To test diamonds, jewelers primarily use thermal and electrical conductivity testers to quickly separate genuine diamonds from common fakes. However, to distinguish between natural and lab-grown diamonds—which are chemically identical—they must rely on far more advanced and specialized gemological equipment that analyzes a stone's growth patterns and reaction to specific wavelengths of light.
The core challenge in diamond testing has shifted. While basic tools can easily identify simulants like cubic zirconia, only sophisticated laboratory instruments can definitively determine a diamond's origin as either natural or lab-grown.
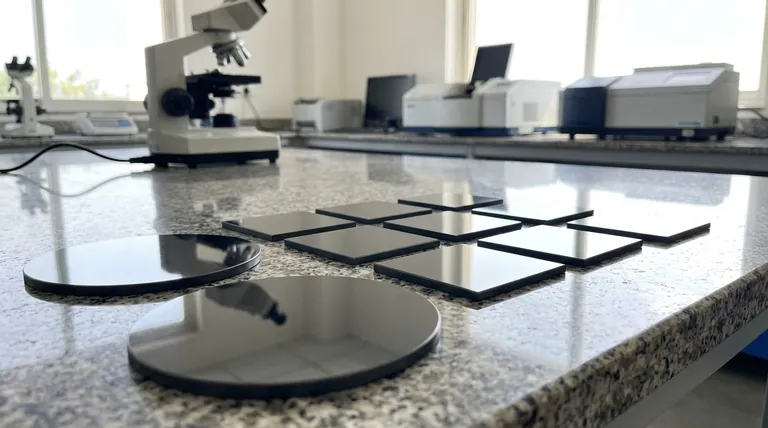

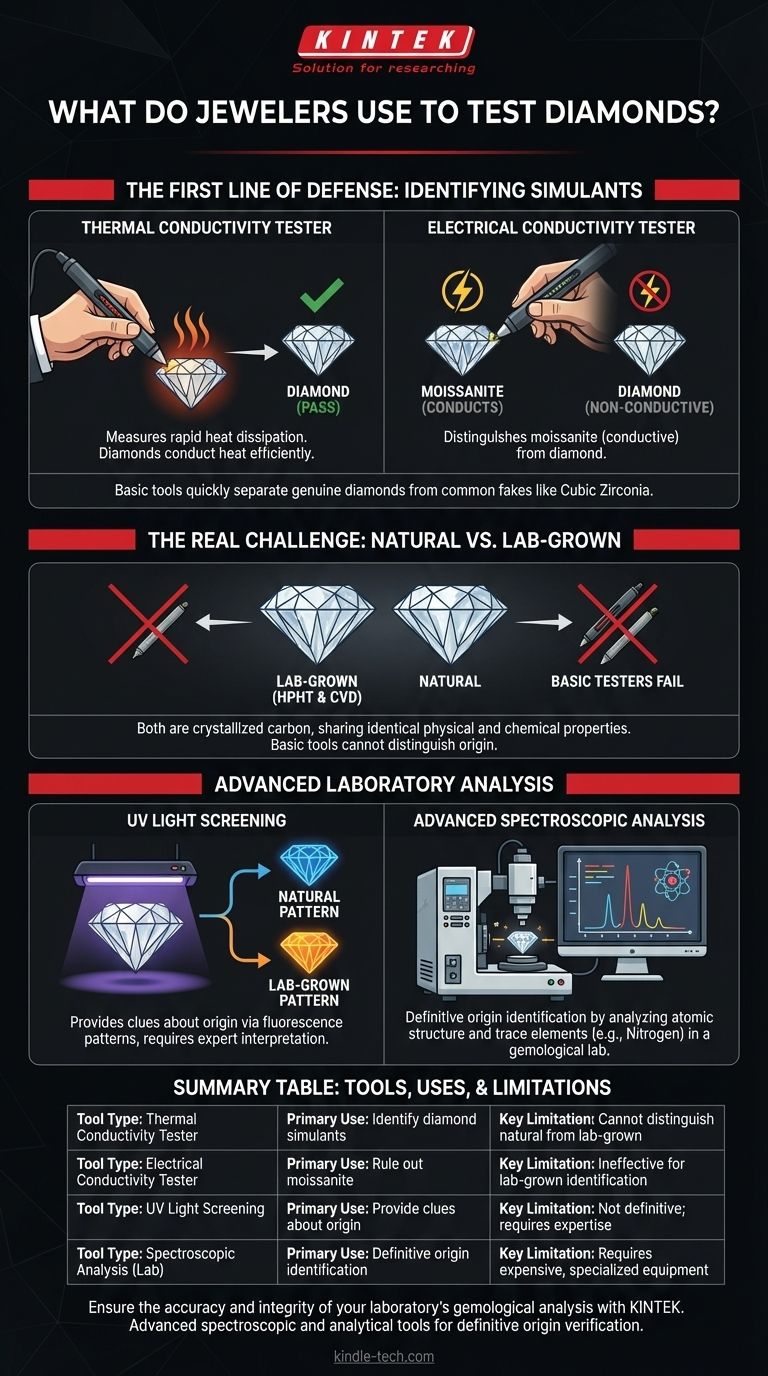
The First Line of Defense: Identifying Simulants
A jeweler's most common task is verifying that a stone is, in fact, a diamond and not a simulant (a look-alike with a different chemical structure). This is where portable, pen-like testers are most effective.
