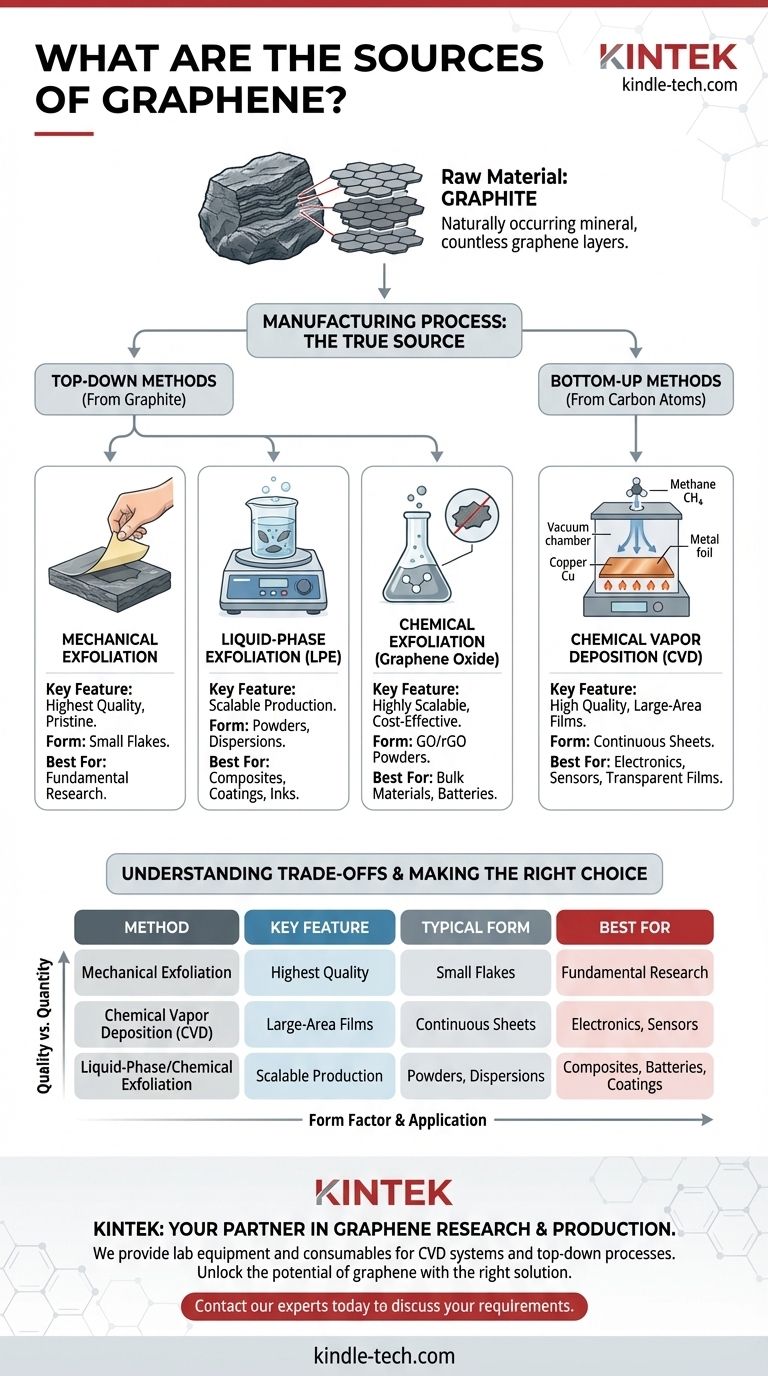
At its most fundamental level, the source of graphene is graphite. This abundant, naturally occurring mineral is composed of countless layers of graphene stacked together. However, obtaining the high-quality, single-atom-thick sheets that give graphene its remarkable properties requires sophisticated manufacturing processes, not simple mining. The "source" of usable graphene is therefore best understood as the production method used to isolate or synthesize it.
While graphite is the raw material, the true source of application-ready graphene is the manufacturing process. The choice between "top-down" methods (exfoliating from graphite) and "bottom-up" methods (synthesizing from carbon atoms) determines the material's quality, scale, and ultimate use case.

The Natural Origin: Graphite
What is Graphite?
Graphite is a common mineral and a natural crystalline form of carbon. Its structure consists of planes of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. Each one of these individual planes is a sheet of graphene.
