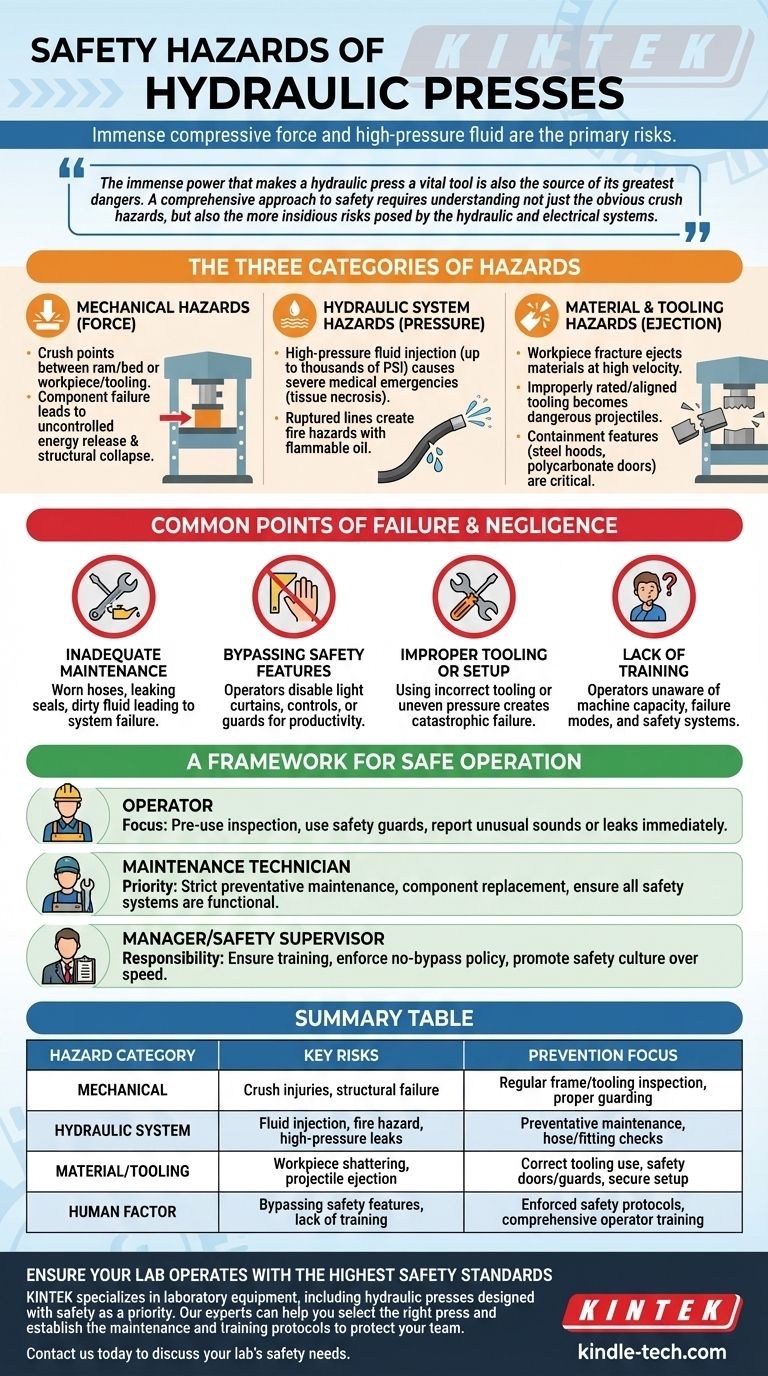
The primary safety hazards of a hydraulic press stem from its immense compressive force and the high-pressure fluid system that generates it. The main risks involve catastrophic mechanical failure, high-pressure fluid injection, and the violent ejection of materials or tooling components.
The immense power that makes a hydraulic press a vital tool is also the source of its greatest dangers. A comprehensive approach to safety requires understanding not just the obvious crush hazards, but also the more insidious risks posed by the hydraulic and electrical systems.
