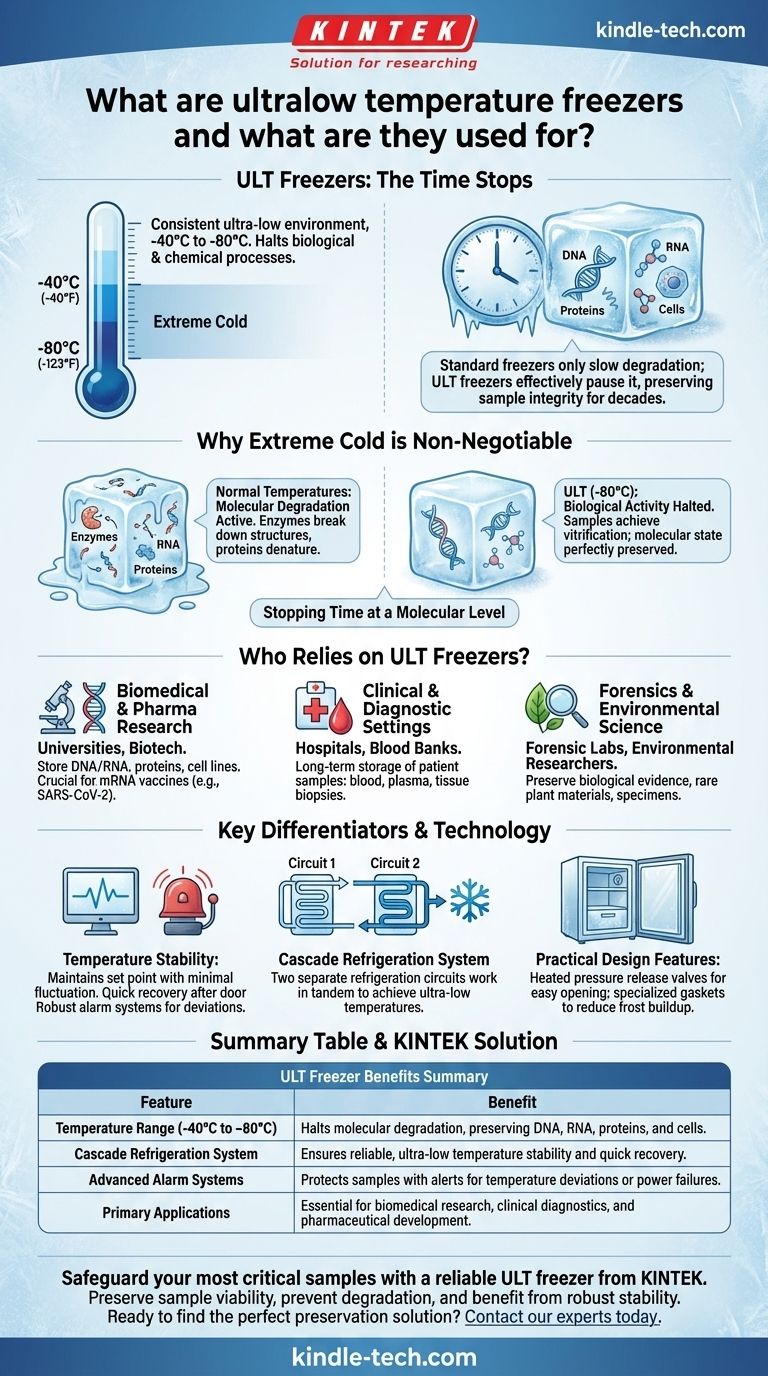
At its core, an ultralow temperature (ULT) freezer is a specialized piece of equipment designed for the long-term preservation of sensitive biological materials. Unlike a standard household freezer, a ULT freezer maintains a consistent and extremely cold environment, typically between -40°C and -80°C (-40°F to -123°F). This intense cold effectively halts the biological and chemical processes that would otherwise degrade critical samples like DNA, RNA, proteins, and cells.
A standard freezer merely slows degradation; a ULT freezer effectively pauses it. By creating an environment where molecular activity all but ceases, these freezers ensure the integrity of invaluable biological samples for years or even decades, making long-term research and medical innovation possible.

Why Extreme Cold is Non-Negotiable
The value of a ULT freezer isn't just about making things cold—it's about stopping time at a molecular level. Without this capability, much of modern biological science would be impossible.
The Enemy: Molecular Degradation
At normal or even standard freezer temperatures, biological molecules remain active. Enzymes continue to break down cellular structures, RNA degrades rapidly, and proteins can denature, or lose their functional shape.
This degradation renders a sample useless for sensitive analysis. It compromises the accuracy of research, the viability of a vaccine, or the integrity of forensic evidence.
Halting Biological Activity
By plunging the temperature to -80°C, a ULT freezer pushes samples past the freezing point of water and into a state of vitrification. All biological activity, including the enzymatic reactions that cause decay, effectively stops.
