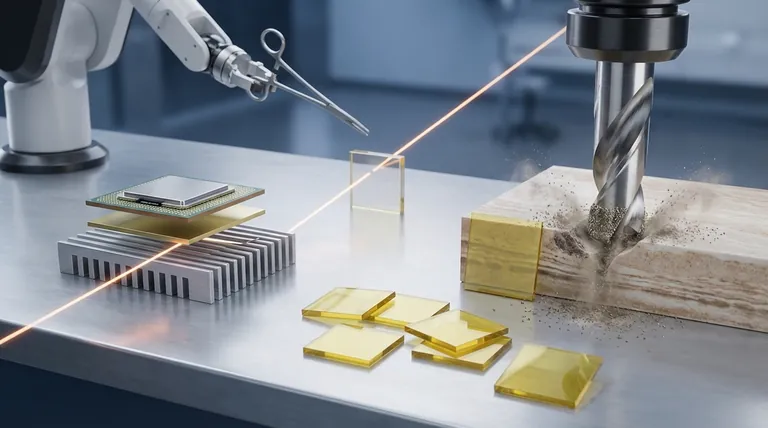
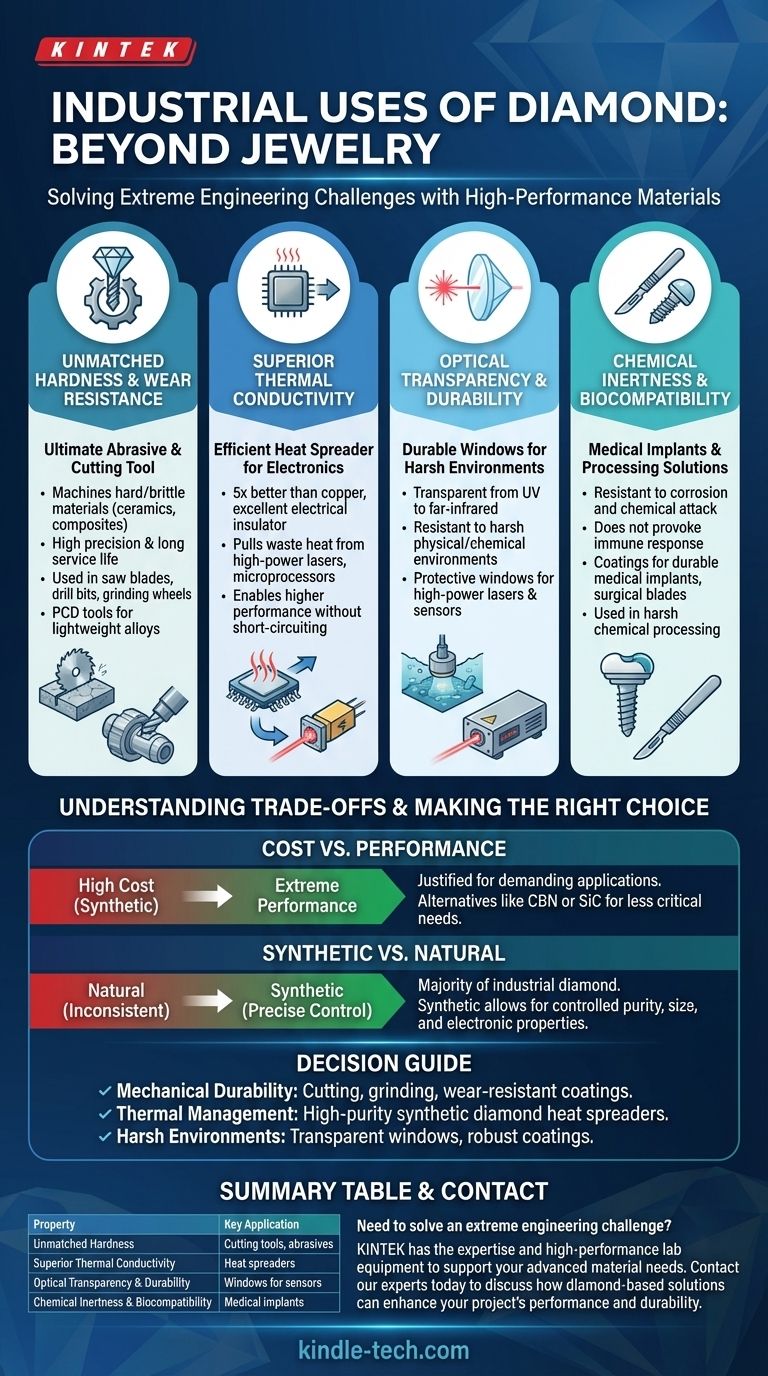
Beyond jewelry, the industrial world relies on diamond as a high-performance material to solve extreme engineering challenges. Its applications are driven by a unique combination of physical properties, making it indispensable in fields like machining, advanced electronics, optics, and medicine. Diamond is used to create ultra-hard cutting tools, manage heat in high-power electronics, and produce durable windows for lasers and sensors.
Diamond's true value in industry isn't just its hardness, but its unique combination of multiple superlative properties. It is often the material of choice when performance requirements for hardness, thermal conductivity, or chemical resistance exceed the limits of all other options.

