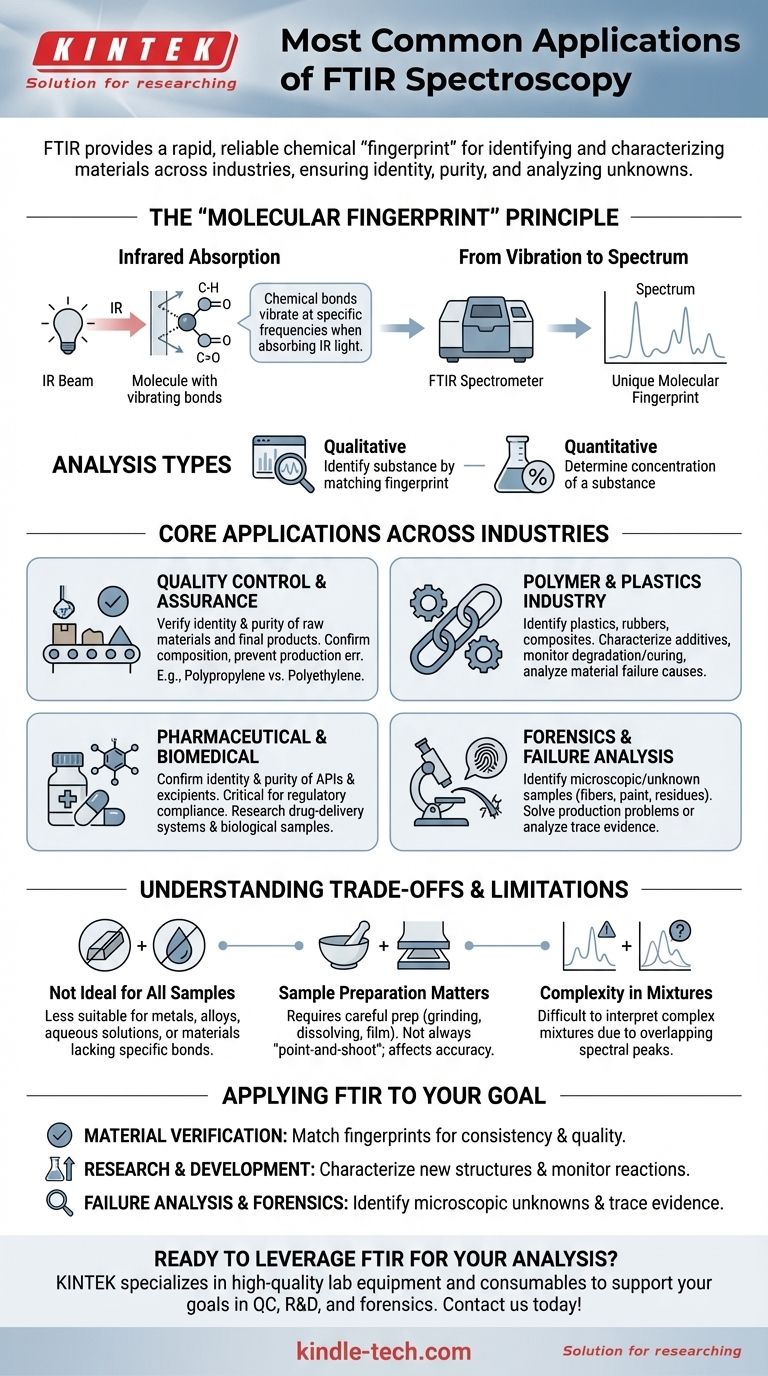
In essence, Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy is a cornerstone analytical technique used across a vast range of industries for its ability to identify and characterize materials. Its most common applications are in quality control, polymer science, pharmaceuticals, and forensic analysis, where it provides a rapid and reliable chemical "fingerprint" of a substance.
The core value of FTIR lies in its versatility. It's not just a tool for identifying a specific substance, but a fundamental method for confirming material identity, ensuring purity, and investigating unknown contaminants across scientific, industrial, and investigative fields.
How FTIR Delivers Its Insights: The 'Molecular Fingerprint'
The Principle of Infrared Absorption
Every chemical bond within a molecule (like a carbon-hydrogen or a carbon-oxygen double bond) vibrates at a specific frequency when it absorbs infrared light.
These vibrational frequencies are unique to the type of bond and its surrounding molecular structure.
From Vibration to a Spectrum
An FTIR spectrometer shines a beam of infrared light through a sample and measures which frequencies of light are absorbed.
