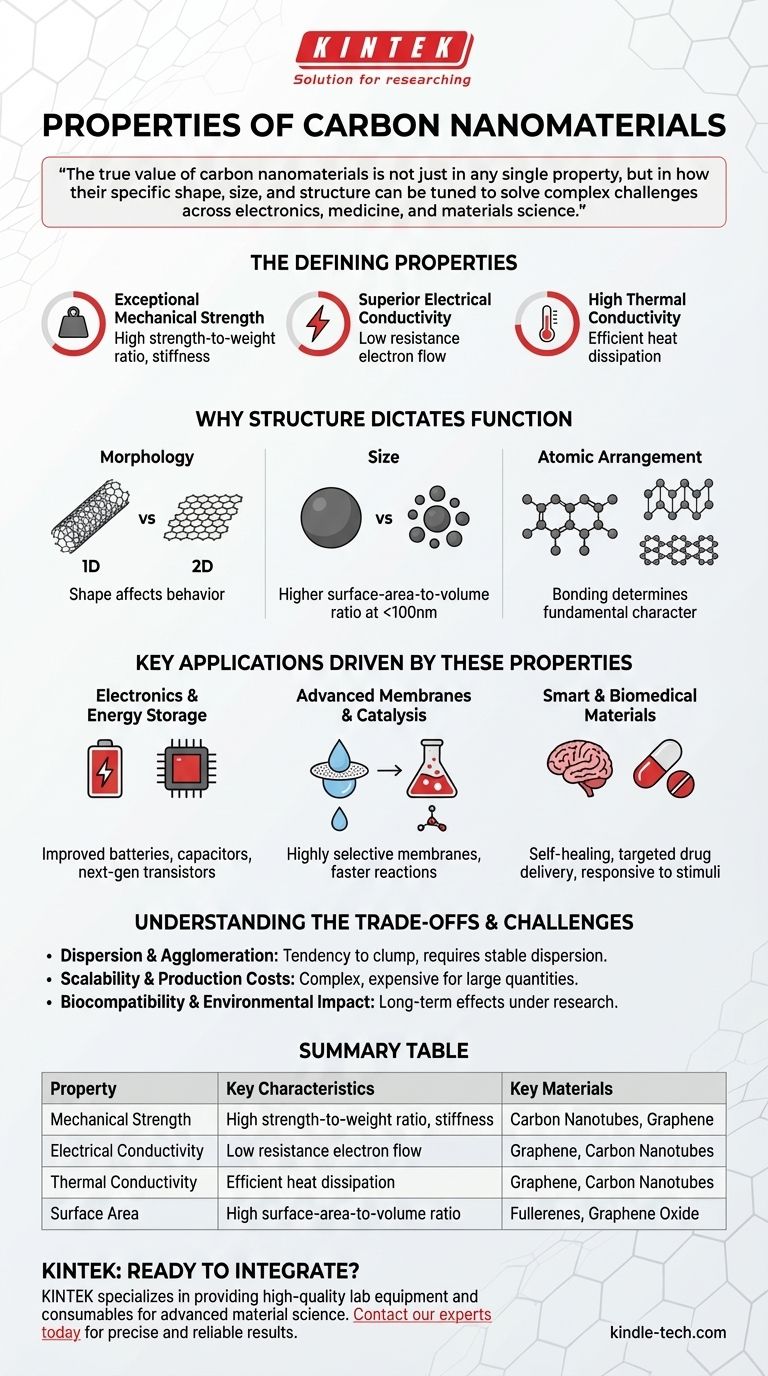
At their core, carbon nanomaterials are defined by a unique combination of exceptional thermal, electrical, and mechanical properties. These characteristics arise because their size, existing at a scale between 1 and 100 nanometers, allows for special physical and chemical behaviors not seen in bulk carbon.
The true value of carbon nanomaterials is not just in any single property, but in how their specific shape, size, and structure can be tuned to solve complex challenges across electronics, medicine, and materials science.
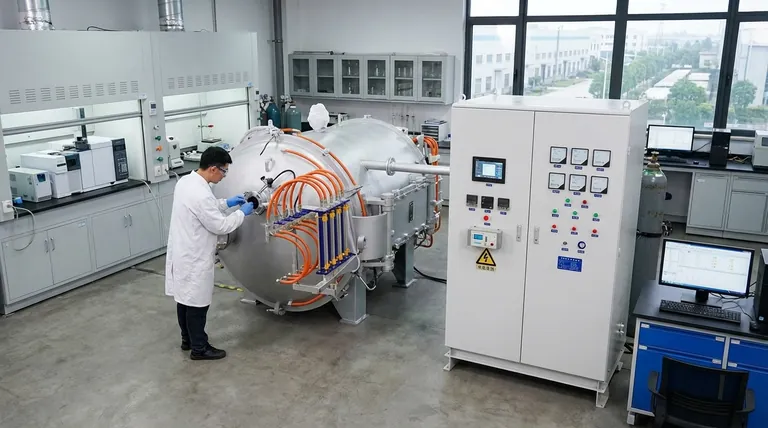

The Defining Properties of Carbon Nanomaterials
The term "carbon nanomaterials" encompasses a family of structures, including nanotubes, graphene, and fullerenes. While each has unique traits, they share a common set of extraordinary foundational properties.