Why Diamond is a Premier Engineering Material
The demand for diamond in technical applications stems from a set of physical properties that are not just excellent, but are often the best of any known material. Understanding these properties is key to understanding its use cases.
Unmatched Hardness and Wear Resistance
As the hardest known material, diamond offers unparalleled resistance to scratching and abrasion. This makes it the ultimate abrasive and cutting tool material.
Tools tipped or coated with diamond can machine hard, brittle, and abrasive materials—like ceramics, composites, and non-ferrous alloys—with high precision and a long service life.
Superior Thermal Conductivity
Counterintuitively, diamond is one of the best thermal conductors at room temperature, exceeding copper by a factor of five. However, it is an excellent electrical insulator.
This unique combination is critical in electronics. It allows diamond to act as a "heat spreader," rapidly pulling damaging waste heat away from sensitive components like high-power laser diodes or microprocessors without short-circuiting them.
Optical Transparency
High-purity diamond is transparent across a broad spectrum of light, from ultraviolet to far-infrared. This, combined with its durability, makes it an exceptional optical material.
It is used to create durable windows for high-power lasers or sensors that must operate in harsh physical or chemical environments where a lesser material would quickly degrade.
Chemical Inertness and Biocompatibility
Diamond is extremely resistant to chemical attack and does not corrode. It is also biocompatible, meaning it does not provoke a significant immune response from the human body.
This inertness allows it to be used in harsh chemical processing and as coatings for durable medical implants or sharp, long-lasting surgical blades.
Key Industrial Applications in Detail
These fundamental properties translate directly into specific, high-value industrial applications where other materials fail.
Machining and Abrasives
This is the largest industrial use for diamond. Tiny diamond crystals are embedded in saw blades, drill bits, and grinding wheels to cut everything from concrete and stone to advanced composite materials.
Polycrystalline diamond (PCD) cutting tools provide the precision and longevity needed to machine lightweight aluminum alloys in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Electronics and Thermal Management
In modern electronics, managing heat is a primary limiting factor for performance and longevity.
Thin layers of synthetic diamond are bonded directly to high-power transistors and laser arrays. The diamond efficiently channels heat to a larger heat sink, allowing the devices to run at higher power or for longer periods without failing.
Advanced Optics and Sensors
Diamond's durability allows it to be used as a protective window for sensors in extreme environments, such as on deep-earth drill heads.
It is also used in high-energy physics research. The robust structure of diamond makes it an ideal material for particle detectors operating in high-radiation environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, diamond is not a universal solution. Its application involves practical and economic considerations.
Cost vs. Performance
Diamond, particularly high-purity synthetic diamond, remains an expensive material to produce. Its use is typically justified only when performance demands are extreme and no other material can suffice.
For less demanding applications, other superhard materials like cubic boron nitride (CBN) or silicon carbide offer a more economical alternative.
Synthetic vs. Natural
The vast majority of industrial diamond is synthetic. Natural diamonds have impurities and structural flaws that make their properties inconsistent for high-tech applications.
Manufacturing synthetic diamond allows for precise control over purity, size, and even electronic properties through doping. This enables applications, such as diamond-based semiconductors, that would be impossible with natural stones.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting diamond is about identifying an engineering problem that can only be solved by its unique profile of extreme properties.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability: Leverage diamond's hardness for cutting, grinding, and creating wear-resistant coatings on tools and parts.
- If your primary focus is thermal management: Use high-purity synthetic diamond as a heat spreader to protect heat-sensitive electronics and enable higher performance.
- If your primary focus is operation in harsh environments: Employ diamond as a transparent window or robust coating to shield optics and sensors from chemical or physical damage.
Ultimately, diamond is the engineer's material of last resort, delivering performance where all other options have been exhausted.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Industrial Application |
|---|---|
| Unmatched Hardness | Cutting tools, abrasives, wear-resistant coatings |
| Superior Thermal Conductivity | Heat spreaders for high-power electronics & lasers |
| Optical Transparency & Durability | Windows for sensors & lasers in harsh environments |
| Chemical Inertness & Biocompatibility | Medical implants, surgical blades, chemical processing |
Need to solve an extreme engineering challenge?
Diamond's unique properties make it the material of choice when performance demands exceed the limits of all other options. Whether you require ultra-hard cutting tools, superior thermal management for electronics, or durable components for harsh environments, KINTEK has the expertise and high-performance lab equipment to support your advanced material needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how diamond-based solutions can enhance your project's performance and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- Is there certification for lab-grown diamonds? Get Independent Verification for Your Purchase
- What are the characteristics and applications of MPCVD? Discover the Secret to High-Purity Lab-Grown Diamonds
- Are CVD diamonds fake? Discover the Truth About Lab-Grown Diamonds
- Do lab diamonds break easily? No, They're as Durable as Mined Diamonds
- How do lab-grown diamonds compare to natural diamonds? Uncover the Truth About Origin, Price, and Value
- What is the fluorescence of a CVD diamond? A Guide to Its Unique Glow and Purpose
- How does chemical vapor deposition work for diamonds? Grow Lab-Created Diamonds Layer by Layer
- What is chemical vapor deposition of diamond? Grow High-Purity Diamonds Atom-by-Atom
















