In short, lab-grown diamonds are used in two primary domains: as high-quality, cost-effective gemstones for jewelry and in advanced technological applications. Because they are chemically and structurally identical to natural diamonds, they are valuable in fields like electronics, aerospace, and radiation detection where the unique properties of diamond are essential.
The ability to manufacture a material with the exceptional properties of diamond—at a lower cost, with greater control, and without the ethical and environmental burdens of mining—has unlocked its use far beyond traditional jewelry into critical high-tech industries.

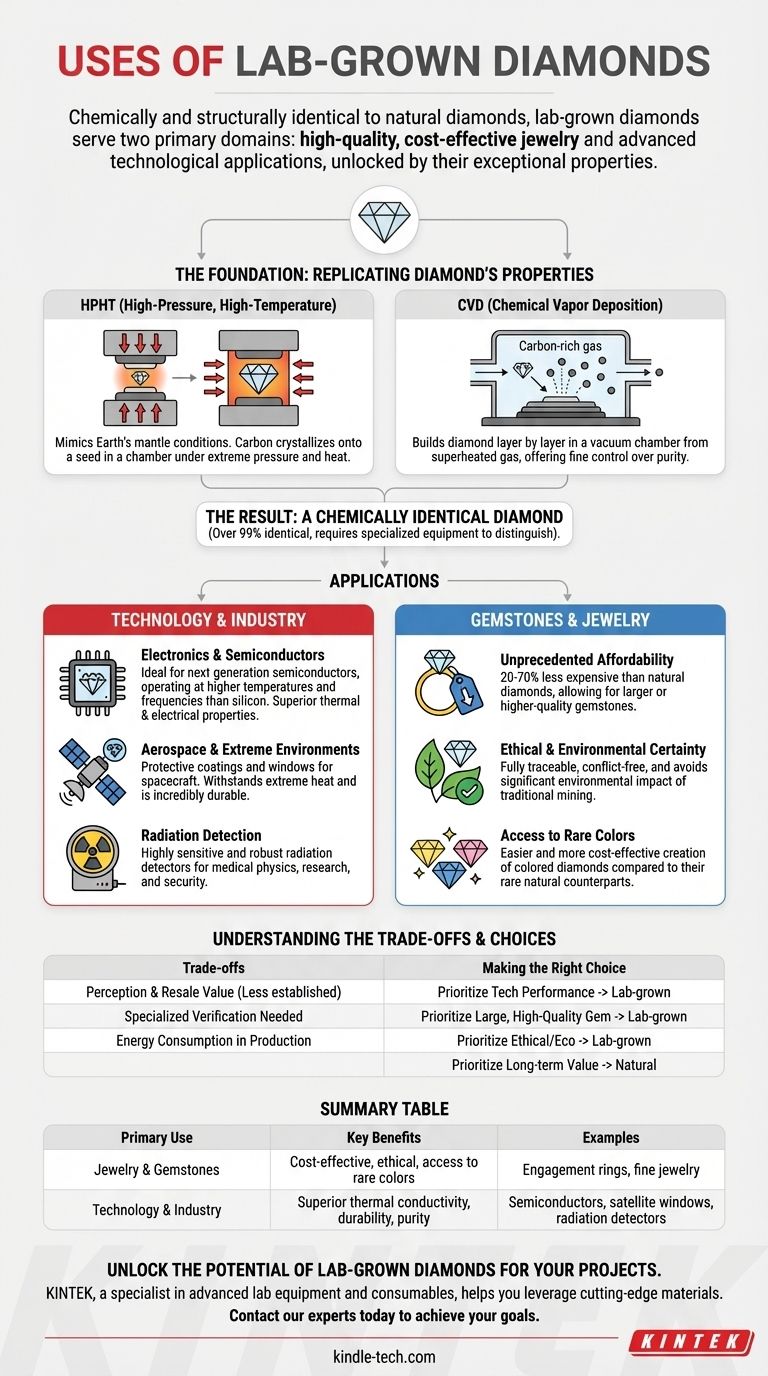
The Foundation: Replicating Diamond's Unmatched Properties
The value of any diamond, whether mined or grown, comes from its unique crystal structure. This structure gives it unparalleled hardness, thermal conductivity, and optical brilliance.
Lab processes are designed to precisely replicate the natural conditions of diamond formation, resulting in a product that is, for all intents and purposes, a true diamond.
High-Pressure, High-Temperature (HPHT)
The HPHT method mimics the intense conditions deep within the Earth's mantle. A small diamond "seed" is placed in a chamber with carbon, which is then subjected to extreme pressure and heat.
This process dissolves the carbon, which then crystallizes onto the diamond seed, growing a larger, complete diamond over time.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
The CVD method builds a diamond layer by layer in a vacuum chamber. A diamond seed is exposed to a superheated gas rich in carbon, like methane.
