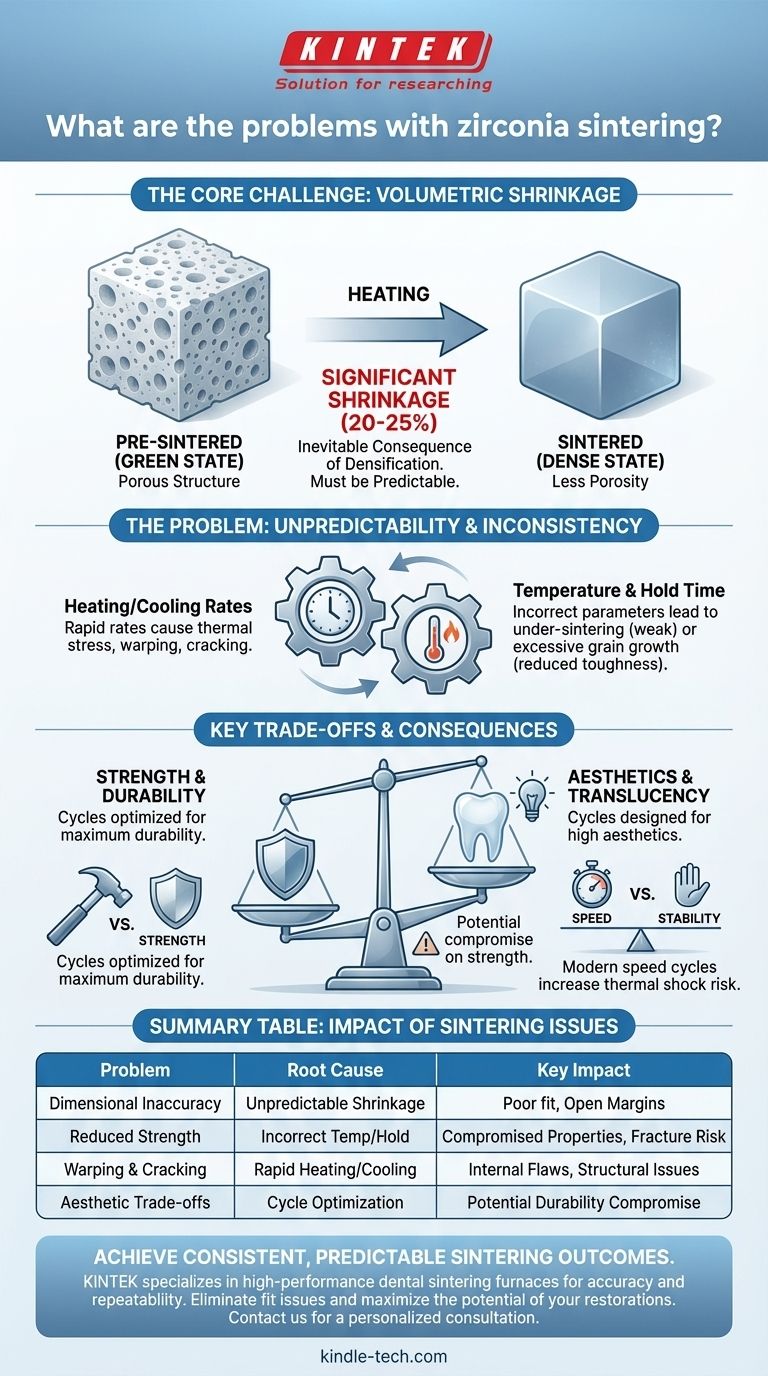
The fundamental problem with zirconia sintering is significant and potentially unpredictable volumetric shrinkage. This process, which is essential for increasing the material's density and strength, can lead to dimensional inaccuracies in the final restoration, causing issues with fit, function, and longevity if not precisely controlled.
Sintering is a necessary step that transforms a weak, porous zirconia structure into a strong, dense ceramic. However, the very mechanism that grants this strength—particle fusion and densification—is also the primary source of its biggest challenge: controlling the substantial shrinkage to ensure the final product is dimensionally accurate.

