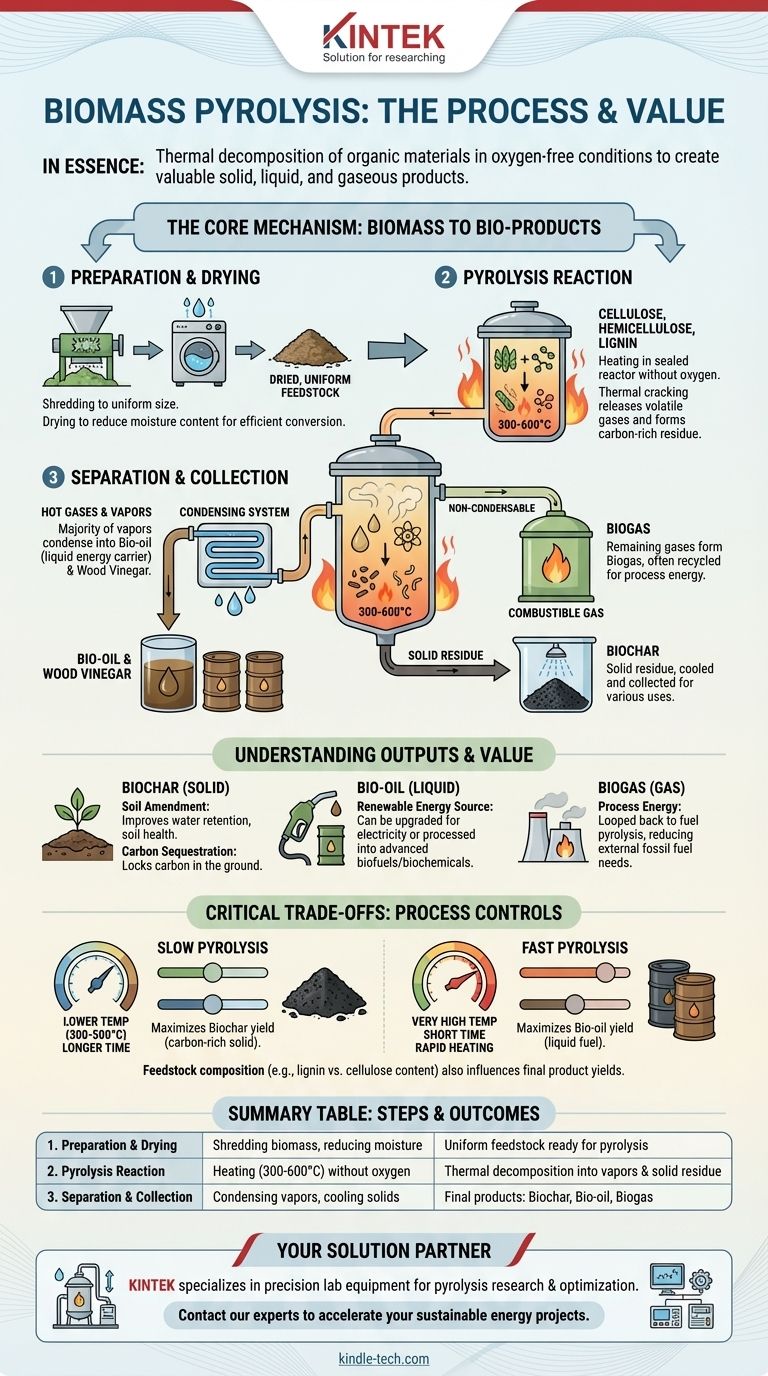
In essence, biomass pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process that occurs in the absence of oxygen, breaking down organic materials into solid, liquid, and gaseous products. The primary steps involve preparing and drying the biomass, subjecting it to high heat in a reactor to trigger the chemical breakdown, and finally, separating and collecting the resulting biochar, bio-oil, and biogas.
The core function of pyrolysis is not merely to burn biomass, but to strategically deconstruct it. By controlling heat in an oxygen-starved environment, you can systematically separate the biomass into a carbon-rich solid (biochar), a liquid energy carrier (bio-oil), and a combustible gas (biogas).
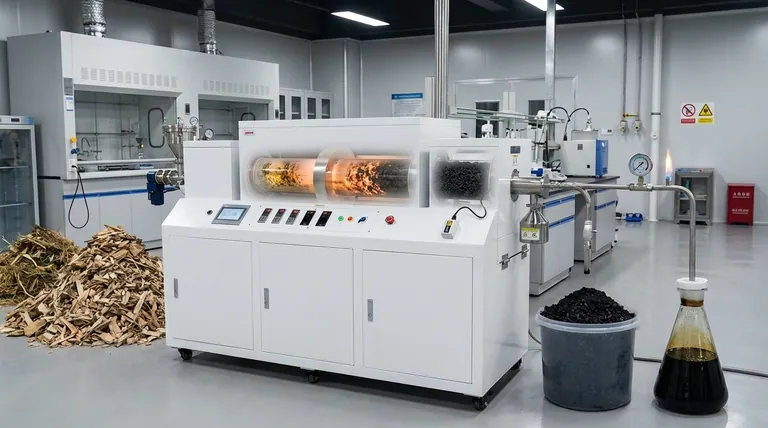

The Core Mechanism: From Biomass to Bio-products
Understanding pyrolysis requires seeing it as a controlled, multi-stage transformation process. It's less about destruction and more about conversion. A pyrolysis plant is designed around this flow, from raw material input to refined product output.