The instrument then plots this absorption data as a graph, or spectrum, with peaks corresponding to the specific bonds present in the sample. This resulting spectrum serves as a unique molecular fingerprint.
Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis
Primarily, FTIR is used for qualitative analysis—identifying what a substance is by matching its fingerprint to a known library.
It can also be used for quantitative analysis—determining the concentration of a substance—though this is often a more complex application.
Core Applications Across Key Industries
Quality Control and Assurance
This is one of the most widespread uses of FTIR. Manufacturers use it to verify the identity and purity of incoming raw materials and to confirm the composition of final products.
For example, a plastics manufacturer can instantly confirm a shipment of raw pellets is polypropylene and not polyethylene, preventing costly production errors.
Polymer and Plastics Industry
FTIR is indispensable for analyzing polymers. It is used to identify different types of plastics, rubbers, and composites.
It also helps in characterizing additives, monitoring polymer degradation or curing processes, and analyzing the causes of material failure.
Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis
In the pharmaceutical industry, FTIR is used to confirm the identity and purity of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients.
It is a critical tool for regulatory compliance and is also used in research to study drug-delivery systems and analyze biological samples like tissues.
Forensics and Failure Analysis
FTIR excels at identifying microscopic or unknown samples. Forensic labs use it to analyze fibers, paint chips, adhesives, and unknown powders found at a crime scene.
In industrial settings, it's used to identify unknown contaminants responsible for a product's failure, such as a residue on a faulty electronic component.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Not Ideal for All Samples
FTIR identifies the covalent bonds found in organic and many inorganic molecules. It is not suitable for identifying materials that lack these bonds, such as metals, alloys, or simple ionic salts.
Furthermore, water has a very strong infrared absorption that can obscure the signal from a sample, making analysis in aqueous solutions challenging.
Sample Preparation Matters
The quality of an FTIR spectrum is highly dependent on how the sample is prepared. While some samples can be analyzed with minimal prep, others may need to be ground into a powder, dissolved in a solvent, or pressed into a thin film.
This is not always a simple "point-and-shoot" technique, and improper preparation can lead to inaccurate results.
Complexity in Mixtures
While FTIR is excellent at identifying pure substances, analyzing complex mixtures can be difficult. The spectral peaks from multiple components can overlap, making it hard to interpret the fingerprint without advanced software and reference libraries.
Applying FTIR to Your Specific Goal
FTIR is a powerful and versatile tool, but its application depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is material verification: Use FTIR to quickly match the fingerprint of incoming materials or finished products against a known standard to ensure consistency and quality.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Employ FTIR to characterize the chemical structure of new materials you are creating or to monitor molecular changes during a chemical reaction.
- If your primary focus is failure analysis or forensics: Leverage FTIR's sensitivity to identify microscopic unknowns, such as contaminants, residues, or trace evidence that could solve a production problem or a crime.
Ultimately, FTIR empowers you to understand the fundamental chemical makeup of your material, providing the clarity needed for confident decision-making.
Summary Table:
| Industry/Field | Primary Application of FTIR |
|---|---|
| Quality Control | Verify raw material identity and final product purity |
| Polymer Science | Identify plastics, rubbers, and analyze additives or degradation |
| Pharmaceuticals | Confirm API identity, purity, and ensure regulatory compliance |
| Forensic Analysis | Identify unknown samples like fibers, paints, or contaminants |
Ready to leverage FTIR for your material analysis needs? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support your laboratory's goals. Whether you're in quality control, R&D, or forensic analysis, our solutions ensure accurate and reliable results. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your analytical capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Thin-Layer Spectral Electrolysis Electrochemical Cell
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Barium Fluoride BaF2 Substrate Window
People Also Ask
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion
- How do you prepare samples for SEM analysis? Achieve Clear, Accurate Imaging Every Time
- What is the difference between filtration and centrifugation? A Guide to Size vs. Density Separation
- What is the long-term stability of viral analytes in plasma stored at -70°C? Proven for Decades of Research
- How are Ultra Freezers designed for easy movement in laboratories? Unlock Lab Flexibility with Swivel Castors
- What is the cheapest biomass fuel? Uncover the True Cost Beyond the Price Tag
- What is a microwave pyrolysis reactor? A Guide to Faster, More Efficient Thermal Processing
- What is the purpose of using heat treatment? Tailor Material Properties for Superior Performance



















