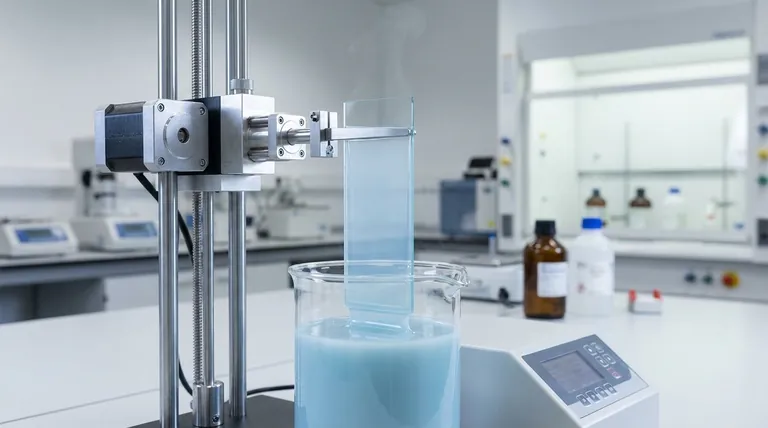
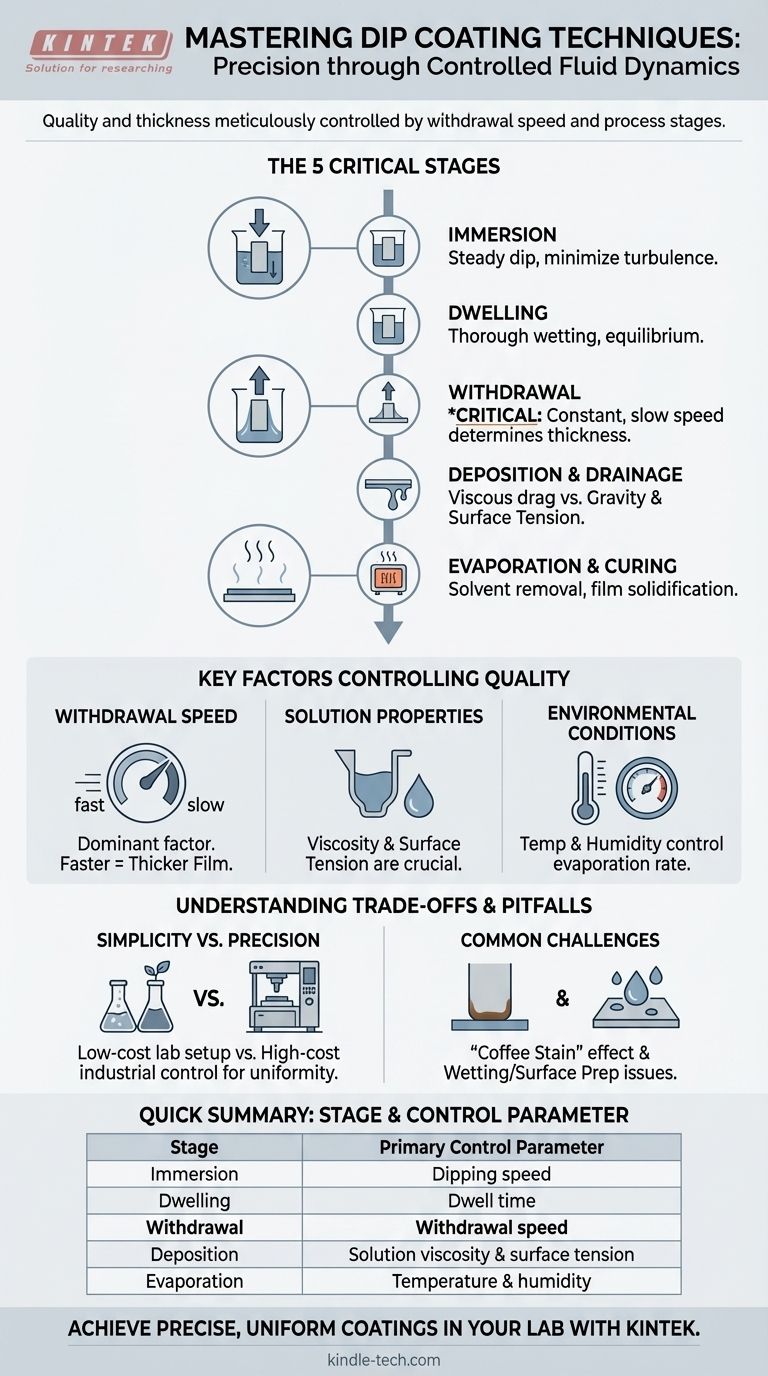
At its core, the dip coating technique consists of five distinct stages: immersion, dwelling, controlled withdrawal, deposition and drainage, and finally, evaporation. While the concept is simple—dipping an object (substrate) into a liquid—the quality and thickness of the final film are meticulously controlled by the parameters of these stages, particularly the speed of withdrawal.