The Core Challenge: Managing Volumetric Shrinkage
Sintering works by heating the "green state" (milled, unsintered) zirconia to a high temperature, below its melting point. This causes the individual zirconia particles to fuse together, eliminating the empty spaces (porosity) between them and dramatically increasing the material's density and strength.
The Inevitable Consequence of Densification
This reduction in porosity directly translates to a reduction in volume. Zirconia can shrink by 20-25% during a properly executed sintering cycle. This is not a flaw in the material but a fundamental aspect of its processing.
The challenge is that this shrinkage must be perfectly uniform and predictable. The design software and milling process must accurately account for this change, enlarging the pre-sintered restoration by the precise amount it is expected to shrink.
When Shrinkage Becomes a Problem
Problems arise when the actual shrinkage deviates from the predicted amount. Even a small deviation can result in a restoration that does not fit the patient's preparation, leading to open margins, poor seating, and ultimately, clinical failure. This variability is the root of most sintering-related issues.
Unpacking Sintering Cycle Complexities
Many failures are traced back to inconsistencies or errors within the sintering cycle itself. The parameters of the heating and cooling process are critical for achieving the desired outcome.
Impact of Temperature and Hold Time
The final temperature and the duration it is held directly influence the final density and grain size of the zirconia. Sintering at too low a temperature or for too short a time can result in an under-sintered part with residual porosity, compromising its mechanical strength.
Conversely, excessively high temperatures can lead to oversized grain growth, which can paradoxically reduce the material's toughness and resistance to fracture.
The Danger of Heating and Cooling Rates
The rate at which the furnace heats up and cools down is equally important. Ramping the temperature too quickly can create thermal gradients within the material, causing internal stresses that can lead to warping or even microscopic cracks that compromise the integrity of the final product.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Optimizing a sintering cycle is often a balancing act between competing properties. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for troubleshooting and achieving consistent results.
Strength vs. Aesthetics
Different sintering temperatures can affect the final translucency of the zirconia. Often, cycles designed for higher translucency and better aesthetics may result in slightly lower flexural strength compared to cycles optimized purely for maximum durability. The choice depends on the clinical demands of the restoration.
Speed vs. Stability
Modern "speed sintering" cycles offer significant time savings, which is a major advantage for clinical workflow. However, these accelerated cycles use much faster heating and cooling rates, which increases the risk of thermal shock and internal stress, demanding a highly accurate and well-maintained furnace to succeed.
Achieving Predictable Sintering Outcomes
Your approach to sintering should be guided by your primary clinical or production goal. Consistency is achieved by meticulously controlling the process variables.
- If your primary focus is predictable fit: Calibrate your furnace regularly and use zirconia from a reputable manufacturer with a consistent, well-documented shrinkage factor.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength: Adhere strictly to the manufacturer's recommended cycle for conventional sintering, avoiding shortcuts on hold times or cooling periods.
- If your primary focus is high aesthetics: Use a zirconia material and a corresponding sintering cycle specifically designed for high translucency, accepting the potential trade-off in absolute strength.
Ultimately, mastering zirconia sintering requires treating it not as a simple heating step, but as a precise thermal engineering process critical to the final restoration's success.
Summary Table:
| Problem | Root Cause | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensional Inaccuracy | Unpredictable or non-uniform volumetric shrinkage (20-25%) | Poor fit, open margins, clinical failure |
| Reduced Strength | Incorrect temperature/hold time (under-sintering or excessive grain growth) | Compromised mechanical properties, risk of fracture |
| Warping & Cracking | Rapid heating/cooling rates causing thermal stress | Internal flaws, structural integrity issues |
| Aesthetic Trade-offs | Cycle optimization for translucency vs. strength | Potential compromise on durability for aesthetics |
Achieve consistent, predictable sintering results for your dental lab. The challenges of volumetric shrinkage, temperature control, and cycle optimization demand precise, reliable equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance dental sintering furnaces designed for accuracy and repeatability. Let our experts help you select the right furnace to eliminate fit issues and maximize the strength and aesthetics of your zirconia restorations.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation to discuss your lab's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability



















