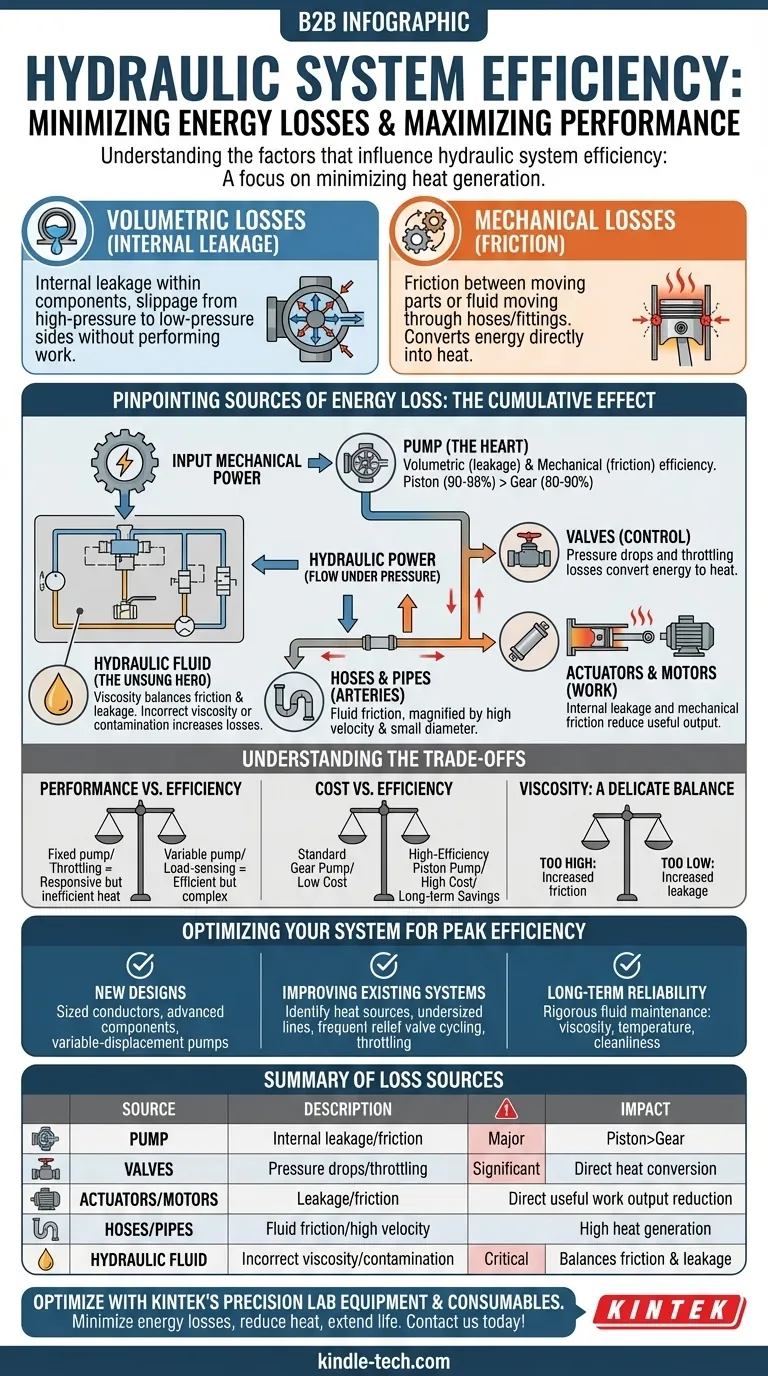
In short, the efficiency of a hydraulic system depends on how well it minimizes two fundamental types of energy loss: volumetric losses from internal leakage and mechanical losses from friction. These losses occur in every component, from the pump and motors to the valves and fluid, and are ultimately converted into wasted heat.
A hydraulic system's efficiency is not a single number but a measure of its ability to transmit power without converting it into heat. The core challenge is minimizing the friction, leakage, and unnecessary pressure drops inherent in every component.
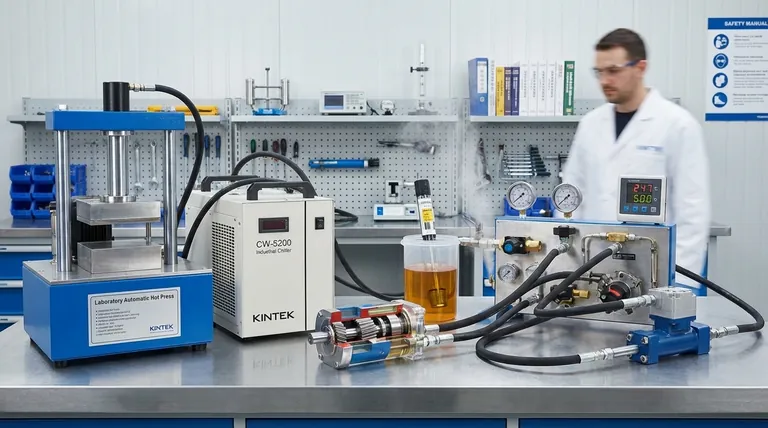

The Two Faces of Inefficiency
To understand efficiency, you must first understand how energy is lost. Every watt of power that doesn't contribute to useful work becomes heat, which reduces fluid viscosity and degrades system components over time.
Mechanical Losses: The Battle Against Friction
Mechanical losses occur when moving parts create friction or when the hydraulic fluid itself experiences friction moving through hoses and fittings.
This energy is directly converted into heat. Key sources include friction between pistons and cylinder walls, in the bearings of a pump or motor, and between the fluid and the inner walls of pipes and hoses.
