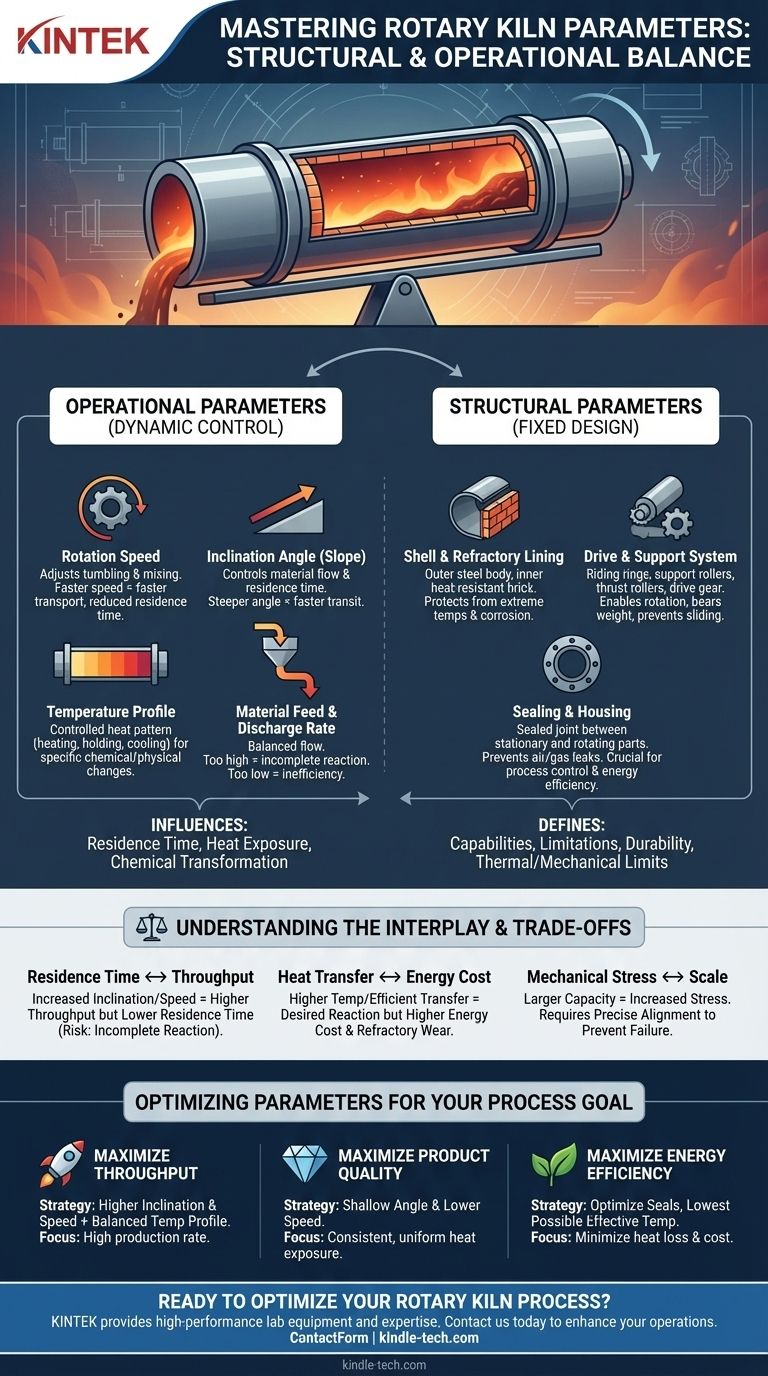
At its core, the parameters of a rotary kiln are the set of design and operational variables that control its function. These are broadly divided into two categories: structural parameters, which define the kiln's physical construction, and operational parameters, which are adjusted during use to control the material processing environment. The most critical operational parameters include temperature, inclination angle, rotation speed, and material feed rate.
A rotary kiln's effectiveness is not determined by a single setting, but by the precise and dynamic balance of its parameters. Mastering this interplay is the key to controlling the material's residence time, heat exposure, and chemical transformation, which ultimately dictates the quality of the final product.

Deconstructing the Core Operational Parameters
Operational parameters are the dynamic variables you control to fine-tune the process. They work together to manage how material moves through the kiln and how it is heated.
Rotation Speed
The speed at which the kiln's cylindrical body rotates is a fundamental control. A faster rotation increases the tumbling and mixing of the material bed.
This enhances heat transfer but also tends to move the material through the kiln more quickly, reducing its total time inside.
