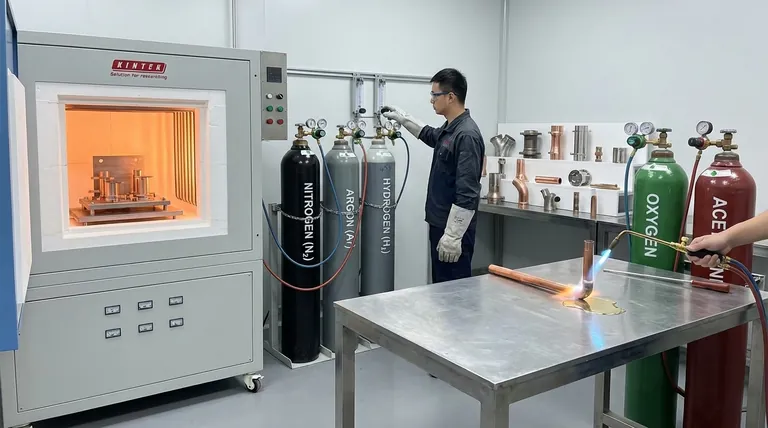
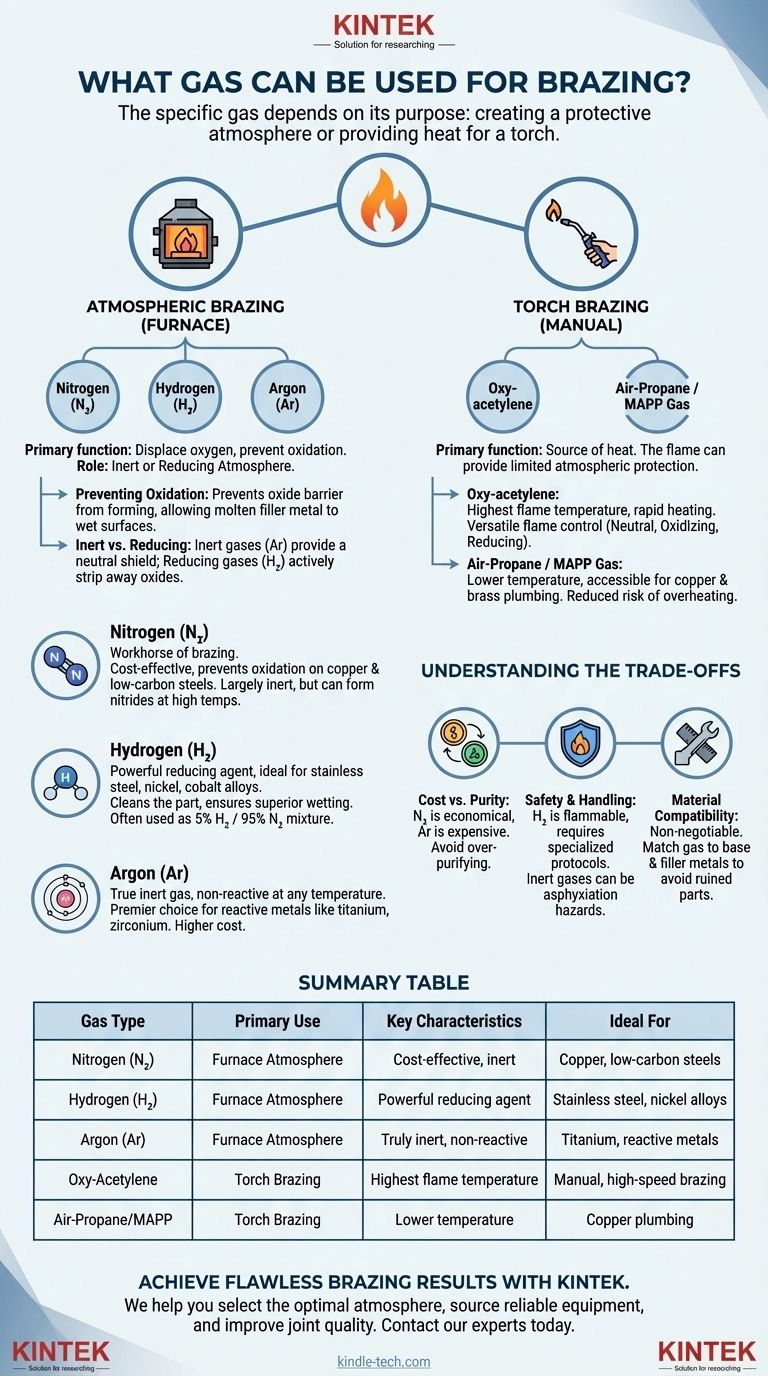
The specific gas used for brazing depends entirely on its purpose: creating a protective atmosphere or providing heat for a torch. For atmospheric brazing in a furnace, the most common gases are Nitrogen, Argon, and Hydrogen, often in mixtures. For torch brazing, fuel gas combinations like oxy-acetylene, air-propane, or air-MAPP are used to generate the flame.
The most critical insight is that gas in brazing is not merely a fuel source, but an active component of the metallurgical process. The right atmospheric gas prevents catastrophic oxidation and ensures the filler metal can bond properly with the base materials, creating a strong, clean joint.

The Role of Gas: Creating the Right Atmosphere
The primary function of an atmospheric gas in furnace brazing is to displace oxygen and other reactive elements from the high-temperature environment. Failure to do so results in a failed braze joint.