Dip coating is not merely a dip; it is a precisely controlled fluid dynamics process. The final film's characteristics are less about the immersion and more about the controlled, steady withdrawal and subsequent drying conditions.

The Five Critical Stages of the Dip Coating Process
To achieve a uniform, high-quality coating, each stage of the process must be carefully managed. These stages flow sequentially to form the final film.
Stage 1: Immersion
The process begins by fully immersing the substrate into the coating solution. This is typically done at a steady, controlled speed to minimize any turbulence or wave generation in the liquid.
Stage 2: Dwelling (Incubation)
Once immersed, the substrate remains stationary in the solution for a set period. This dwell time ensures the entire surface of the substrate is thoroughly wetted, allowing the solution to reach equilibrium.
Stage 3: Withdrawal
This is the most critical stage. The substrate is pulled out of the solution at a constant, slow speed. A thin layer of the liquid clings to the surface and is drawn up with the substrate.
Stage 4: Deposition and Drainage
As the substrate is withdrawn, a liquid film is deposited. The thickness of this film is determined by a balance of forces: the viscous drag of the liquid pulling it up versus the force of gravity and surface tension pulling it down. Excess liquid drains from the surface.
Stage 5: Evaporation and Curing
The solvent begins to evaporate from the liquid layer, leaving behind the desired coating material. In some processes, like those involving sol-gel solutions, this stage may also involve a chemical reaction or a thermal treatment (curing) to solidify and densify the film.
Key Factors Controlling Film Quality
The simplicity of dip coating is deceptive. Achieving a repeatable, high-quality film requires precise control over several interconnected variables.
Withdrawal Speed
This is the single most dominant factor influencing film thickness. A faster withdrawal speed results in a thicker film because it gives the liquid less time to drain back into the reservoir.
Solution Properties
The viscosity and surface tension of the coating solution are critical. Higher viscosity generally leads to thicker films. The solution's density also plays a role in the gravitational draining force.
Environmental Conditions
The atmosphere into which the substrate is withdrawn has a significant impact. Temperature and humidity control the rate of solvent evaporation, which can affect the final film structure and introduce defects if not properly managed.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While powerful, the dip coating technique has limitations and common challenges that must be anticipated.
Simplicity vs. Precision
The method is famously low-cost and simple to set up, making it excellent for lab-scale research and prototyping. However, achieving industrial-scale precision and uniformity requires highly sophisticated and expensive equipment to control withdrawal speed and the environment.
The "Coffee Stain" Effect
A common issue is the tendency for the coating to be thicker at the very bottom edge of the substrate where the last droplet drains and evaporates. This non-uniformity can be a critical defect in applications like optics.
Material and Solvent Compatibility
The technique is entirely dependent on the solution properly wetting the substrate. If the surface energy of the substrate is too low, the liquid will bead up rather than form a continuous film. Substrate cleaning and preparation are therefore paramount.
Applying This to Your Process
Your specific goal will determine which variables you need to control most rigorously.
- If your primary focus is repeatable film thickness: Concentrate on achieving an absolutely constant withdrawal speed and maintaining a consistent solution viscosity.
- If your primary focus is a defect-free optical surface: Prioritize a vibration-free environment, a cleanroom setting to eliminate dust, and carefully controlled atmospheric conditions to manage evaporation.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or low-cost coating: The inherent simplicity of the method is your greatest asset, allowing for quick tests of different materials and solutions.
Mastering these fundamental stages and variables allows you to leverage the simple elegance of dip coating for a wide range of advanced applications.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Primary Control Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Immersion | Substrate is dipped into the solution | Dipping speed |
| 2. Dwelling | Substrate rests in solution | Dwell time |
| 3. Withdrawal | Substrate is pulled out | Withdrawal speed |
| 4. Deposition | Liquid film drains and deposits | Solution viscosity & surface tension |
| 5. Evaporation | Solvent evaporates, film solidifies | Temperature & humidity |
Ready to achieve precise, uniform coatings in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables you need to perfect your dip coating process. Whether you require precise withdrawal speed controllers, stable coating solutions, or expert advice on optimizing your parameters for materials research, we are here to support your laboratory's success.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you enhance your coating quality and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- What is hot press moulding? Achieve Superior Density and Complex Shapes with Heat and Pressure
- Why is a vacuum hot-pressing furnace preferred for C_fiber/Si3N4 composites? Achieve High Density & Fiber Protection
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot stamping? Unlock Ultra-High Strength for Automotive Parts
- What is vacuum lamination? Achieve a Flawless, Durable Finish on Complex Shapes
- Which features of vacuum hot pressing equipment are utilized by the dual-step vacuum hot press process? Optimize AlMgTi



















