At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a multi-stage vacuum deposition process. It involves three primary physical phases: vaporizing a solid source material, transporting that vapor through a vacuum environment, and condensing it onto a target component to form a high-performance thin film. The entire process is meticulously controlled to achieve specific material properties.
The critical takeaway is that successful PVD coating is not just about the deposition itself. It is a comprehensive process where the pre-treatment and cleaning of the substrate are just as crucial as the vacuum environment and the physical deposition method used.
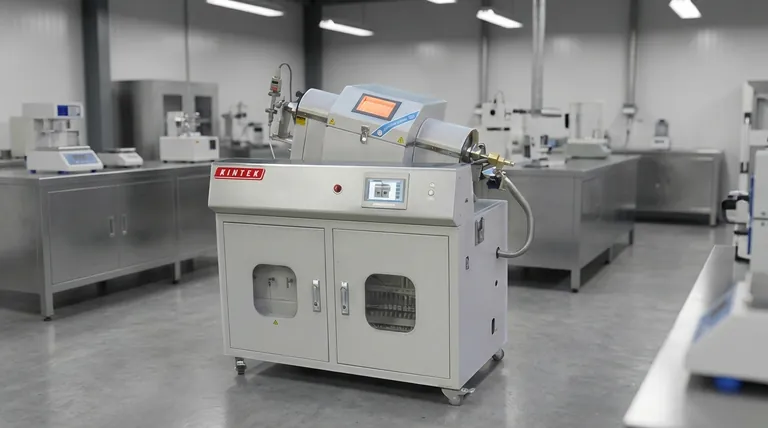

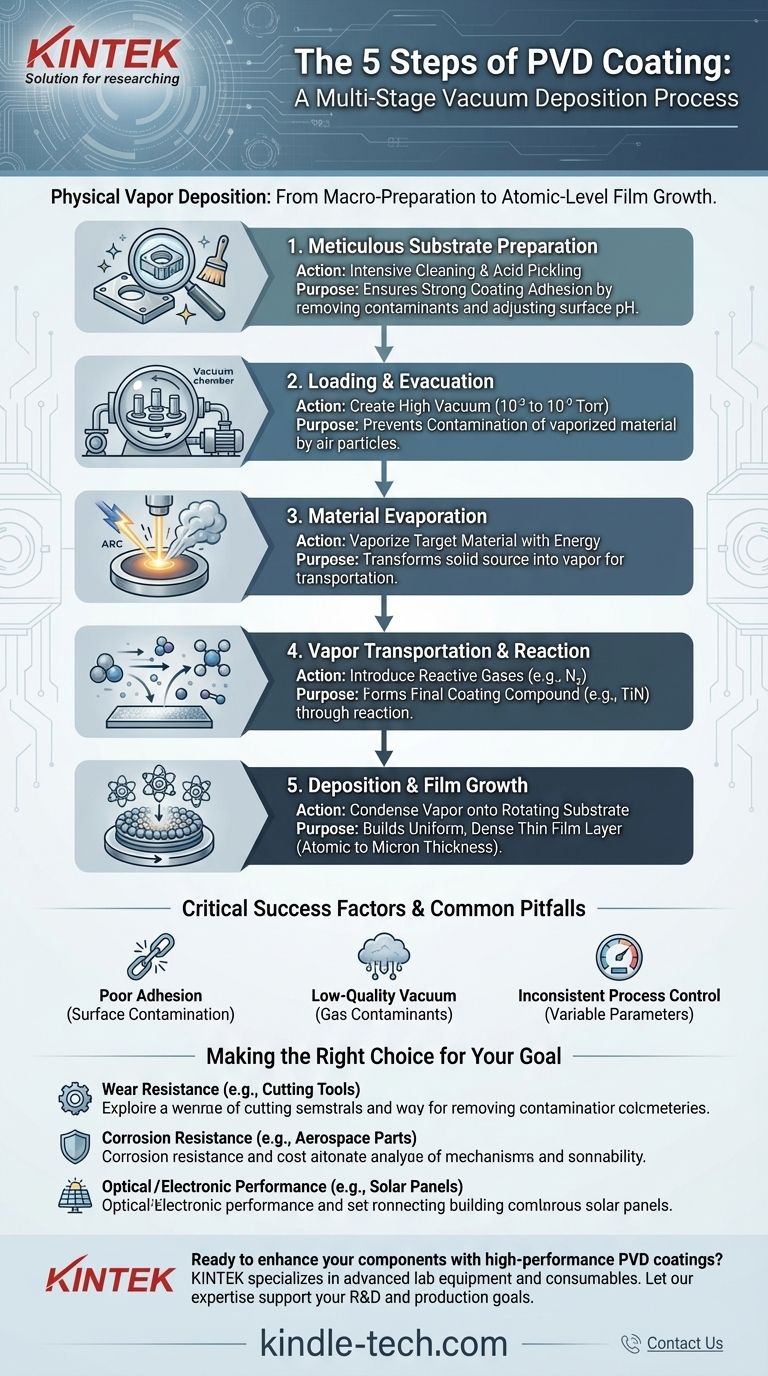
The PVD Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To understand how a durable, high-quality PVD coating is formed, it's essential to view it as a sequence of controlled stages, each with a distinct purpose. The process moves from macro-level preparation to atomic-level film growth.