Volumetric Losses: The Problem of Internal Leakage
Volumetric loss is the internal leakage of fluid within a component, such as a pump, motor, or cylinder.
This is fluid that slips from the high-pressure side to the low-pressure side without performing any useful work. While some internal leakage is necessary for lubrication, excessive leakage represents a significant loss of efficiency.
Pinpointing the Sources of Energy Loss
Efficiency isn't lost in one place; it's a cumulative effect across the entire system. Understanding where these losses occur is the first step toward optimization.
The Pump: The System's Heart
The pump's job is to convert mechanical power into hydraulic power (flow under pressure). It is often the single largest source of inefficiency.
Its overall efficiency is a product of its volumetric efficiency (how well it prevents internal leakage) and its mechanical efficiency (how well it overcomes internal friction). Piston pumps are typically the most efficient (90-98%), while gear pumps are less so (80-90%).
Actuators and Motors: Where Work Gets Done
Like pumps, hydraulic motors and cylinders suffer from both mechanical friction and internal leakage. The energy that is lost here fails to be converted into the final mechanical output (torque or force).
Valves: The Necessary Evil of Control
Valves control the direction, pressure, and flow of the fluid, but they are a major source of inefficiency.
Anytime fluid passes through a valve, it experiences a pressure drop, which is a direct energy loss. Throttling—using a valve to intentionally restrict flow to control speed—is particularly inefficient, converting large amounts of energy directly into heat.
Hoses and Pipes: The System's Arteries
Fluid moving through hoses and pipes loses energy due to friction. This loss is magnified by high fluid velocity.
Using conductors that are too small for the required flow rate is a common design error. This forces high fluid velocities, which dramatically increases friction losses and generates significant heat.
The Hydraulic Fluid: The Unsung Hero
The fluid itself is a critical component. Its viscosity—its resistance to flow—is the single most important property affecting system efficiency.
An incorrect viscosity for the system's operating temperature leads to significant losses. Fluid contamination also accelerates wear on components, which in turn increases internal leakage and friction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Designing an efficient system requires balancing competing factors. There is no single "best" solution for every application.
Performance vs. Efficiency
The most responsive control is often the least efficient. For example, using a simple fixed-displacement pump with relief and flow control valves provides good control but is highly inefficient, as excess flow is constantly dumped back to the tank as heat.
A more complex load-sensing or pressure-compensated system is far more efficient but adds cost and complexity.
Cost vs. Efficiency
Higher efficiency components almost always come with a higher initial cost. A high-efficiency piston pump costs significantly more than a standard gear pump.
The decision must be based on the application's duty cycle. For a system that runs continuously, the long-term energy savings from a more efficient pump can easily justify the initial investment.
Viscosity: A Delicate Balance
Choosing the right fluid viscosity is a critical trade-off.
- Too high (too thick): Increases friction losses as the pump struggles to move the fluid through the system.
- Too low (too thin): Increases volumetric losses as the fluid more easily leaks past internal seals in pumps and actuators.
Optimizing Your System for Peak Efficiency
Your approach to improving efficiency depends entirely on your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is designing a new high-performance system: Prioritize correctly sized conductors and advanced components like variable-displacement, load-sensing pumps to ensure you only generate the flow and pressure the system actually needs.
- If your primary focus is improving an existing system: Identify the largest sources of heat, as this points directly to the biggest inefficiencies—often an undersized line, a frequently cycling relief valve, or throttling controls.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability and cost-effectiveness: Implement a rigorous fluid maintenance program. Ensuring proper fluid viscosity, temperature, and cleanliness is the foundation of sustained hydraulic efficiency.
Ultimately, a highly efficient hydraulic system is one where every component is correctly chosen and sized to minimize the conversion of useful work into wasted heat.
Summary Table:
| Source of Loss | Description | Impact on Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Pump | Converts mechanical to hydraulic power; internal leakage and friction cause losses. | Major impact; piston pumps (90-98%) are more efficient than gear pumps (80-90%). |
| Valves | Control flow and pressure but cause pressure drops and throttling losses. | Significant; throttling converts energy directly into heat. |
| Actuators/Motors | Convert hydraulic power to mechanical work; internal leakage and friction reduce output. | Directly affects useful work output. |
| Hoses/Pipes | Fluid friction increases with high velocity in undersized conductors. | High friction losses generate heat and reduce efficiency. |
| Hydraulic Fluid | Incorrect viscosity (too thick or thin) or contamination increases losses. | Critical; proper viscosity balances friction and leakage losses. |
Optimize your hydraulic system's efficiency with KINTEK's precision lab equipment and consumables. Whether you're designing a new system or maintaining an existing one, our solutions help minimize energy losses, reduce heat generation, and extend component life. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's hydraulic performance and reliability needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 80L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Water Bath Cooling and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between a power press and a power hammer? Choose the Right Forging Method for Your Metal
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press reduce interface impedance in solid-state batteries? Achieve Peak Ion Conductivity
- Can a hydraulic press press anything? Understanding the Real Limits of Its Power
- What are the advantages of metal pressing? Unlock High-Speed, Low-Cost Mass Production
- What role does a laboratory uniaxial hydraulic press play in LATP green body preparation? Essential Forming Guide
- Where is compression moulding used? For High-Strength Parts in Automotive, Aerospace & Electrical
- What material can withstand a hydraulic press? Understanding Compressive Strength vs. Pressure
- What is the difference between injection molding and pressure molding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Process