Exceptional Mechanical Strength
Carbon nanomaterials are among the strongest and stiffest materials ever discovered in terms of tensile strength and elastic modulus. They possess an incredibly high strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for reinforcing composites and creating lightweight, durable materials.
Superior Electrical Conductivity
Many carbon nanomaterials are highly effective conductors of electricity. Their unique electronic structures allow electrons to move with very little resistance, a property essential for applications in advanced electronics, transparent conductive films, and energy storage devices.
High Thermal Conductivity
These materials are also excellent thermal conductors, capable of transferring heat more efficiently than traditional materials like copper. This makes them valuable for thermal management in electronics, where dissipating heat is a critical challenge.
Why Structure Dictates Function
The specific properties of a carbon nanomaterial are not fixed; they are directly influenced by its physical form. This principle is the key to unlocking their potential for specific applications.
The Impact of Morphology
The shape of the nanomaterial has a profound effect on its behavior. For example, a one-dimensional carbon nanotube behaves very differently from a two-dimensional sheet of graphene, even though both are made of pure carbon.
The Role of Size
Within the 1-100 nanometer range, size matters. As a particle gets smaller, its surface-area-to-volume ratio increases dramatically, which is a critical factor for applications in catalysis and sensing.
The Influence of Atomic Arrangement
The way carbon atoms bond and arrange themselves (their phase) determines the material's fundamental electronic and mechanical character. This structural variance is what gives rise to the diverse family of carbon nanomaterials.
Key Applications Driven by These Properties
The unique properties of carbon nanomaterials make them enabling technologies across a vast range of fields. Their function is a direct result of their form.
Electronics and Energy Storage
High electrical conductivity makes carbon nanomaterials ideal for improving the performance and efficiency of batteries, capacitors, and next-generation transistors.
Advanced Membranes and Catalysis
The high surface area and tunable structures are perfect for creating highly selective membranes for water treatment or serving as platforms for heterogeneous catalysis, speeding up chemical reactions.
Smart and Biomedical Materials
Their ability to conduct electricity allows them to respond to external stimuli, such as an electric field. This enables "smart" functions like the self-healing of materials through induction heating or targeted drug delivery in medicine.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Despite their immense potential, working with carbon nanomaterials presents practical challenges that must be addressed for successful implementation.
Dispersion and Agglomeration
Due to strong intermolecular forces, nanomaterials have a natural tendency to clump together. This agglomeration can negate their unique properties, and achieving a stable, uniform dispersion is a significant engineering hurdle.
Scalability and Production Costs
Producing high-quality, uniform carbon nanomaterials in large quantities can be a complex and expensive process, which can limit their use in cost-sensitive applications.
Biocompatibility and Environmental Impact
The long-term effects of carbon nanomaterials on human health and the environment are still an area of active research. Understanding potential toxicity is critical for applications in biological and medical sciences.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of which property is most critical for your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is on lightweight structural reinforcement: Prioritize materials with exceptional mechanical strength and a high aspect ratio, like carbon nanotubes.
- If your primary focus is on next-generation electronics or energy storage: High electrical conductivity and surface area, found in materials like graphene and certain nanotubes, will be your most critical properties.
- If your primary focus is on advanced filtration or catalysis: The morphology and high surface-area-to-volume ratio are the key factors to consider for maximizing reactive sites.
Understanding and harnessing these remarkable properties is the key to unlocking the next wave of technological innovation.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristics | Key Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | High strength-to-weight ratio, stiffness | Carbon Nanotubes, Graphene |
| Electrical Conductivity | Low resistance electron flow | Graphene, Carbon Nanotubes |
| Thermal Conductivity | Efficient heat dissipation | Graphene, Carbon Nanotubes |
| Surface Area | High surface-area-to-volume ratio | Fullerenes, Graphene Oxide |
Ready to integrate carbon nanomaterials into your research or product development?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored for advanced material science. Whether you are developing next-generation electronics, energy storage devices, or high-performance composites, our expertise and products can help you achieve precise and reliable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs and accelerate your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum working temperature of graphite? Unlock High-Temp Performance with the Right Atmosphere
- How does graphite react to heat? Unlocking Its Unique High-Temperature Strengths
- Is graphite good in high temperature? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab
- Why can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking Its Extreme Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















