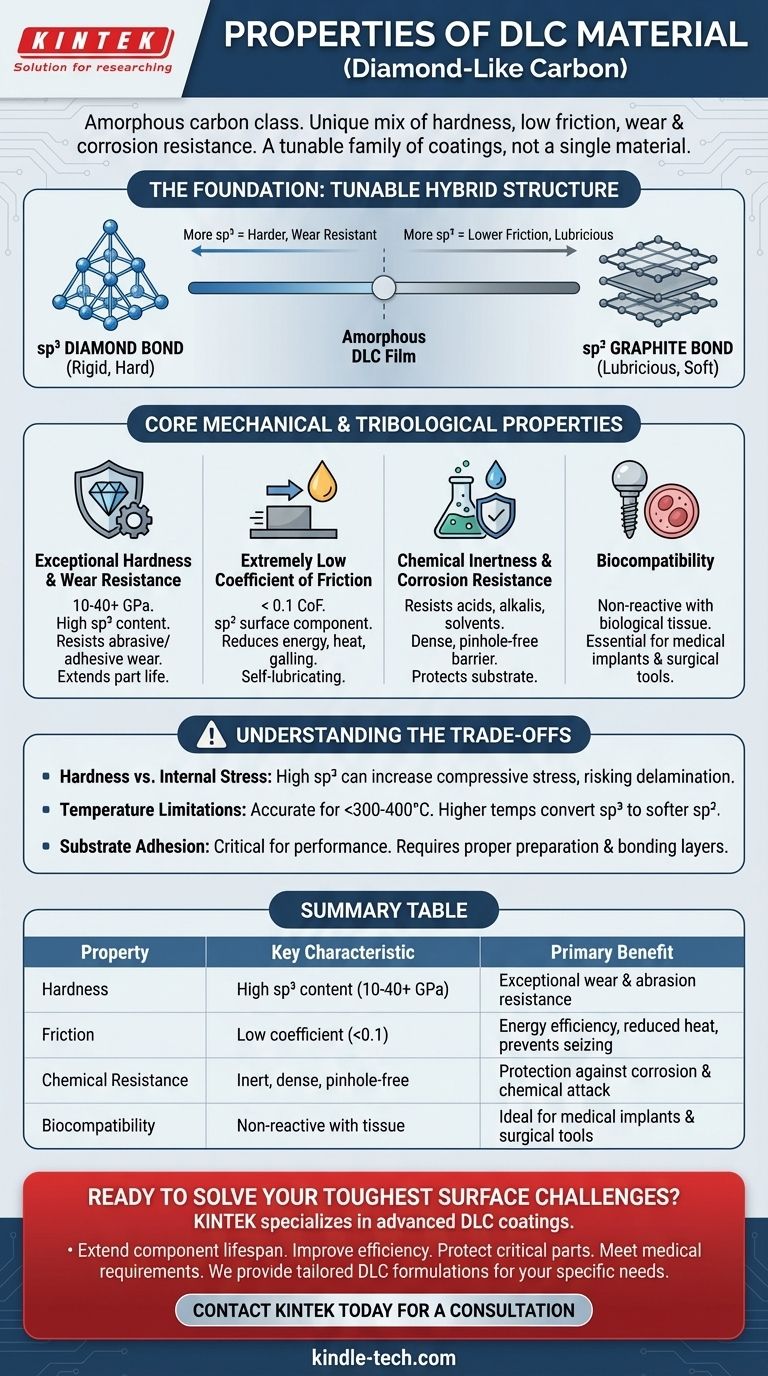
At its core, Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) is a class of amorphous carbon material prized for its unique combination of properties. Its defining characteristics are exceptional hardness, an extremely low coefficient offriction, and high resistance to wear and corrosion, making it a premier choice for enhancing the surface performance of critical components.
The key to understanding DLC is realizing it is not a single material, but a family of coatings. Its properties are precisely tuned by controlling the ratio of diamond-like (hard) and graphite-like (lubricious) atomic bonds within its structure.
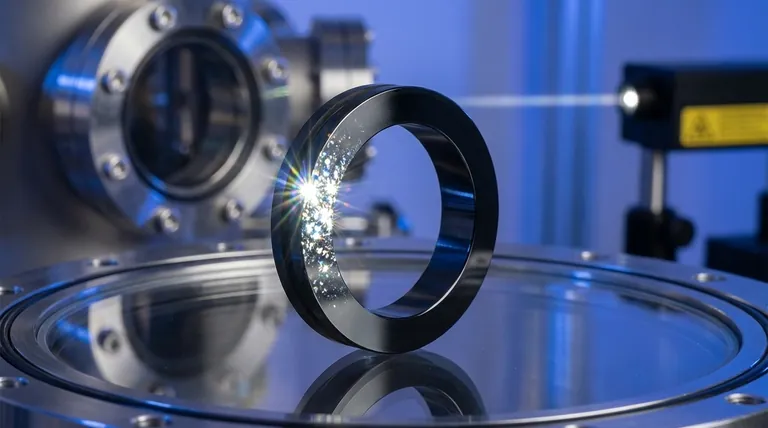

The Foundation: Understanding Carbon's Dual Nature
The remarkable properties of DLC stem from its ability to blend two different structural forms of carbon at the atomic level. This unique hybrid structure is the source of its performance.