The high temperature breaks the gas down, allowing carbon atoms to deposit onto the seed and slowly build up a diamond crystal. This method offers fine control over the diamond's purity and properties.
The Result: A Chemically Identical Diamond
Both HPHT and CVD produce a crystal that is over 99% chemically identical to a mined diamond.
Without specialized gemological equipment to detect minute differences in growth patterns or trace elements, even experts cannot distinguish them by sight alone.
Applications in Technology and Industry
The ability to create pure, customized diamonds has made them a critical component in demanding technological fields.
Electronics and Semiconductors
The unique thermal and electrical properties of diamond make it an ideal material for next-generation semiconductors.
Lab-grown diamonds can be used to create highly efficient and durable electronic components that can operate at higher temperatures and frequencies than silicon-based devices.
Aerospace and Extreme Environments
Diamond's incredible durability and ability to withstand heat make it perfect for protective coatings and windows on spacecraft.
As an example, NASA has utilized lab-grown diamonds in satellites to protect sensitive instruments from the extreme conditions of atmospheric re-entry.
Radiation Detection
The purity and stable atomic structure of lab-grown diamonds allow them to be used as highly sensitive and robust radiation detectors.
These devices are crucial in medical physics, scientific research, and security applications.
The Revolution in Gemstones and Jewelry
Beyond industry, lab-grown diamonds have fundamentally changed the consumer jewelry market.
Unprecedented Affordability
Lab-grown diamonds typically cost between 20% and 70% less than natural diamonds of the same size, cut, and clarity.
This price difference allows consumers to acquire a larger or higher-quality gemstone for their budget.
Ethical and Environmental Certainty
Because they are created in a controlled laboratory environment, the origin of every lab-grown diamond is fully traceable.
This guarantees they are conflict-free and avoids the significant environmental impact associated with traditional diamond mining.
Access to Rare Colors
The production process allows for the creation of colored diamonds, such as yellows, blues, and pinks, with greater ease and at a much lower cost than their incredibly rare natural counterparts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While they offer significant advantages, it is important to consider the complete picture.
Perception and Resale Value
The primary trade-off is market perception. As a newer product, the long-term resale value of lab-grown diamonds is less established compared to the centuries-old market for natural diamonds.
The Need for Specialized Verification
Because they are visually identical to mined diamonds, verifying their origin requires specialized tools that can analyze thermal conductivity or examine microscopic growth patterns. This distinction is impossible for the naked eye.
Energy Consumption in Production
While they avoid the environmental disruption of mining, both the HPHT and CVD processes are energy-intensive. The overall environmental benefit depends heavily on the source of the electricity used in their production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between a lab-grown and a natural diamond depends entirely on your priorities.
- If your primary focus is technological performance: Lab-grown diamonds offer superior purity, customization, and cost-effectiveness for industrial and scientific applications.
- If your primary focus is obtaining a large, high-quality gemstone: Lab-grown diamonds provide significantly more carat weight and clarity for your budget than a comparable mined diamond.
- If your primary focus is ethical and environmental impact: Lab-grown diamonds offer a fully traceable, conflict-free option with a lower environmental footprint than mining.
- If your primary focus is long-term investment or resale value: The established market and perceived rarity of natural diamonds currently give them an advantage in holding value over time.
Ultimately, lab-grown diamond technology empowers you to access the remarkable properties of this material with greater choice and transparency.
Summary Table:
| Primary Use | Key Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Jewelry & Gemstones | Cost-effective, ethical, access to rare colors | Engagement rings, fine jewelry |
| Technology & Industry | Superior thermal conductivity, durability, purity | Semiconductors, satellite windows, radiation detectors |
Unlock the potential of lab-grown diamonds for your projects.
Whether you're developing next-generation electronics or seeking high-quality, ethically sourced materials, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your needs. As a specialist in advanced lab equipment and consumables, we help laboratories and industries leverage cutting-edge materials like lab-grown diamonds.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve your material and research goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- Are CVD diamonds worth it? Unlock Brilliant Value & Ethical Clarity
- How can you tell the difference between a diamond and a CVD? The Expert's Guide to Identification
- What are the industrial uses of CVD diamond? Unlock Extreme Performance in Your Applications
- Are artificial diamonds as strong as natural diamonds? Discover the Truth About Lab-Grown Diamond Durability
- Do lab grown diamonds pass a diamond tester? Yes, They're Chemically Identical.
- Can CVD diamonds change color? No, their color is permanent and stable.
- What is the process of chemical vapor deposition diamond? Grow High-Purity, Engineered Diamonds from Gas
- What are diamond films used for? Enhancing Tools, Electronics, and Implants with Diamond Surfaces








