At its core, vapor deposition is a high-precision manufacturing process used to apply extremely thin, high-performance films of material onto a surface. It is the go-to method for creating protective coatings on cutting tools and aerospace parts, manufacturing the intricate layers in semiconductors and solar cells, and even growing advanced nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes.
The true value of vapor deposition lies in its ability to build materials atom by atom from a gaseous state. This atomic-level control is what enables the creation of exceptionally pure, durable, and uniform films that are essential for modern high-technology applications.

How the Process Unlocks Unique Capabilities
Vapor deposition isn't a single technique but a family of processes. They all share a fundamental principle that makes them uniquely powerful for surface engineering.
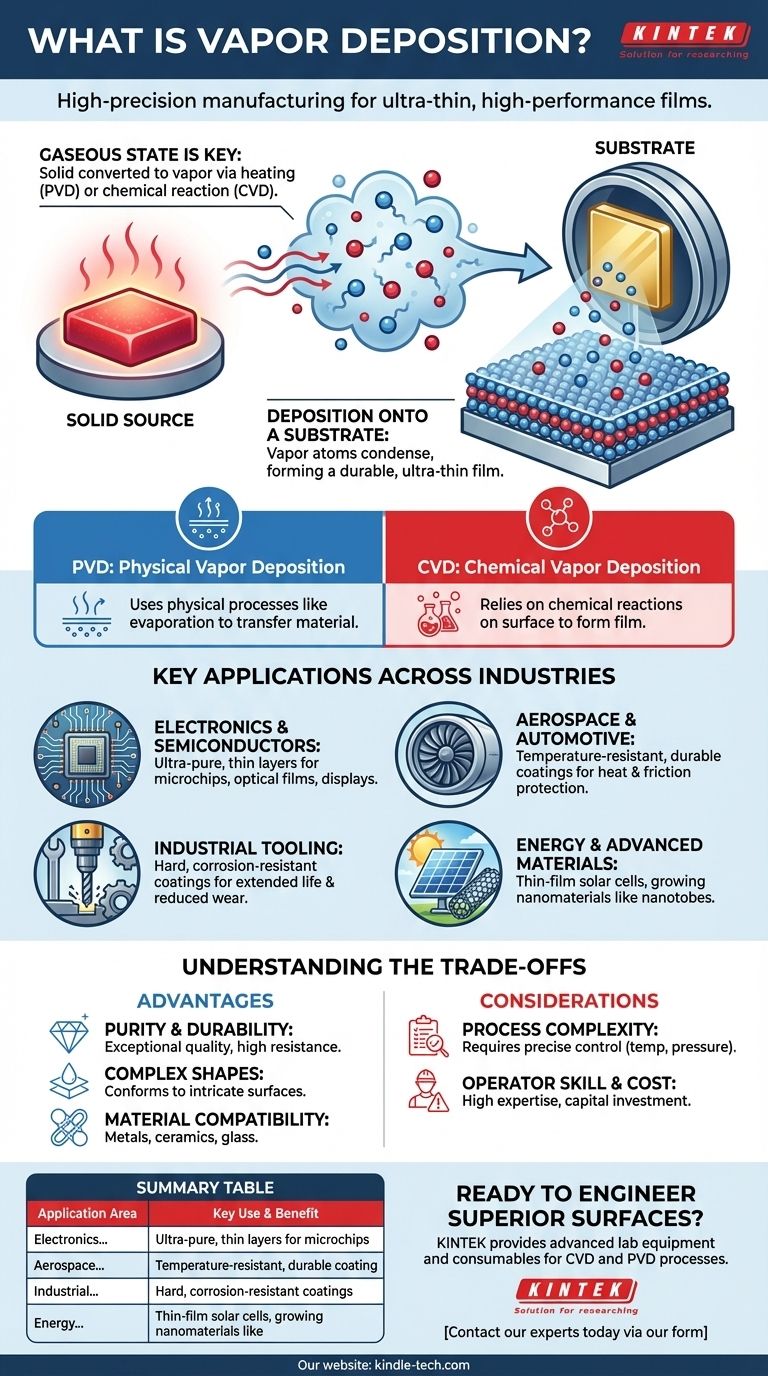
The Gaseous State is Key
First, a solid source material—such as a metal, ceramic, or semiconductor—is converted into a gaseous vapor. This can be done through physical means like heating (evaporation) or by using a chemical reaction to release the desired atoms.
