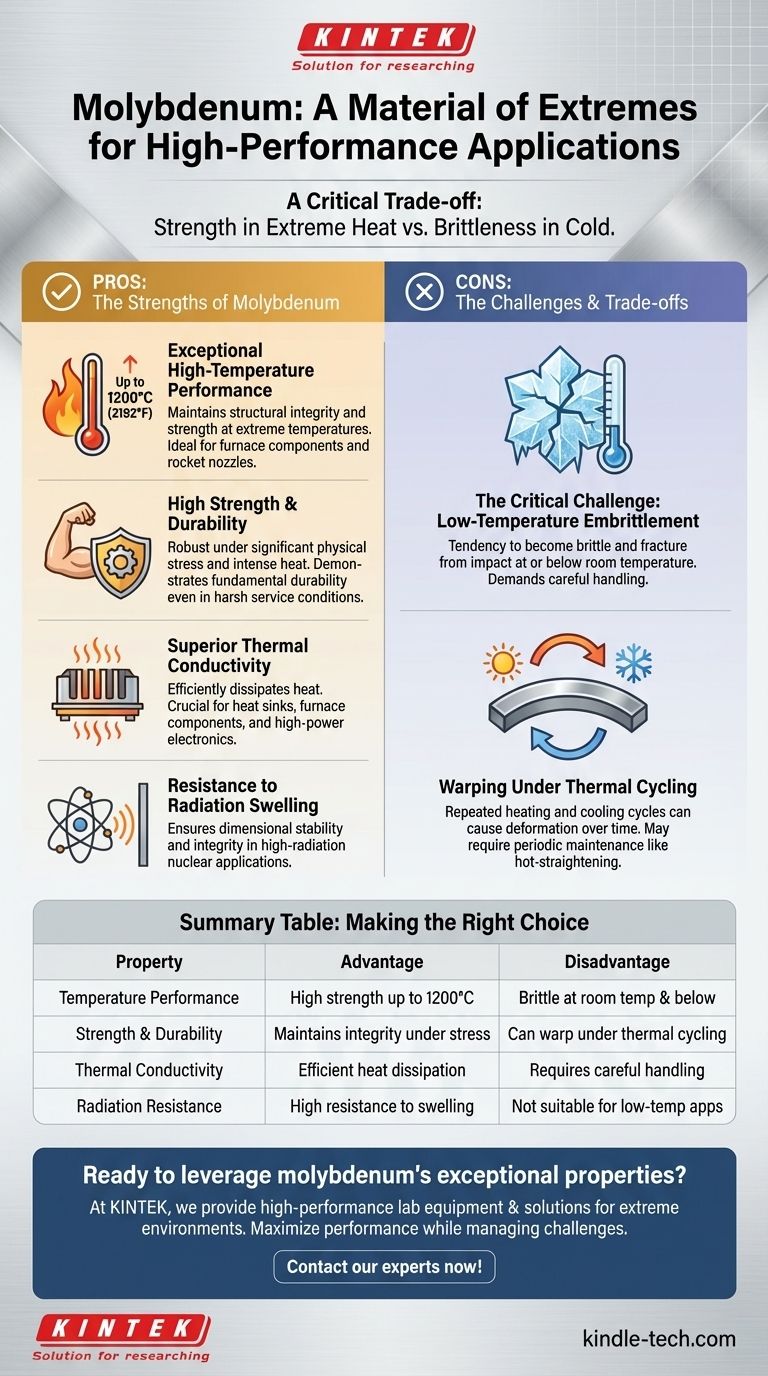
At its core, molybdenum is a material of extremes, prized for its exceptional strength and stability at very high temperatures. Its primary advantages include high thermal conductivity and resistance to radiation, making it invaluable for demanding industrial applications. However, this high-temperature performance comes with a significant trade-off: a tendency to become brittle at low temperatures.
Molybdenum's value is defined by a critical trade-off. It offers outstanding performance in extreme heat, but its inherent brittleness at or below room temperature requires careful engineering and handling to prevent failure.

The Strengths of Molybdenum
Molybdenum and its alloys offer a unique combination of properties that make them suitable for environments where other metals would fail. Understanding these strengths is key to knowing where it can be applied most effectively.
Exceptional High-Temperature Performance
Molybdenum maintains its structural integrity and strength at extreme temperatures. It can be used in applications up to 1200ºC (2192°F) without the risk of recrystallization, a process that can weaken other metals.
This makes it a material of choice for components like furnace hearths, rocket nozzles, and other high-temperature structural parts.
High Strength and Durability
Molybdenum alloys possess a high level of inherent strength. This robustness is critical for components that must withstand significant physical stress while also being exposed to intense heat.
Even after recrystallization, thicker sections of molybdenum are not easily damaged, demonstrating their fundamental durability in harsh service conditions.
Superior Thermal Conductivity
The material exhibits good thermal conductivity, allowing it to efficiently dissipate heat. This is a crucial advantage in applications like heat sinks, furnace components, and high-power electronics where managing thermal loads is critical for performance and longevity.
Resistance to Radiation Swelling
A key advantage in nuclear applications is molybdenum's high resistance to radiation-induced swelling. This property ensures dimensional stability and integrity for components used within nuclear reactors and other high-radiation environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Weaknesses
No material is without its limitations. For molybdenum, the primary disadvantages are directly related to its physical behavior at different temperature ranges and under specific conditions.
The Critical Challenge: Low-Temperature Embrittlement
The principal disadvantage of molybdenum is its tendency toward low-temperature embrittlement. At or below room temperature, the material can become very brittle and susceptible to fracture from impact or stress.
This property demands careful consideration during design, fabrication, and handling to avoid catastrophic failure in non-operating conditions.
Warping Under Thermal Cycling
While robust, molybdenum components can be affected by long-term, repeated heating and cooling cycles.
Components like molybdenum hearth rails may warp over time due to this thermal cycling. This deformation may require periodic maintenance, such as hot-straightening, to restore their original shape and function.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision to use molybdenum should be based on a clear understanding of its strengths relative to its operational challenges.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability: Molybdenum is an excellent choice for furnace components, aerospace parts, and other structures that must perform reliably in extreme heat.
- If your application involves ambient or low temperatures: You must design and handle the material to mitigate its inherent brittleness, as it can fracture easily under these conditions.
- If your component will undergo frequent thermal cycles: Plan for potential warping over its service life and incorporate maintenance procedures like hot-straightening into your operational plan.
Successfully leveraging molybdenum's power depends on engineering around its fundamental trade-offs.
Summary Table:
| Property | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Performance | High strength & stability up to 1200°C | Brittle at or below room temperature |
| Strength & Durability | Maintains integrity under physical stress | Can warp under repeated thermal cycling |
| Thermal Conductivity | Efficient heat dissipation | Requires careful handling to prevent fracture |
| Radiation Resistance | High resistance to swelling in nuclear environments | Not suitable for low-temperature applications |
Ready to leverage molybdenum's exceptional properties in your lab or production process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including solutions designed for extreme environments. Our expertise ensures you get the right materials and equipment to maximize performance while managing technical challenges like brittleness and thermal cycling.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your high-temperature applications and drive your success.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
People Also Ask
- What material is used for furnace heating? Select the Right Element for Your Process
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- What are the heating elements for high temperature furnaces? Select the Right Element for Your Atmosphere
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C