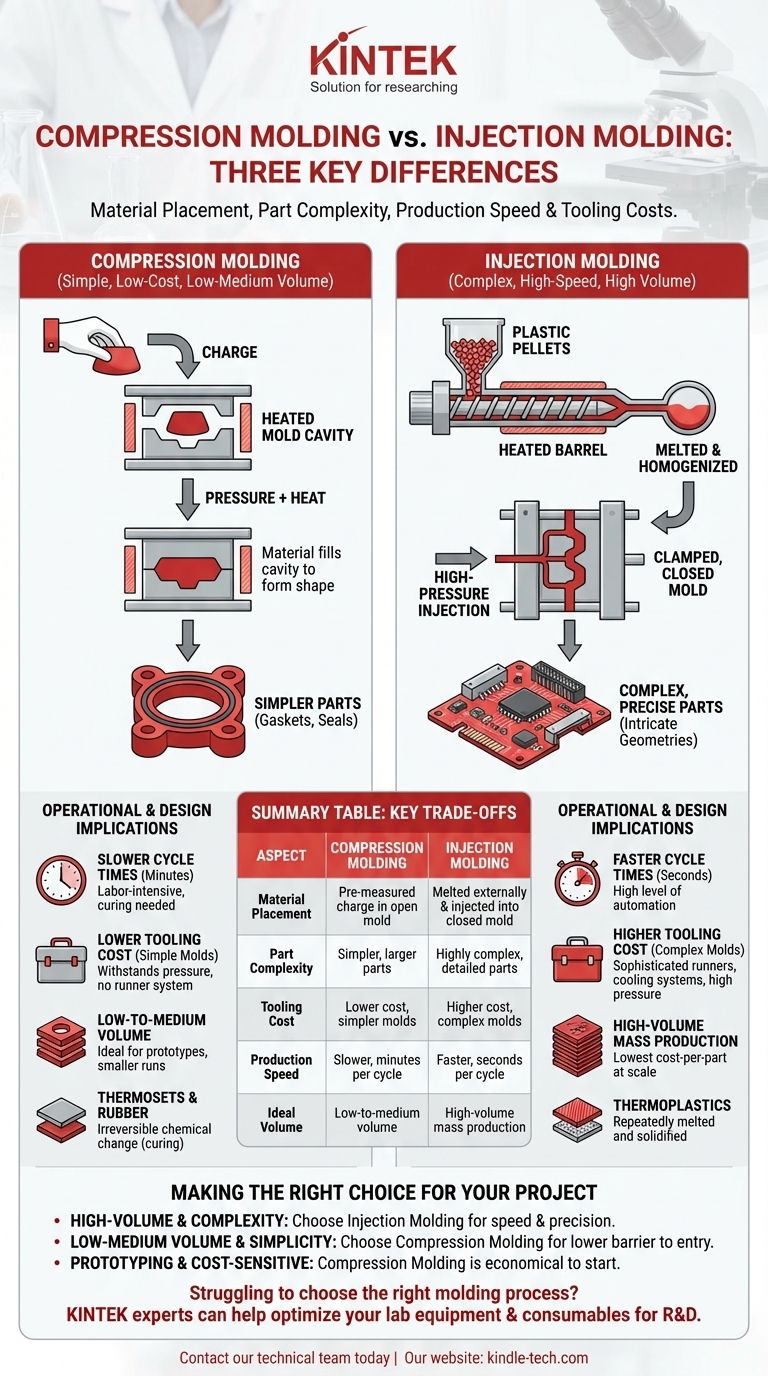
To put it simply, the three primary differences between compression molding and injection molding are the method of material placement, the complexity of the parts they can produce, and the associated production speed and tooling costs. In compression molding, material is placed directly into a heated mold cavity which then closes to form the part, whereas injection molding melts the material externally and then injects it under high pressure into a closed mold.
The core distinction lies in a trade-off: compression molding is a simpler, lower-cost process ideal for large, less complex parts in low-to-medium volumes, while injection molding is a high-speed, automated process suited for producing intricate, high-precision parts in high volumes.

The Fundamental Process Difference
The most significant distinction is how and where the raw material is prepared and formed into the final product. This initial step dictates the capabilities and limitations of each process.
How Compression Molding Works
In compression molding, a pre-measured amount of molding material, called the charge, is placed directly into the bottom half of a heated, open mold cavity.