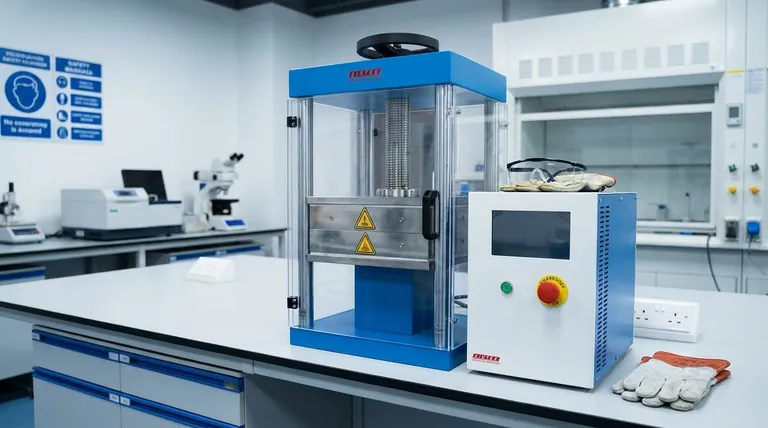

The Three Categories of Hydraulic Press Hazards
A hydraulic press concentrates extreme force in a small area. Understanding the specific ways this energy can be dangerously released is the first step toward safe operation.
Mechanical Hazards: The Danger of Force
The most intuitive danger is the mechanical force of the press itself. This includes crush points between the ram and the bed, or between the workpiece and the tooling.
Any component under pressure is storing potential energy. A failure in the frame, ram, or tooling can result in the sudden, uncontrolled release of this energy, leading to flying metal shards or total structural collapse.
Hydraulic System Hazards: The Danger of Pressure
Hydraulic systems operate at thousands of pounds per square inch (PSI). A pinhole leak in a hose or fitting can release a fine jet of fluid powerful enough to penetrate skin and clothing.
This event, known as fluid injection, is a severe medical emergency. The injected fluid can cause tissue necrosis and requires specialized surgical intervention.
Furthermore, a ruptured hydraulic line can spray hot, flammable oil, creating a significant fire hazard, especially in the presence of an ignition source.
Material and Tooling Hazards: The Danger of Ejection
When a workpiece is subjected to immense pressure, it can fracture, shatter, and be ejected from the press at high velocity. This is especially true for brittle materials or improperly supported work.
Similarly, if the tooling (dies, punches, etc.) is not correctly rated, aligned, or secured, it can fail and become a dangerous projectile. Safety features like the steel hoods and polycarbonate doors mentioned in laboratory presses are designed specifically to contain these ejections.
Common Points of Failure and Negligence
Accidents are rarely caused by a single equipment failure but often involve a combination of factors, including human error. Understanding these common pitfalls is critical for prevention.
Inadequate Maintenance
Hydraulic systems require regular inspection. Worn hoses, leaking seals, and dirty fluid can all contribute to system failure, leading to both mechanical and hydraulic hazards.
Bypassing Safety Features
Operators under pressure for productivity may be tempted to bypass or disable safety mechanisms like light curtains, two-hand controls, or physical guards. This is a leading cause of severe injury.
Improper Tooling or Setup
Using tooling that is not designed for the specific press or the force being applied is a direct path to catastrophic failure. Incorrectly setting up the workpiece can also create uneven pressure, leading to material shattering and ejection.
Lack of Training
An operator who does not fully understand the machine's capacity, its failure modes, and its safety systems is a danger to themselves and others. Comprehensive, machine-specific training is non-negotiable.
A Framework for Safe Operation
Mitigating these hazards requires a systematic approach based on your role and responsibilities.
- If you are an operator: Your focus must be on pre-use inspection, always using the designated safety guards, and immediately reporting any unusual sounds or leaks.
- If you are a maintenance technician: Your priority is adhering to a strict preventative maintenance schedule, replacing components before they fail, and ensuring all safety systems are fully functional.
- If you are a manager or safety supervisor: Your responsibility is to ensure operators are thoroughly trained, safety features are never bypassed, and a strong culture of safety over production speed is enforced.
True safety is achieved when the equipment is properly maintained, and its operators are empowered with the knowledge to respect its inherent dangers.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Category | Key Risks | Prevention Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Crush injuries, structural failure | Regular frame/tooling inspection, proper guarding |
| Hydraulic System | Fluid injection, fire hazard, high-pressure leaks | Preventative maintenance, hose/fitting checks |
| Material/Tooling | Workpiece shattering, projectile ejection | Correct tooling use, safety doors/guards, secure setup |
| Human Factor | Bypassing safety features, lack of training | Enforced safety protocols, comprehensive operator training |
Ensure your lab operates with the highest safety standards. KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment, including hydraulic presses designed with safety as a priority. Our experts can help you select the right press and establish the maintenance and training protocols to protect your team. Contact us today to discuss your lab's safety needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy



















