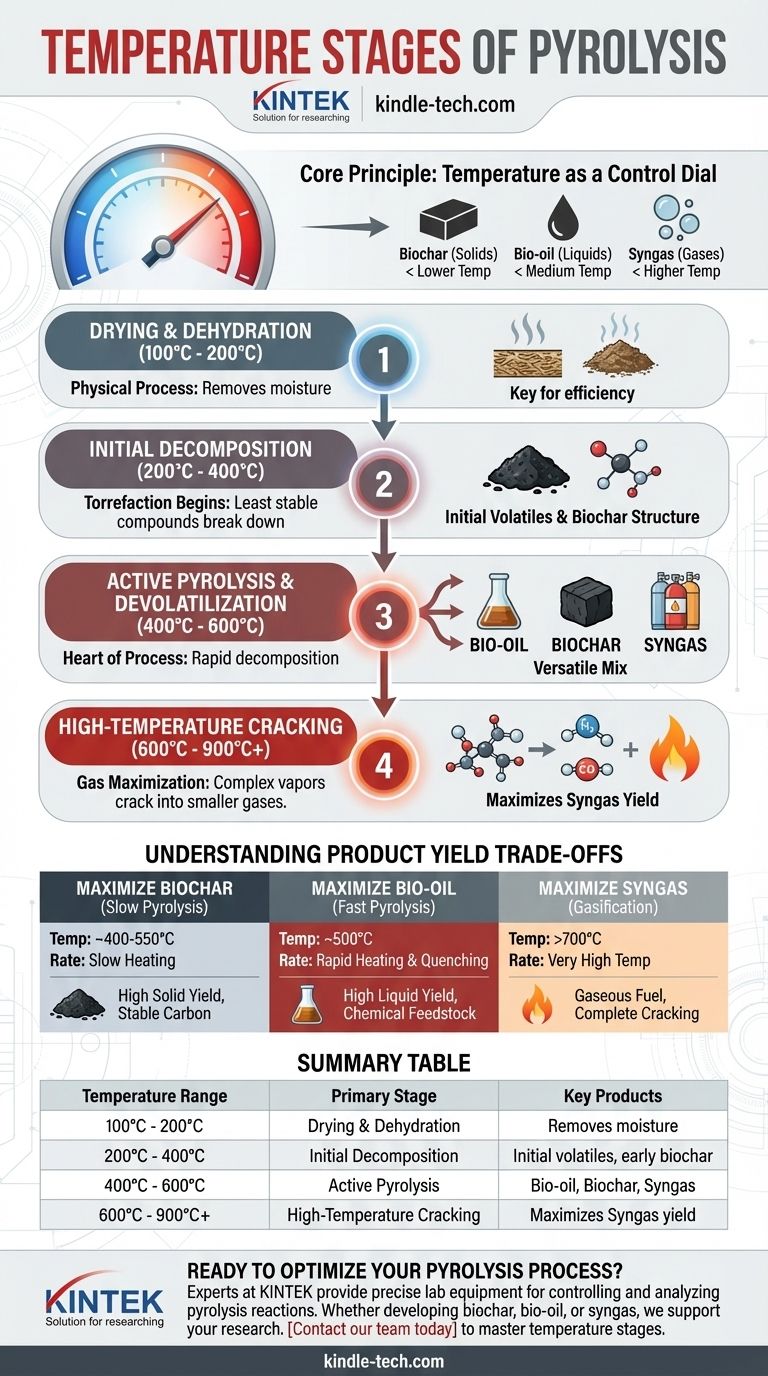
While pyrolysis is a continuous process, its effects can be understood by examining distinct temperature stages. The process begins with drying around 100°C, followed by the main decomposition events occurring between 400°C and 900°C. The specific temperature within this range is the most critical factor, as it dictates whether the final output will be dominated by solid char, liquid bio-oil, or combustible gases.
The core principle to understand is that temperature is not just a setting, but a control dial. Lower temperatures favor the production of solids (biochar), while progressively higher temperatures shift the output first toward liquids (bio-oil) and ultimately toward gases (syngas).
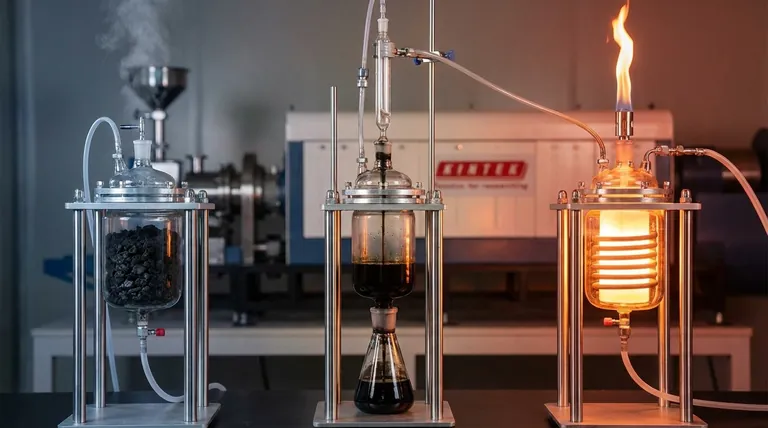

The Role of Temperature in Material Transformation
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials in the absence of oxygen. As temperature increases, different chemical bonds within the feedstock break, leading to a predictable sequence of reactions and products. Understanding these stages is key to controlling the outcome.