Deposition onto a Substrate
This vapor is then introduced into a vacuum chamber containing the object to be coated, known as the substrate. The vaporized atoms travel and condense onto the substrate's surface, forming a solid, ultra-thin film that is tightly bonded to the material.
Two Primary Methods: CVD and PVD
The two main categories are Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). CVD relies on chemical reactions on the substrate surface to form the film, while PVD uses physical processes like evaporation to transfer the material.
Key Applications Across Industries
The precision and versatility of vapor deposition have made it indispensable in a wide range of demanding fields. Its ability to create tailored surfaces solves critical engineering challenges.
Electronics and Semiconductors
This is perhaps the most well-known application. The process is used to deposit the highly pure, microscopically thin layers of conducting and insulating materials that form the basis of microchips, optical films for displays, and electronic packaging.
Aerospace and Automotive
Components in these industries must withstand extreme conditions. Vapor deposition applies dense, temperature-resistant and durable coatings that protect parts from heat, friction, and environmental degradation, enhancing both performance and lifespan.
Industrial Tooling
To extend the life of cutting tools, drills, and molds, a hard, corrosion-resistant coating is applied via vapor deposition. This layer significantly reduces wear and friction, allowing tools to function effectively in harsh industrial environments.
Energy and Advanced Materials
The technology is crucial for manufacturing thin-film solar cells, where photovoltaic materials are deposited onto a substrate. It is also used in research and development to grow specialized structures like carbon nanotubes and nanowires.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, vapor deposition is a specialized process. Understanding its strengths and limitations is key to using it effectively.
The Purity and Durability Advantage
The primary benefit is the quality of the film. These coatings are exceptionally durable and can be optimized for specific properties like corrosion resistance, abrasion resistance, or high purity, making them ideal for high-stress environments.
The Ability to Coat Complex Shapes
Because the material is applied from a vapor, it can conform to and coat intricate and complex surfaces with a high degree of uniformity. This is a significant advantage over many liquid-based coating methods.
Process Complexity and Skill
Achieving a perfect film requires precise control over variables like temperature, pressure, and gas composition. While some systems are accessible, industrial-scale production requires significant capital investment and a high level of operator skill, particularly for CVD processes.
Material Compatibility
A major strength of vapor deposition is its versatility. The process can be used to apply films to a wide range of base materials, including metals, ceramics, and glass, opening up a vast array of engineering possibilities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right surface treatment depends entirely on your end goal. Vapor deposition excels where performance and precision are non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability: Vapor deposition is the standard for creating hard, protective coatings on tools and industrial components that must resist wear and corrosion.
- If your primary focus is high-purity electronic performance: The process is essential for manufacturing semiconductors, optical films, and solar cells where atomic-level precision is critical.
- If your primary focus is performance in harsh environments: It is the leading method for applying thermal and corrosion barriers to mission-critical aerospace and automotive parts.
Ultimately, vapor deposition provides a powerful toolkit for engineering material surfaces with properties that are simply unattainable through other methods.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Use & Benefit |
|---|---|
| Electronics & Semiconductors | Deposits ultra-pure, thin layers for microchips and optical films. |
| Aerospace & Automotive | Applies heat-resistant, durable coatings to protect critical components. |
| Industrial Tooling | Extends tool life with hard, wear-resistant coatings. |
| Energy & Advanced Materials | Manufactures thin-film solar cells and grows nanomaterials like nanotubes. |
Ready to engineer superior surfaces with precision coatings?
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed for vapor deposition processes like CVD and PVD. Whether you are developing next-generation semiconductors, enhancing the durability of industrial tools, or creating advanced materials, our solutions support the high-precision demands of your research and production.
Contact our experts today via our form to discuss how we can help you achieve unparalleled performance and durability in your applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- How does a Hot Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition (HFCVD) reactor function? Expert Guide to Diamond Film Fabrication
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth



















