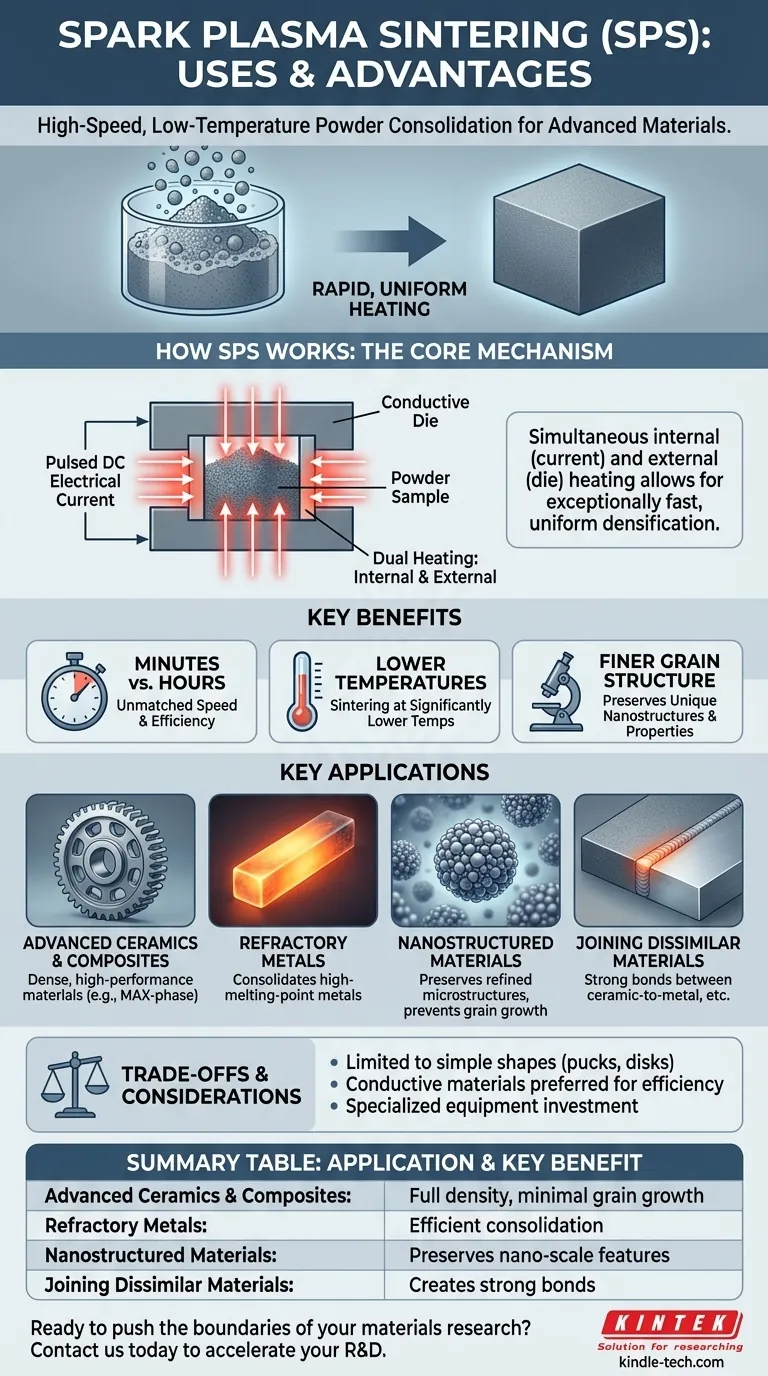
At its core, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is a high-speed, low-temperature powder consolidation technique used to create dense, high-performance materials. It is primarily used to fabricate advanced ceramics, refractory metals, and composites, as well as to join dissimilar materials like ceramic to metal. Its key advantage is the ability to achieve full densification in minutes rather than hours, at significantly lower temperatures than conventional methods.
SPS is not just another way to heat powders; it's a fundamentally different approach that uses an electrical current for rapid, uniform heating. This unique mechanism enables the creation of highly dense, fine-grained materials, preserving unique properties that would otherwise be lost during slower, high-temperature processing.
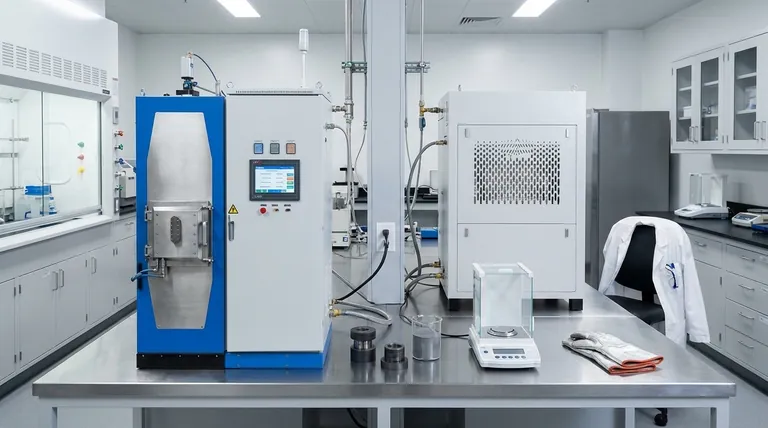

How SPS Redefines Material Consolidation
Spark Plasma Sintering, also known as a field-assisted sintering technique (FAST), works by passing a pulsed DC electrical current through a conductive die (typically graphite) and, in many cases, through the powder sample itself. This process fundamentally changes the dynamics of sintering.