Inclination Angle (Slope)
Rotary kilns are installed at a slight downward angle. This slope, combined with the rotation, is what causes the solid material to travel from the feed end to the discharge end.
Adjusting this angle is a primary way to control the residence time—the total duration the material spends being processed. A steeper angle means a faster transit and shorter residence time.
Temperature Profile
The process requires a specific temperature, often extremely high, to drive the desired chemical or physical changes. However, it's rarely a single temperature.
Instead, operators establish a temperature profile along the length of the kiln. This controlled heat pattern ensures the material is heated, held at temperature, and sometimes cooled in a precise sequence for optimal results.
Material Feed & Discharge Rate
The rate at which raw material is fed into the kiln must be carefully balanced with the kiln's capacity to process it.
This flow rate is directly linked to the other parameters. An overload of material can lead to incomplete reactions, while an insufficient feed rate can be inefficient and waste energy.
The Anatomy of a Rotary Kiln: Structural Parameters
Structural parameters are the fixed design and construction elements of the kiln itself. While not adjusted during operation, they define the kiln's capabilities and limitations.
The Shell and Refractory Lining
The shell is the kiln's outer cylindrical steel body. Inside, a refractory lining of heat-resistant brick or castable material protects the shell from extreme temperatures and chemical attack.
The choice of refractory material is a critical design parameter based on the process temperature and the corrosiveness of the material being handled.
The Drive and Support System
This system enables the kiln to rotate smoothly and reliably. It consists of several key components:
- Support Tyres (Riding Rings): Massive steel rings that encircle the shell and ride on rollers.
- Support Rollers (Trunnion Wheels): These rollers bear the entire weight of the kiln and allow it to rotate.
- Thrust Rollers: These prevent the kiln from sliding downhill due to its inclination.
- Drive Gear: A large gear, typically wrapped around the shell, that is driven by a motor to turn the kiln.
Sealing and Housing
The stationary feed and outlet housings must be sealed against the rotating kiln shell. Effective seals are crucial for preventing air from leaking into the kiln (or process gases from leaking out), ensuring process control, and maximizing energy efficiency.
Understanding the Interplay and Trade-offs
The parameters of a rotary kiln are deeply interconnected. Changing one inevitably affects the others, creating a series of trade-offs that must be managed.
Residence Time vs. Throughput
Increasing the inclination angle or rotation speed will increase throughput (the amount of material processed per hour). However, this directly reduces the material's residence time.
If the residence time becomes too short, the material may exit the kiln before the chemical reaction or physical change is complete, resulting in a poor-quality product.
Heat Transfer vs. Energy Cost
Achieving high temperatures and efficient heat transfer is essential for many processes. However, this comes at a significant energy cost.
Furthermore, extremely high temperatures accelerate the wear and tear on the expensive refractory lining, leading to more frequent and costly downtime for maintenance.
Mechanical Stress vs. Scale
Building a larger kiln increases its processing capacity. However, the immense weight and length create significant mechanical challenges.
Proper alignment of the support rollers is absolutely critical to distribute the load evenly and prevent destructive stress on the shell, tyres, and drive system. Even minor misalignment can lead to catastrophic failure.
Optimizing Parameters for Your Process Goal
Your ideal parameter settings depend entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput: You will operate at a higher inclination and rotation speed, balanced with a temperature profile just sufficient to complete the reaction within that shorter residence time.
- If your primary focus is product quality and uniformity: You will prioritize a slower material flow via a shallower angle and lower rotation speed, ensuring every particle gets consistent and sufficient heat exposure.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: You will optimize the sealing systems to prevent heat loss, utilize internal heat exchangers or baffles, and run at the lowest possible temperature that still achieves the desired product specification.
Ultimately, mastering a rotary kiln is the art and science of balancing these interconnected variables to achieve your specific process outcome reliably and efficiently.
Summary Table:
| Parameter Category | Key Variables | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Operational | Rotation Speed, Inclination Angle, Temperature Profile, Feed Rate | Control material flow, heat exposure, and reaction completeness during operation. |
| Structural | Shell & Refractory Lining, Drive/Support System, Seals | Define the kiln's physical capabilities, durability, and thermal/mechanical limits. |
Ready to Optimize Your Rotary Kiln Process?
Achieving the perfect balance of parameters is critical for maximizing throughput, ensuring product quality, and improving energy efficiency. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for thermal processing. Our expertise can help you select the right equipment and optimize your process parameters for superior results.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your operations.
[#ContactForm]
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products



