Stage 1: Drying and Dehydration (100°C - 200°C)
Before any chemical decomposition begins, the free and loosely bound water within the feedstock must be evaporated. This stage is a physical process, not a chemical one.
Removing moisture is a critical preparatory step. Inefficient drying consumes significant energy and can lead to less effective pyrolysis in the later stages.
Stage 2: Initial Decomposition (200°C - 400°C)
In this range, the least stable organic compounds, primarily hemicellulose, begin to break down. This is sometimes referred to as torrefaction.
This stage produces water vapor, carbon dioxide, and small amounts of acetic acid and other volatiles. The solid material begins to darken and form the initial structure of biochar.
Stage 3: Active Pyrolysis & Devolatilization (400°C - 600°C)
This is the heart of the pyrolysis process. The bulk of the material, primarily cellulose, decomposes rapidly, releasing a dense mix of volatile vapors.
These vapors, if condensed, form bio-oil. The remaining solid material continues to consolidate into carbon-rich biochar. The non-condensable vapors form syngas. This temperature range is a versatile middle ground, producing a mix of all three products.
Stage 4: High-Temperature Cracking (600°C - 900°C+)
At these higher temperatures, the primary reactions shift. The complex vapor molecules released during active pyrolysis become unstable and "crack" into smaller, simpler gas molecules.
This stage maximizes the production of syngas (primarily hydrogen and carbon monoxide). It comes at the expense of liquid bio-oil yield, as the oil's precursor molecules are broken down before they can be condensed and collected.
Understanding the Product Yield Trade-offs
The choice of temperature is a deliberate decision based on the desired end product. You cannot maximize all outputs simultaneously; you must choose which product to prioritize.
Maximizing Solid Biochar: Slow Pyrolysis
To produce the highest yield of stable, high-quality biochar, lower temperatures (around 400-500°C) and slower heating rates are used.
This gives the carbon atoms time to arrange themselves into stable aromatic structures, resulting in more solid char and fewer volatile products.
Maximizing Liquid Bio-oil: Fast Pyrolysis
To maximize bio-oil, the goal is to rapidly decompose the feedstock and immediately remove the resulting vapors before they can crack into gases.
This requires moderate temperatures (around 500°C) but very high heating rates and a short residence time for the vapors, which are then quickly quenched (cooled) to condense them into liquid bio-oil.
Maximizing Gaseous Syngas: Gasification
To get the most syngas, very high temperatures (typically 700°C or higher) are necessary. This ensures the complete thermal cracking of all volatile matter and even some of the carbon char into the simplest gas molecules.
This process is often considered a step beyond pyrolysis, bordering on gasification, as it prioritizes gaseous fuel above all other products.
Selecting the Right Temperature for Your Goal
Your target temperature depends entirely on the product you value most. Each pathway involves a fundamental trade-off against the others.
- If your primary focus is producing biochar for soil or carbon sequestration: Operate at lower temperatures (~400-550°C) with slower heating to maximize solid yield.
- If your primary focus is generating bio-oil as a liquid fuel or chemical feedstock: Use moderate temperatures (~500°C) with extremely rapid heating and vapor quenching to capture liquids.
- If your primary focus is creating syngas for energy or synthesis: Push to high temperatures (>700°C) to ensure all organic matter is cracked into non-condensable gases.
Ultimately, temperature is the most powerful lever you can pull to direct the outcome of the pyrolysis process.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Primary Stage | Key Products |
|---|---|---|
| 100°C - 200°C | Drying & Dehydration | Removes moisture |
| 200°C - 400°C | Initial Decomposition | Initial volatiles, early biochar |
| 400°C - 600°C | Active Pyrolysis | Bio-oil, Biochar, Syngas |
| 600°C - 900°C+ | High-Temperature Cracking | Maximizes Syngas yield |
Ready to Optimize Your Pyrolysis Process?
Choosing the right temperature is critical for achieving your target product yield. The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to control and analyze your pyrolysis reactions.
Whether you are developing biochar for carbon sequestration, producing bio-oil for fuel, or generating syngas for energy, we have the solutions to support your research and development.
Contact our team today to discuss how our specialized equipment can help you master the temperature stages of pyrolysis for superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy



















