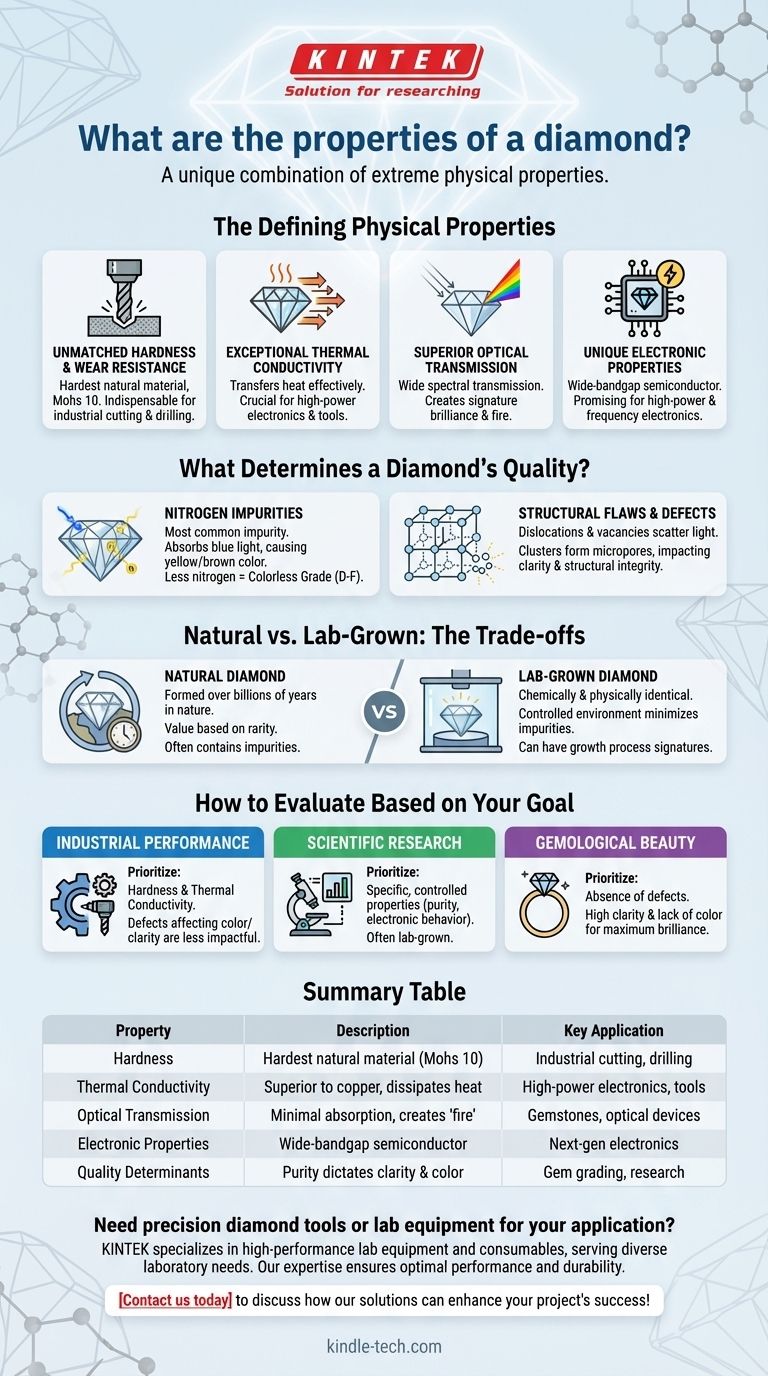
From industrial tools to iconic jewels, a diamond's value stems from a unique combination of extreme physical properties. Fundamentally, these include exceptional hardness and wear resistance, the highest thermal conductivity of any natural material, a wide band of optical transparency, and superior electronic characteristics. These inherent qualities make it one of the most remarkable and versatile materials known.
A diamond's extraordinary properties are universal, but its ultimate quality and performance are dictated by the purity of its crystal structure. The absence of internal defects is what separates a flawless, brilliant gem from a functional, industrial-grade stone.

The Defining Physical Properties
A diamond is a crystal of carbon where the atoms are arranged in a specific cubic structure called a diamond lattice. This rigid, tightly bonded arrangement is the source of its legendary characteristics.
Unmatched Hardness and Wear Resistance
A diamond is the hardest known natural material, ranking 10 on the Mohs scale of hardness. This extreme stiffness and resistance to scratching are why diamonds are indispensable in industrial cutting, grinding, and drilling applications.