Step 1: Meticulous Substrate Preparation
Before any coating can occur, the component's surface must be perfectly prepared. This is arguably the most critical stage for ensuring the final coating will adhere properly.
This step involves intensive cleaning to remove any surface contaminants like oils, waxes, grease, or etching inks.
Following cleaning, a process like acid pickling may be used. This adjusts the surface pH and creates an ideal environment for the coating to bond with the substrate.
Step 2: Loading and Evacuation
Once cleaned, the components (now called substrates) are carefully loaded into the PVD vacuum chamber. They are typically placed on rotating fixtures to ensure even coating.
The chamber is then sealed, and a series of pumps evacuates the air, creating an extremely low-pressure vacuum (typically 10⁻³ to 10⁻⁹ Torr). This vacuum is essential to prevent the vaporized coating material from reacting with particles in the air.
Step 3: Material Evaporation
This is the stage where the PVD process truly begins. A high-purity source material, known as the target, is bombarded with energy inside the chamber.
This energy, often in the form of an electric arc or ion beam, dislodges atoms from the target, transforming the solid material into a vapor.
Step 4: Vapor Transportation and Reaction
The vaporized atoms travel in a straight line through the vacuum chamber toward the substrate.
During this transport, reactive gases like nitrogen or oxygen can be introduced into the chamber. This allows the metal vapor to react and form new compounds, such as metal nitrides or oxides, which will become the final coating material.
Step 5: Deposition and Film Growth
When the vaporized atoms reach the substrate, they condense on the surface. This is the deposition stage.
The coating builds up layer by layer, starting with nucleation sites and growing into a dense, thin film. The thickness can range from a few atoms to several microns.
To ensure a uniform coating across complex geometries, the substrate is often rotated at a constant speed throughout this final step.
Common Pitfalls and Critical Success Factors
The quality of a PVD coating is highly sensitive to process variables. A failure in any one area can compromise the entire result.
The Impact of Surface Contamination
The most common cause of coating failure is poor adhesion. If the initial cleaning and preparation stage is insufficient, the coating will not form a strong bond and can peel or flake off.
The Necessity of a High-Quality Vacuum
If the vacuum is not sufficiently low, residual gases (like oxygen or water vapor) will remain in the chamber. These contaminants can get incorporated into the growing film, creating defects and compromising its density, hardness, and corrosion resistance.
The Role of Process Control
The rate of deposition, chamber temperature, and pressure of reactive gases must be precisely monitored and controlled. Inconsistent parameters lead to a film with poor structural integrity and unpredictable performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The PVD process is tailored to achieve specific outcomes. Understanding your primary goal helps focus on the most critical aspects of the process.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance (e.g., cutting tools): The key is forming a hard, dense coating like Titanium Nitride (TiN) through the precise introduction of nitrogen gas.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance (e.g., aerospace parts): The goal is a non-porous, fully-formed film, which demands exceptional surface cleanliness and a high-quality vacuum to prevent defects.
- If your primary focus is optical or electronic performance (e.g., solar panels): Success depends on extreme material purity and precise control over the film's thickness, often monitored in real-time.
Ultimately, PVD is a process of atomic-scale engineering, capable of creating exceptionally high-performance surfaces when every step is executed with precision.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Substrate Preparation | Intensive cleaning & acid pickling | Ensures strong coating adhesion |
| 2. Loading & Evacuation | Create high vacuum in chamber | Prevents contamination during deposition |
| 3. Material Evaporation | Vaporize target material with energy | Creates vapor for transportation |
| 4. Vapor Transport & Reaction | Introduce reactive gases (e.g., N₂) | Forms final coating compound (e.g., TiN) |
| 5. Deposition & Film Growth | Condense vapor onto rotating substrate | Builds uniform, dense thin film layer |
Ready to enhance your components with high-performance PVD coatings? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise PVD processes, helping laboratories achieve superior wear resistance, corrosion protection, and optical performance. Let our expertise support your R&D and production goals—contact us today to discuss your specific coating needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
People Also Ask
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- Is sputtering a PVD? Discover the Key Coating Technology for Your Lab
- How does a sputtering machine work? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings
- What is deposition in environmental chemistry? Understanding How Air Pollution Harms Ecosystems
- What is a sputtering system? Achieve Unmatched Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab



