Step 1: Feedstock Preparation and Drying
Before the main reaction can begin, the raw biomass must be prepared. This usually involves shredding or chipping the material to a uniform size to ensure even heating.
Most critically, the biomass is dried to reduce its moisture content. Water consumes a significant amount of energy to vaporize and can interfere with the efficiency of the pyrolysis reaction, so this preparatory step is vital for an effective process.
Step 2: The Pyrolysis Reaction
This is the heart of the process. The prepared biomass enters a sealed reactor, which is heated to high temperatures (typically 300-600°C or higher) in a near-total absence of oxygen.
The intense heat causes the primary components of biomass—cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin—to break down chemically. This thermal cracking releases volatile gases and leaves behind a solid, carbon-rich residue.
Step 3: Product Separation and Collection
The mix of hot gases and solid residue exits the reactor and enters the separation stage.
The solid residue, known as biochar or biocoal, is typically cooled with water and discharged for collection.
The hot vapors are directed into a condensing system. As they cool, the majority of the vapors turn into a liquid known as bio-oil (or tar) and wood vinegar, which are collected in tanks.
The remaining gases that do not condense form what is called biogas or syngas. This gas is often recycled to provide the heat for the pyrolysis reactor, making the entire system more energy-efficient.
Understanding the Outputs and Their Value
Each product from the pyrolysis process has a distinct use, which is why pyrolysis is considered a key technology for a circular economy.
The Solid: Biochar
This stable, carbon-rich material is the solid remnant of the biomass. It is not charcoal for grilling.
Its primary applications are as a powerful soil amendment to improve water retention and soil health, and as a tool for long-term carbon sequestration, effectively locking carbon from the atmosphere into the ground.
The Liquid: Bio-oil
Bio-oil is a dense, dark liquid that can be thought of as a type of crude oil derived from plants. It is a potential renewable energy source.
After upgrading and refining, it can be used to generate electricity or processed into advanced biofuels and biochemicals.
The Gas: Biogas
This mixture of combustible gases is a valuable byproduct. Its most immediate use is to be looped back to fuel the pyrolysis plant's heating chamber.
This creates a partially self-sustaining energy loop, reducing the need for external fossil fuel inputs to run the process.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
The ratio of biochar, bio-oil, and biogas is not fixed. It can be manipulated by adjusting process conditions, which presents a critical trade-off depending on your desired outcome.
The Impact of Heating Rate and Temperature
Slow pyrolysis, which involves lower temperatures and longer reaction times, maximizes the production of biochar. The slower process allows more carbon to remain in the solid structure.
Fast pyrolysis, characterized by very high heating rates and short reaction times, is designed to maximize the yield of bio-oil. The rapid breakdown cracks the biomass into smaller volatile molecules before they can further decompose into char and gas.
The Role of Feedstock Composition
The specific type of biomass used—be it wood chips, agricultural waste, or manure—significantly influences the final products.
Materials rich in lignin, for example, tend to produce a higher yield of biochar, while those rich in cellulose are often better for producing bio-oil.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" way to run a pyrolysis process is entirely dependent on the primary product you wish to create.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration or soil improvement: Your goal is to maximize biochar, which requires a slow pyrolysis process at moderate temperatures.
- If your primary focus is producing renewable liquid fuel: Your goal is to maximize bio-oil, which demands a fast pyrolysis process with rapid heating and cooling.
- If your primary focus is on-site energy production or waste reduction: Your goal is to balance the outputs, using the biogas to power the system and converting the solid waste into a smaller volume of valuable biochar.
Ultimately, pyrolysis offers a flexible platform for converting organic waste into valuable resources, contributing to both a sustainable energy future and a healthier environment.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Primary Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation & Drying | Shredding biomass and reducing moisture | Uniform feedstock ready for efficient pyrolysis |
| 2. Pyrolysis Reaction | Heating biomass (300-600°C) without oxygen | Thermal decomposition into vapors and solid residue |
| 3. Separation & Collection | Condensing vapors and cooling solids | Final products: biochar, bio-oil, and biogas |
Ready to transform your biomass into valuable resources?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment for pyrolysis research and process optimization. Whether you're developing biofuels, studying carbon sequestration with biochar, or analyzing feedstock, our reactors and analytical tools provide the control and reliability you need.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can accelerate your sustainable energy and environmental projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion
- Why are high temperatures required when sintering stainless steels? Unlock Pure, High-Density Results
- What is the difference between pyrolysis combustion and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity
- How is a high-temperature calcination furnace utilized in BZY20 Sol-gel? Achieve Pure Cubic Perovskite Phases



