Exceptional Thermal Conductivity
Counterintuitively, diamonds are incredible thermal conductors, transferring heat more effectively than metals like copper. This allows them to rapidly dissipate heat, a crucial property for high-power electronics and precision cutting tools that generate intense friction.
Superior Optical Transmission
A diamond's ability to transmit light across a wide spectrum with minimal absorption is the foundation of its brilliance as a gemstone. This high optical clarity, combined with its crystal structure, allows it to bend and reflect light, creating its signature "fire" and sparkle.
Unique Electronic Properties
As a wide-bandgap semiconductor, diamond possesses superior electronic properties. It can withstand high voltages and temperatures, making it a promising material for next-generation high-power and high-frequency electronic devices.
What Determines a Diamond's Quality? The Role of Defects
While all diamonds share these core properties, not all are created equal. The presence of impurities and structural flaws within the crystal lattice determines its grade, clarity, and color.
Nitrogen Impurities
Nitrogen is the most common impurity found in diamonds. Even in trace amounts, nitrogen atoms absorb blue light, which causes the crystal to appear yellow or brownish. The most valuable gem-quality diamonds are those with little to no nitrogen, earning them a colorless grade (D, E, or F).
Structural Flaws: Dislocations and Vacancies
Imperfections in the crystal lattice, such as dislocations (misaligned rows of atoms) or vacancies (missing carbon atoms), can scatter light and reduce clarity. When these vacancies cluster, they can form microscopic voids, or micropores, that impact the diamond's structural integrity and appearance.
Polycrystalline Imperfections
During very rapid crystal formation, multiple small crystals can fuse together. The boundaries between these grains can create internal stress and non-diamond carbon inclusions, sometimes called 'black organisation,' which significantly degrade the stone's transparency and grade.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Natural vs. Lab-Grown
Lab-grown diamonds are chemically and physically identical to natural diamonds. However, the controlled environment in which they are created leads to different characteristics and trade-offs.
Controlled Environments, Higher Purity
Because the growth environment is tightly controlled, manufacturers can minimize the introduction of impurities like nitrogen. This allows for the consistent production of diamonds with very high clarity and colorless grades, which are rare in nature.
The Growth Process Signature
Methods like CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) involve growing diamond layers in a vacuum chamber. This process can sometimes result in rough graphite edges or an initial brown color that must be removed with post-growth treatment. These are tell-tale signs of the manufacturing process.
The Question of Value
While lab-grown diamonds can exhibit fewer flaws, the market often differentiates their value from natural diamonds based on rarity. Natural diamonds are a finite resource formed over billions of years, a factor that is independent of their physical properties but central to their perceived value as a gem.
How to Evaluate a Diamond Based on Your Goal
The "best" diamond is entirely dependent on its intended application. Focusing on the right properties will guide you to the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is industrial performance: Prioritize hardness and thermal conductivity, as defects affecting color or minor clarity have little impact on functional use.
- If your primary focus is scientific research: Seek diamonds with specific, controlled properties—often lab-grown—to ensure purity and predictable electronic or optical behavior.
- If your primary focus is gemological beauty: The absence of defects is paramount. Aim for high clarity (minimal inclusions) and a lack of color (grades D-F) to maximize brilliance and fire.
Understanding these fundamental properties empowers you to look beyond the surface and assess a diamond based on its true structural integrity and purpose.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Hardest natural material (Mohs 10) | Industrial cutting, drilling |
| Thermal Conductivity | Superior to copper, dissipates heat rapidly | High-power electronics, tools |
| Optical Transmission | Transmits light with minimal absorption, creating 'fire' | Gemstones, optical devices |
| Electronic Properties | Wide-bandgap semiconductor, withstands high voltages/temperatures | Next-generation electronics |
| Quality Determinants | Purity, absence of nitrogen/defects dictates clarity & color | Gem grading, scientific research |
Need precision diamond tools or lab equipment for your application? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, serving diverse laboratory needs. Whether you require diamond-based instruments for cutting-edge research or reliable tools for industrial use, our expertise ensures optimal performance and durability. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your project's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is the future value of lab grown diamond? Understanding Its Depreciating Financial Worth
- What is the future of CVD diamond? Unlocking Next-Gen Electronics & Thermal Management
- Are CVD diamonds fake? Discover the Truth About Lab-Grown Diamonds
- What are the common sources of contamination during CVD diamond growth? Improve Purity and Quality Control
- What is the difference between CVD and original diamond? Choose the Right Diamond for Your Needs