The Diamond Bond (sp³): The Source of Hardness
The sp³ bond is the same three-dimensional tetrahedral bond found in natural diamond. This rigid, tightly interlocked structure is what gives DLC its exceptional hardness, rigidity, and high wear resistance.
The Graphite Bond (sp²): The Key to Low Friction
The sp² bond is the planar bond found in graphite. These atoms form strong sheets that are weakly bonded to each other. This allows the layers to slide past one another with very little force, imparting DLC with its characteristic low-friction, self-lubricating surface.
A Tunable Hybrid Structure
DLC is not pure diamond or pure graphite; it is an amorphous film containing a mixture of both sp³ and sp² bonds. By adjusting the deposition process, manufacturers can control the ratio of these bonds, tailoring the coating for specific applications. More sp³ content yields a harder, more wear-resistant film, while more sp² content can enhance its lubricity.
Core Mechanical and Tribological Properties
The hybrid atomic structure of DLC translates directly into a set of highly desirable engineering properties that solve common failure modes like friction, wear, and corrosion.
Exceptional Hardness and Wear Resistance
Due to the high concentration of sp³ bonds, DLC coatings are exceptionally hard, often ranging from 10 to over 40 GPa. This makes them highly resistant to abrasive and adhesive wear, significantly extending the life of parts subjected to contact and motion.
Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction
The presence of a graphitic (sp²) component on the coating's surface creates an ultra-low coefficient of friction, often below 0.1 in dry conditions. This reduces the energy required to move parts, minimizes heat generation, and prevents galling or seizing between sliding components.
Chemical Inertness and Corrosion Resistance
DLC is chemically inert and does not react with most acids, alkalis, or solvents. This property, combined with its dense, pinhole-free structure, creates an effective barrier that protects the underlying substrate material from corrosion and chemical attack.
Biocompatibility
Many forms of DLC are biocompatible, meaning they do not provoke an adverse reaction when in contact with biological tissue. This has made them an essential material for medical implants, surgical tools, and other biomedical applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, DLC coatings are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is critical for successful implementation.
The Hardness vs. Internal Stress Dilemma
Generally, increasing the sp³ content to maximize hardness also increases the coating's internal compressive stress. If this stress becomes too high, it can lead to poor adhesion or delamination from the substrate, especially with thicker coatings.
Temperature Limitations
DLC coatings are primarily for low-to-moderate temperature applications. At elevated temperatures (typically above 300-400°C), the hard sp³ bonds can begin to convert into softer sp² graphitic bonds, causing the coating to lose its hardness and protective qualities.
Substrate Adhesion and Preparation
The performance of a DLC coating is critically dependent on its adhesion to the base material. Proper surface preparation, cleaning, and the potential use of intermediate bonding layers are absolutely essential for a durable and effective coating. A poorly bonded coating will fail regardless of its inherent properties.
Matching the DLC Type to Your Application
Choosing the right DLC formulation requires aligning its properties with your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear and abrasion resistance: Opt for a DLC with a high percentage of sp³ bonds (e.g., tetrahedral amorphous carbon, or ta-C), but be mindful of internal stress and coating thickness.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible friction: Choose a hydrogenated DLC (a-C:H) or a graphite-rich formulation that prioritizes lubricity, even if it means sacrificing some ultimate hardness.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance or biocompatibility: The dense structure of most DLC types is effective, but ensure the specific formulation is certified for your environment, especially for medical use.
By understanding its fundamental structure, you can leverage DLC not just as a coating, but as a true design tool to solve critical surface engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | High sp³ bond content (10-40+ GPa) | Exceptional wear and abrasion resistance |
| Friction | Low coefficient (<0.1) due to sp² bonds | Energy efficiency, reduced heat, prevents seizing |
| Chemical Resistance | Inert, dense, pinhole-free structure | Protection against corrosion and chemical attack |
| Biocompatibility | Non-reactive with biological tissue | Ideal for medical implants and surgical tools |
Ready to solve your toughest surface engineering challenges?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced coating solutions. Our expertise in DLC coatings can help you:
- Extend component lifespan with superior wear resistance.
- Improve efficiency by minimizing friction and energy loss.
- Protect critical parts from harsh chemicals and corrosion.
- Meet stringent requirements for medical and biocompatible applications.
We provide tailored DLC formulations to match your specific needs, whether it's maximum hardness, the lowest friction, or superior corrosion resistance. Let our experts help you select and apply the perfect coating for your laboratory equipment and components.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and see how our DLC solutions can enhance your project's performance and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer
- How long does diamond coating last? Maximize Lifespan with the Right Coating for Your Application