Thermal Conductivity Testers
Diamonds are exceptionally efficient conductors of heat. A thermal tester has a small, heated metal tip that is pressed against the stone.
The device measures how quickly heat is pulled away from the tip. If it dissipates rapidly, the tester signals that the stone is a diamond.
Electrical Conductivity Testers
Some simulants, most notably moissanite, have thermal conductivity very similar to a diamond and can fool a basic thermal tester.
However, moissanite also conducts electricity, while diamonds do not (with the rare exception of blue diamonds). A jeweler will often use a combination device or a separate electrical tester to rule out moissanite.
The Real Challenge: Natural vs. Lab-Grown
The rise of high-quality lab-grown diamonds has presented a new challenge. Because they are physically and chemically identical to natural diamonds, they pass basic thermal and electrical tests. Distinguishing them requires specialized laboratory-grade equipment.
Why Basic Testers Fail
Both HPHT (High-Pressure/High-Temperature) and CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) methods create stones that are crystallized carbon.
They have the same hardness, specific gravity, and thermal properties as a mined diamond. To a standard tester, a lab-grown diamond is a real diamond.
The Role of UV Light
Advanced screening devices use shortwave ultraviolet light to provide clues about a diamond's origin.
Natural and lab-grown diamonds often fluoresce differently. The specific color and pattern of this fluorescence can be a strong indicator, helping gemologists separate batches of stones for further analysis.
Advanced Spectroscopic Analysis
The definitive test requires analyzing the diamond on an atomic level. This is done in a gemological lab, not at a jeweler's counter.
Instruments like spectrometers analyze how the diamond interacts with light, revealing subtle differences in its atomic structure and the presence of trace elements like nitrogen, which are characteristic of natural formation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
It is critical to understand the difference between the tools a retail jeweler has on hand and the equipment used by a major gemological laboratory.
The Jeweler's Counter
The pen-style testers used by most jewelers are screening tools. They are designed to be fast and effective at weeding out non-diamonds (simulants).
They are not designed, nor are they capable of, distinguishing a natural diamond from a lab-grown one.
The Gemological Lab
Definitive origin identification requires equipment that costs tens of thousands of dollars and requires expert interpretation.
This is why official grading reports from institutions like the GIA (Gemological Institute of America) are the ultimate source of truth. They have the necessary instruments to perform conclusive tests.
What This Means for You
Understanding these tools and their limitations empowers you to make an informed decision. The right verification method depends entirely on your goal.
- If your primary focus is avoiding fakes (simulants): A standard diamond tester used by any reputable jeweler is a highly reliable tool for this purpose.
- If your primary focus is verifying a diamond's origin (natural vs. lab-grown): You must insist on a recent grading report from a major, independent gemological laboratory.
Ultimately, the most reliable tool for verification is not a machine, but the certified documentation that accompanies the stone.
Summary Table:
| Tool Type | Primary Use | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity Tester | Identify diamond simulants (e.g., cubic zirconia) | Cannot distinguish natural from lab-grown diamonds |
| Electrical Conductivity Tester | Rule out moissanite (conducts electricity) | Ineffective for lab-grown diamond identification |
| UV Light Screening | Provide clues about diamond origin via fluorescence | Not definitive; requires expert interpretation |
| Spectroscopic Analysis (Lab) | Definitive origin identification via atomic structure | Requires expensive, specialized lab equipment |
Ensure the accuracy and integrity of your laboratory's gemological analysis with KINTEK.
As a leading supplier of precision lab equipment and consumables, we understand the critical need for reliable instrumentation in distinguishing natural from lab-grown diamonds. Our advanced spectroscopic and analytical tools are designed to meet the rigorous demands of gemological laboratories, providing the definitive data required for confident origin verification.
Why partner with KINTEK?
- Precision Instruments: Access cutting-edge technology for accurate diamond analysis
- Expert Support: Leverage our technical expertise in gemological laboratory equipment
- Quality Assurance: Ensure consistent, reliable results with our trusted consumables
Ready to enhance your diamond verification capabilities? Contact our equipment specialists today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK solutions can support your gemological analysis.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Stirring Bar Recovery Rod
- Infrared High Resistance Single Crystal Silicon Lens
- High Performance Lab Homogenizer for Pharma Cosmetics and Food R&D
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- What are some examples of inert gases in real life? From Balloons to Welding, Discover Their Uses
- What type of plastic is usually used with compression molding and transfer molding? Master Thermosets for Superior Performance
- What is the charcoal yield in fast pyrolysis? A Low-Yield Feature for Maximum Bio-Oil
- What are the four stages of sintering? A Guide to Precise Material Densification
- Are thin films used as coatings on lenses? The Key to Superior Optical Performance
- What is the temperature stability of graphite? Unlocking Extreme Heat Resistance in the Right Environment
- What is the sputtering method of deposition? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Coating
- What is the purpose of calcination? Transform and Purify Materials for Industrial Use




