prevent Slagging
- What is KBr disc method? A Complete Guide to IR Spectroscopy Sample Prep
- What is the function of a bench-top laboratory hydraulic press for XRF? Maximize Accuracy in Prosopis juliflora Analysis



