The Core Mechanism: Internal and External Heating
Unlike a conventional furnace that heats a material slowly from the outside in, SPS provides dual heating. The conductive die acts as an external heat source, while the electrical current passing through the powder generates heat internally.
This simultaneous internal and external heating is extremely rapid and uniform, which is the primary reason for the technology's effectiveness.
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
The direct heating method allows for exceptionally fast heating rates. This shortens the entire sintering process from many hours to just a few minutes.
Because the material reaches the target temperature so quickly and is held there for a very short time, there is less opportunity for unwanted grain growth, leading to a finer, stronger final material.
Sintering at Lower Temperatures
Perhaps the most significant advantage is that SPS achieves full densification at much lower temperatures—often several hundred degrees Celsius lower than required for conventional sintering.
This is critical for advanced materials where preserving a specific nanostructure or phase is essential for performance. Higher temperatures would destroy these delicate features.
Key Applications of Spark Plasma Sintering
The unique capabilities of SPS make it invaluable for applications where material properties and microstructure are paramount.
Fabricating Advanced Materials
SPS is exceptionally effective for producing dense, high-performance materials that are difficult to create with other methods. This includes technical ceramics, MAX-phase materials, and amorphous materials like metallic glass.
Consolidating Metals and Composites
In powder metallurgy, SPS is used to consolidate metal powders, especially for refractory metals with very high melting points. It's also ideal for creating novel composites and gradient materials with tailored properties throughout their structure.
Preserving Nanostructures
Processes like cryogenic milling can produce powders with refined, nano-scale microstructures. SPS is one of the few techniques that can consolidate these powders into a solid part without coarsening the grains, thereby preserving the unique properties achieved during milling.
Joining Dissimilar Materials
SPS enables the "welding" or bonding of materials that are typically incompatible. It can create strong, reliable joints between two different ceramics or between a ceramic and a metal, with or without an intermediate layer. This is extremely difficult to achieve with traditional methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, SPS is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Geometry and Size Constraints
The process requires the powder to be contained within a conductive die, which is then placed under pressure. This setup generally limits the final parts to simple shapes like pucks, disks, or squares. Producing large or complex geometries is often impractical.
Dependence on Electrical Conductivity
The highest efficiency is achieved when the material itself is electrically conductive, allowing for internal heat generation. While insulating materials like some ceramics can still be sintered, the process relies solely on heat transfer from the die, making it less efficient than for conductive materials.
Equipment and Operational Costs
SPS equipment is more complex and has a higher initial investment cost compared to a standard high-temperature furnace. While the process is fast and highly automated ("simple operation"), it is a specialized technique requiring specific expertise and infrastructure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a sintering method depends entirely on the final objective for your material.
- If your primary focus is preserving novel microstructures or nano-scale features: SPS is the superior choice due to its low-temperature and rapid processing, which prevents grain growth.
- If your primary focus is producing large volumes of simple, low-cost parts: Conventional powder metallurgy and furnace sintering are more established and cost-effective solutions.
- If your primary focus is creating parts with highly complex geometries: Additive manufacturing (3D printing) combined with a subsequent sintering step is likely the more appropriate pathway.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density in next-generation composites or refractory metals: SPS offers unparalleled capability for consolidating these challenging materials quickly and effectively.
Ultimately, leveraging SPS effectively means understanding that its true power lies in its precise control over a material's microstructure.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Advanced Ceramics & Composites | Achieves full density with minimal grain growth. |
| Refractory Metals | Consolidates high-melting-point materials efficiently. |
| Nanostructured Materials | Preserves nano-scale features via low-temperature processing. |
| Joining Dissimilar Materials | Creates strong bonds between ceramics and metals. |
Ready to push the boundaries of your materials research?
Spark Plasma Sintering from KINTEK enables you to fabricate high-performance materials with precise microstructural control, faster and at lower temperatures than conventional methods. Whether you are developing advanced ceramics, metal composites, or need to join dissimilar materials, our expertise and specialized lab equipment are here to support your innovation.
Contact us today to discuss how SPS can accelerate your R&D projects. Let's achieve your material goals together.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What are the parameters for spark plasma sintering? Master Speed, Pressure & Temperature Control
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application



