The top half of the mold is then closed, applying immense pressure. This pressure, combined with the heat, causes the material to spread and fill the entire cavity, forming it into the desired shape.
How Injection Molding Works
Injection molding is a more complex, automated process. Plastic pellets are fed into a hopper, then melted and homogenized by a reciprocating screw inside a heated barrel.
Once fully molten, this plastic is forcefully injected under high pressure into a clamped, closed mold. The material fills the mold's intricate pathways and cavities before being cooled and ejected.
Key Operational and Design Implications
The difference in process mechanics leads to significant variations in tooling, part design capabilities, and production efficiency.
Part Complexity and Precision
Injection molding excels at producing highly complex and detailed parts. The high-pressure injection can force material into tiny, intricate features, enabling complex geometries, thin walls, and high-precision tolerances.
Compression molding is better suited for simpler, often larger, and bulkier parts like gaskets, seals, and electrical components. It struggles to fill the fine details that injection molding handles with ease.
Tooling (Molds) and Initial Investment
Tooling for compression molding is significantly simpler and less expensive. The mold only needs to withstand clamping pressure and does not require the complex system of runners and gates needed to manage material flow.
Injection molds are highly complex and expensive engineering projects. They must withstand immense injection pressures and incorporate sophisticated channels (runners, gates, sprues) and cooling systems, leading to much higher upfront costs.
Production Speed and Cycle Times
Due to its high level of automation, injection molding is extremely fast, with cycle times often measured in seconds. This makes it the clear choice for high-volume mass production.
Compression molding is a slower, more labor-intensive process. The cycles of loading the charge, closing the press, curing, and removing the part can take several minutes, making it suitable for lower-to-medium volume production runs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these methods requires a clear understanding of your project's goals, as the advantages of one are often the disadvantages of the other.
The Cost-per-Part Equation
While injection molding has a very high initial tooling cost, its fast cycle times lead to a very low cost-per-part at high volumes.
Compression molding has a low initial tooling cost, making it ideal for prototypes and smaller runs. However, its slower, more manual process results in a higher cost-per-part as production volume increases.
Material Considerations
Compression molding is exceptionally well-suited for thermosetting plastics and elastomers like rubber. These materials undergo an irreversible chemical change (curing) when heated, which the compression process facilitates perfectly.
While some thermosets can be injection molded, the process is predominantly used for thermoplastics. These materials can be repeatedly melted and solidified without degradation, fitting the injection molding cycle perfectly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Your decision should be guided by your specific requirements for volume, complexity, budget, and material.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of complex parts: Injection molding is the superior choice due to its speed, precision, and low per-unit cost at scale.
- If your primary focus is low-to-medium volume production of large, simple parts: Compression molding offers a much lower barrier to entry with its affordable tooling.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive prototyping or initial production runs: Compression molding's low tooling investment makes it the most economical option to get started.
Understanding these core operational differences empowers you to select the manufacturing process that aligns perfectly with your technical and financial goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Compression Molding | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Material Placement | Pre-measured charge placed in open mold | Material melted externally & injected into closed mold |
| Part Complexity | Simpler, larger parts (gaskets, seals) | Highly complex, detailed parts with thin walls |
| Tooling Cost | Lower cost, simpler molds | Higher cost, complex molds with runners/gates |
| Production Speed | Slower, minutes per cycle | Faster, seconds per cycle |
| Ideal Volume | Low-to-medium volume | High-volume mass production |
| Material Suitability | Excellent for thermosets & rubber | Primarily for thermoplastics |
Struggling to choose the right molding process for your materials? The experts at KINTEK can help! We specialize in providing laboratory equipment and consumables that support both compression and injection molding R&D. Whether you're prototyping with compression molding or scaling up with injection molding, our solutions ensure precision and efficiency.
Contact our technical team today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK can optimize your molding processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between injection molding and pressure molding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Process
- What is the application of injection moulding machine? Powering Mass Production for Complex Parts
- What is the injection molding process? A Guide to High-Volume Part Production
- What is a positive of injection moulding? Achieve High-Volume Production with Unmatched Efficiency
- What can you make with an injection moulding machine? Mass-Produce High-Quality Plastic Parts Efficiently

