Preventing Oxidation
When metals are heated to brazing temperatures, their surfaces react rapidly with oxygen in the air. This forms a layer of oxides, which acts as a barrier.
This oxide barrier prevents the molten filler metal from "wetting" the surfaces of the parts you are trying to join, leading to a weak or non-existent bond. A controlled atmosphere of a specific gas prevents this from ever happening.
Inert vs. Reducing Atmospheres
Brazing atmospheres fall into two main categories:
Inert atmospheres, like those using Argon, simply provide a neutral shield. They displace oxygen but do not react with the metal surfaces.
Reducing atmospheres, which contain Hydrogen, go a step further. They not only displace oxygen but can also actively strip away light surface oxides that may have been present on the parts before they entered the furnace.
Common Atmospheric Gases Explained
Choosing the correct atmospheric gas is a function of the base metals being joined, the filler metal, and cost considerations.
Nitrogen (N₂)
Nitrogen is the workhorse of brazing atmospheres. It is relatively inexpensive and effective at preventing oxidation on common materials like copper and low-carbon steels.
It is considered largely inert but can react with certain metals at high temperatures, such as titanium and some stainless steels, forming brittle nitrides.
Hydrogen (H₂)
Hydrogen is a powerful reducing agent, making it ideal for materials that form stubborn oxides, like stainless steel, nickel, and cobalt alloys. Its ability to "clean" the part in-process ensures superior wetting.
Pure hydrogen provides the strongest reducing potential but is highly flammable and requires stringent safety protocols. More commonly, it is used in a non-flammable mixture with nitrogen, such as 5% Hydrogen / 95% Nitrogen.
Argon (Ar)
Argon is a true inert gas, meaning it will not react with any metal at any temperature. This makes it the premier choice for highly reactive metals like titanium, zirconium, and magnesium.
Its high purity and complete inertness come at a significantly higher cost than nitrogen, so its use is typically reserved for specialized, high-value applications.
Fuel Gases for Torch Brazing
When brazing manually with a torch, the gas mixture is the source of heat. The flame itself can also provide a limited amount of atmospheric protection.
Oxy-acetylene
This combination produces the highest flame temperature, offering rapid heating and immense versatility. An experienced operator can adjust the torch to create a neutral flame (ideal for most work), a slightly oxidizing flame, or a reducing (carburizing) flame.
Air-Propane and MAPP Gas
These are common, accessible options for lower-temperature brazing, particularly for copper and brass plumbing applications. The flame temperature is lower than oxy-acetylene, which can be an advantage as it reduces the risk of overheating the parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a gas is never just about performance; it involves balancing cost, safety, and material compatibility.
Cost vs. Required Purity
Nitrogen is by far the most economical choice for an atmospheric gas. Argon is the most expensive. The cost of a hydrogen-nitrogen mix falls in between. Using a gas that is more pure or powerful than necessary is a waste of money.
Safety and Handling
Hydrogen is highly flammable and explosive under certain conditions. Facilities using hydrogen require specialized ventilation, leak detection, and safety protocols. Inert gases like Nitrogen and Argon are asphyxiation hazards in confined spaces.
Material Compatibility Is Non-Negotiable
This is the most critical factor. Using nitrogen with titanium will ruin the part. Using a simple air-propane torch on stainless steel will likely result in a heavily oxidized, failed joint. Always match the gas to the specific metallurgical requirements of the base and filler metals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of gas should be driven by the materials you are joining and the process you are using.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective brazing of copper or carbon steel: Use nitrogen for furnace brazing or an air-propane torch for manual work.
- If your primary focus is brazing stainless steel or other high-alloy metals: Use a hydrogen-nitrogen atmosphere to ensure a clean, oxide-free surface for strong bonding.
- If your primary focus is brazing highly reactive metals like titanium: Use high-purity argon as it is the only way to guarantee a completely non-reactive environment.
- If your primary focus is versatile, high-speed manual brazing: Use an oxy-acetylene torch and master the control of a neutral flame.
Choosing the correct gas transforms it from a simple consumable into a critical tool for metallurgical success.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Primary Use | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Furnace Atmosphere | Cost-effective, inert for many metals | Copper, low-carbon steels |
| Hydrogen (H₂) | Furnace Atmosphere | Powerful reducing agent, cleans surfaces | Stainless steel, nickel alloys |
| Argon (Ar) | Furnace Atmosphere | Truly inert, non-reactive at any temperature | Titanium, zirconium, reactive metals |
| Oxy-Acetylene | Torch Brazing | Highest flame temperature, versatile | Manual, high-speed brazing |
| Air-Propane/MAPP | Torch Brazing | Lower temperature, accessible | Copper plumbing, lower-risk applications |
Achieve Flawless Brazing Results with KINTEK
Selecting the right brazing gas is critical for preventing oxidation and creating strong, clean joints. The wrong choice can lead to catastrophic failure. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and expert guidance you need to master your brazing process.
We help you:
- Select the optimal atmosphere for your specific base and filler metals.
- Source reliable gas mixtures and equipment for both furnace and torch brazing.
- Improve joint quality and production efficiency with proven metallurgical solutions.
Don't let gas selection compromise your project. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and ensure metallurgical success.
Contact KINTEK for a Consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the use of electric muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between a furnace and an oven in a laboratory? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Heat Needs
- What is the use of furnace in laboratory? Unlock Material Transformation for Your Research
- What is the use of high temperature muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- What are the disadvantages of dry ashing? Key Limitations for Accurate Elemental Analysis

















