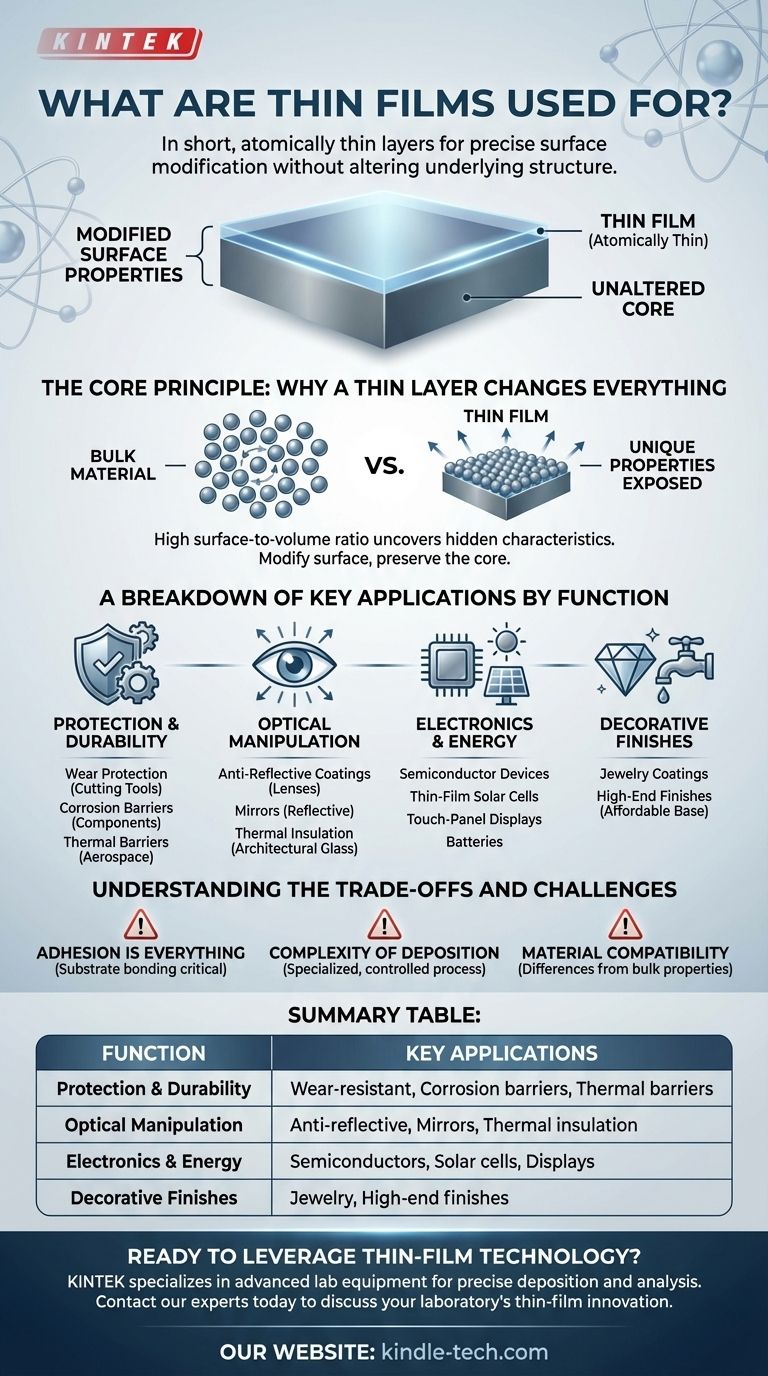
In short, thin films are used to precisely modify the surface properties of an object without altering its underlying structure. These atomically thin layers are applied to everything from eyeglass lenses and solar panels to microchips and protective packaging, serving to manipulate light, conduct electricity, provide protection, or add a decorative finish.
The core value of a thin film is not the material itself, but the unique physical, optical, and electrical properties that emerge when that material is reduced to an ultra-thin layer. This allows us to give a bulk material new surface capabilities—like reflectivity, durability, or conductivity—in a highly efficient and controlled way.

The Core Principle: Why a Thin Layer Changes Everything
The versatility of thin films comes from a fundamental concept in material science. By reducing a material to a layer that can be just a few atoms thick, we fundamentally change how it behaves.
The Power of the Surface
In a bulk material, most atoms are surrounded by other atoms. In a thin film, a huge proportion of atoms are at the surface. This high surface-to-volume ratio exposes unique properties that are otherwise hidden.
Modifying the Surface, Preserving the Core
Thin films allow us to add a specific function to a material without changing its core characteristics. You can apply an incredibly hard, wear-resistant film to a lightweight and inexpensive tool, getting the best of both worlds.
Engineering at the Atomic Scale
These films can be engineered with incredible precision. They can be a single, homogenous layer or a complex, multi-layered structure designed to achieve a very specific outcome, like selectively filtering wavelengths of light.
A Breakdown of Key Applications by Function
Instead of just listing industries, it's more useful to understand the primary functions that thin films are engineered to perform.
For Protection and Durability
One of the most common uses is to create a barrier. This includes applying hard coatings to cutting tools for wear protection, corrosion-resistant layers on components, and thermal barriers on aerospace parts to protect them from extreme heat.
For Optical Manipulation
Thin films are masters at controlling light. A household mirror is simply a thin metallic film on glass. More advanced applications include multi-layer anti-reflective coatings on ophthalmic lenses and camera optics, and films on architectural glass for thermal insulation.
For Electronics and Energy
Modern electronics would not exist without thin films. They form the critical active layers in semiconductor devices and microchips. They are also essential for thin-film solar cells, touch-panel displays, computer memory, and the next generation of thin-film batteries.
For Decorative Finishes
Thin films are also used for aesthetic purposes. A thin layer of a precious or colored material can be applied to jewelry or bathroom fittings to provide a high-end finish on a more affordable base material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While incredibly powerful, working with thin films involves specific technical challenges that are critical to understand.
Adhesion is Everything
A thin film is only as effective as its ability to stick to the underlying material, known as the substrate. Poor adhesion can lead to peeling, cracking, or flaking, causing the component to fail.
Complexity of Deposition
Creating a uniform, high-quality thin film requires highly specialized and often expensive equipment. The process must be meticulously controlled to ensure the film has the desired thickness, composition, and structure.
Material Compatibility
Not all materials can be easily deposited as a thin film. Furthermore, the properties of a material in its thin-film form can sometimes differ from its properties in bulk, which must be accounted for during the design phase.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific application of a thin film is dictated entirely by the problem you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is improving durability: You will use hard, inert coatings for wear, corrosion, or thermal resistance.
- If your primary focus is controlling light: Your solution lies in optical coatings, from simple metallic mirrors to complex multi-layer dielectric stacks.
- If your primary focus is building electronic components: You will use thin films to create the active semiconducting, conducting, or insulating layers in a device.
- If your primary focus is enhancing aesthetics or value: You will leverage decorative films to apply a high-quality finish over a cost-effective base material.
Ultimately, thin-film technology is a cornerstone of modern engineering, enabling us to give ordinary materials extraordinary capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Protection & Durability | Wear-resistant coatings, corrosion barriers, thermal barriers |
| Optical Manipulation | Anti-reflective coatings, mirrors, thermal insulation films |
| Electronics & Energy | Semiconductor devices, solar cells, touch-panel displays |
| Decorative Finishes | Jewelry coatings, high-end finishes on affordable materials |
Ready to leverage thin-film technology for your project? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise thin-film deposition and analysis. Whether you're developing protective coatings, optical layers, or next-generation electronics, our solutions help you achieve superior surface properties with reliability and precision. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's thin-film innovation and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process


