The Challenge of Isolation
In graphite, these graphene sheets are held together by relatively weak van der Waals forces. The core challenge in producing graphene from this source is to overcome these forces to peel away a single, pristine layer without introducing defects or impurities.
"Top-Down" Methods: Starting from Graphite
Top-down approaches begin with bulk graphite and break it down to isolate graphene sheets. These methods are often used to produce graphene flakes, powders, and dispersions.
Mechanical Exfoliation
This is the original, Nobel Prize-winning method, often called the "Scotch tape" technique. It involves using adhesive tape to peel layers from a piece of graphite until a single-layer flake is isolated.
While it produces extremely high-quality, pristine graphene flakes, this method is not scalable for industrial production and is primarily used in fundamental research.
Liquid-Phase Exfoliation (LPE)
In LPE, graphite powder is suspended in a specialized solvent and subjected to high-energy processes, such as sonication. This energy agitates the material, breaking the graphite apart into flakes, which can include single or few-layer graphene.
This method is scalable and excellent for producing graphene dispersions used in inks, composites, and coatings.
Chemical Exfoliation (Graphene Oxide)
This is a highly scalable chemical process. Graphite is treated with strong oxidizing agents, forcing the layers apart and creating graphite oxide. This material is then exfoliated in water to form graphene oxide (GO), which can be chemically or thermally reduced to create reduced graphene oxide (rGO).
While cost-effective for bulk production, this process can introduce structural defects, impacting the final material's electrical conductivity.
"Bottom-Up" Methods: Building from Carbon Atoms
Bottom-up approaches construct graphene atom-by-atom from carbon-containing precursors. This is the primary way to create large, continuous sheets of high-quality graphene for electronics.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is the leading method for producing high-quality, large-area graphene films. The process involves heating a catalytic metal substrate (typically copper foil) in a vacuum chamber and introducing a carbon-containing gas, such as methane.
The high temperature breaks down the gas, and carbon atoms deposit onto the surface of the foil, self-assembling into a continuous, single-layer graphene sheet.
The Pursuit of Uniformity
A key challenge in CVD is ensuring the product is a perfect monolayer. Small patches of bilayer or trilayer graphene can form, disrupting the material's uniform electronic properties.
Advanced purification techniques are required to solve this. For example, some processes use a carbon-absorbing tungsten (W) foil to selectively remove these thicker patches, leaving behind a pure monolayer graphene film on the copper substrate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Quality vs. Quantity
Mechanical exfoliation produces the highest-quality graphene but in minuscule quantities. Conversely, chemical methods like GO reduction can produce tons of material, but with more defects. CVD strikes a balance, offering high quality over large areas, but at a higher cost.
Form Factor and Application
The source dictates the form. Top-down methods typically produce flakes and powders (nanoplatelets), ideal for mixing into other materials. Bottom-up CVD produces continuous films, which are essential for applications in electronics, sensors, and transparent conductive films.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right type of graphene requires understanding how its source and production method align with your needs.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics or sensors: Your source will be large-area films produced via Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
- If your primary focus is bulk materials like composites, coatings, or batteries: Your source will be graphene nanoplatelets or rGO powders derived from top-down methods like liquid-phase or chemical exfoliation.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research on pristine material properties: Your source will be small, perfect flakes created through mechanical exfoliation.
Ultimately, the source of your graphene is defined by the manufacturing process that best aligns with your application's requirements for quality, scale, and cost.
Summary Table:
| Production Method | Key Feature | Typical Form | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Exfoliation | Highest Quality | Small Flakes | Fundamental Research |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Large-Area Films | Continuous Sheets | Electronics, Sensors |
| Liquid-Phase/Chemical Exfoliation | Scalable Production | Powders, Dispersions | Composites, Batteries, Coatings |
Unlock the Potential of Graphene for Your Lab
Choosing the right graphene source is critical for your research or product development. Whether you need pristine flakes for fundamental studies, large-area films for advanced electronics, or cost-effective powders for composite materials, the quality of your graphene directly impacts your results.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. We provide the tools and expertise to support your graphene research and production, from CVD systems for high-quality film synthesis to materials for top-down exfoliation processes.
Let us help you achieve your goals with the right graphene solution. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our products can enhance your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition



