This ensures that a sample's molecular state is perfectly preserved from the moment it is frozen. A cell line, protein, or piece of tissue can be stored for years and remain virtually identical to its original state when thawed.
Who Relies on ULT Freezers?
The ability to reliably preserve biological materials makes ULT freezers indispensable across numerous scientific and medical fields.
Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Research
Labs in universities, medical centers, and biotech companies use ULT freezers to store the building blocks of their research. This includes DNA and RNA for genetic studies, proteins for drug discovery, and entire cell lines for developmental biology.
The shipment and storage of mRNA vaccines, such as those for SARS-CoV-2, depend entirely on this technology to prevent the fragile mRNA molecules from breaking down.
Clinical and Diagnostic Settings
Hospitals, blood banks, and clinical laboratories rely on ULT freezers for the long-term storage of patient samples. This includes blood, plasma, tissue biopsies, and other bodily fluids that may be needed for future diagnostics, research, or treatment verification.
Forensics and Environmental Science
In forensics, ULT freezers preserve biological evidence like tissue samples or autopsy materials, ensuring they are not compromised over time.
Environmental researchers also use them to store unique biological samples, such as rare plant materials, insect specimens, or bacteria, for future study.
Understanding the Key Differentiators
A ULT freezer is a highly engineered device, and its critical features go far beyond simple cooling. These elements are what guarantee the safety of irreplaceable materials.
Beyond Temperature: The Importance of Stability
The most critical feature is temperature stability. The freezer must maintain its set point with minimal fluctuation. Quick temperature recovery after a door opening is vital.
To ensure this, ULT freezers are equipped with robust visual and audible alarm systems that alert staff to temperature deviations, power failures, or door-ajar events.
The Cascade Refrigeration System
Achieving temperatures of -80°C requires more than a standard compressor. ULT freezers use a cascade refrigeration system, which involves two separate refrigeration circuits working in tandem.
The first circuit cools the second, allowing the second circuit to reach a much lower temperature than a single system ever could. This engineering is central to their function.
Practical Design Features
ULT freezers are built to combat the physical challenges of extreme cold. They often include heated pressure release valves to make doors easier to open and specialized gaskets to reduce the significant frost buildup that can compromise seals and efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the role of a ULT freezer helps clarify when and why this technology is essential.
- If your primary focus is long-term research: You need a ULT freezer to guarantee sample integrity over many years, preventing molecular degradation from invalidating your results.
- If your primary focus is clinical diagnostics or biobanking: The security, alarm, and stability features of a ULT freezer are paramount for protecting irreplaceable patient samples and maintaining regulatory compliance.
- If your primary focus is pharmaceutical development: A ULT freezer is non-negotiable for preserving the viability of sensitive biologics, from research-grade proteins to finished vaccines.
Ultimately, ULT freezers are the silent guardians of scientific and medical progress, preserving the invaluable materials that unlock future discoveries.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range (-40°C to -80°C) | Halts molecular degradation, preserving DNA, RNA, proteins, and cells. |
| Cascade Refrigeration System | Ensures reliable, ultra-low temperature stability and quick recovery. |
| Advanced Alarm Systems | Protects samples with alerts for temperature deviations or power failures. |
| Primary Applications | Essential for biomedical research, clinical diagnostics, and pharmaceutical development. |
Safeguard your most critical samples with a reliable ULT freezer from KINTEK.
Whether you are conducting long-term biomedical research, managing a clinical biobank, or developing next-generation pharmaceuticals, the integrity of your biological samples is paramount. KINTEK specializes in providing high-performance lab equipment, including ultralow temperature freezers, designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern laboratories.
We help you:
- Preserve sample viability for decades, ensuring research accuracy and compliance.
- Prevent molecular degradation of sensitive materials like cell lines, vaccines, and forensic evidence.
- Benefit from robust stability and security features that protect your invaluable investments.
Ready to find the perfect preservation solution for your lab's needs? Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can support your mission.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 158L Precision Vertical Ultra Low Freezer for Laboratory Applications
- 708L Ultra Low Temperature Freezer High Performance Laboratory Freezer
- 28L Compact Upright Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Laboratory
- 58L Precision Laboratory Ultra Low Temperature Upright Freezer for Critical Sample Storage
- 508L Advanced Vertical Ultra Low Temperature Freezer for Critical Laboratory Storage
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of physical vapour deposition method? Achieve Superior, Durable Surface Coatings
- What are some of the limitations of powder metallurgy technique? Understanding Part Size, Complexity, and Strength Constraints
- What types of furnaces are used for sintering ceramics? Choose the Right Kiln for Your Production
- What is heat treatment in simple terms? A Guide to Transforming Material Properties
- What is the effect of residence time on pyrolysis? Control Product Yields from Bio-oil to Biochar
- What is sintering glass? A Low-Temperature Process for Complex Glass Parts
- What is the thickness of coating? A Guide from Nanoscale to Macroscale Applications
- How does heat treating affect the strength of a metal? A Guide to Tailoring Metal Properties



















