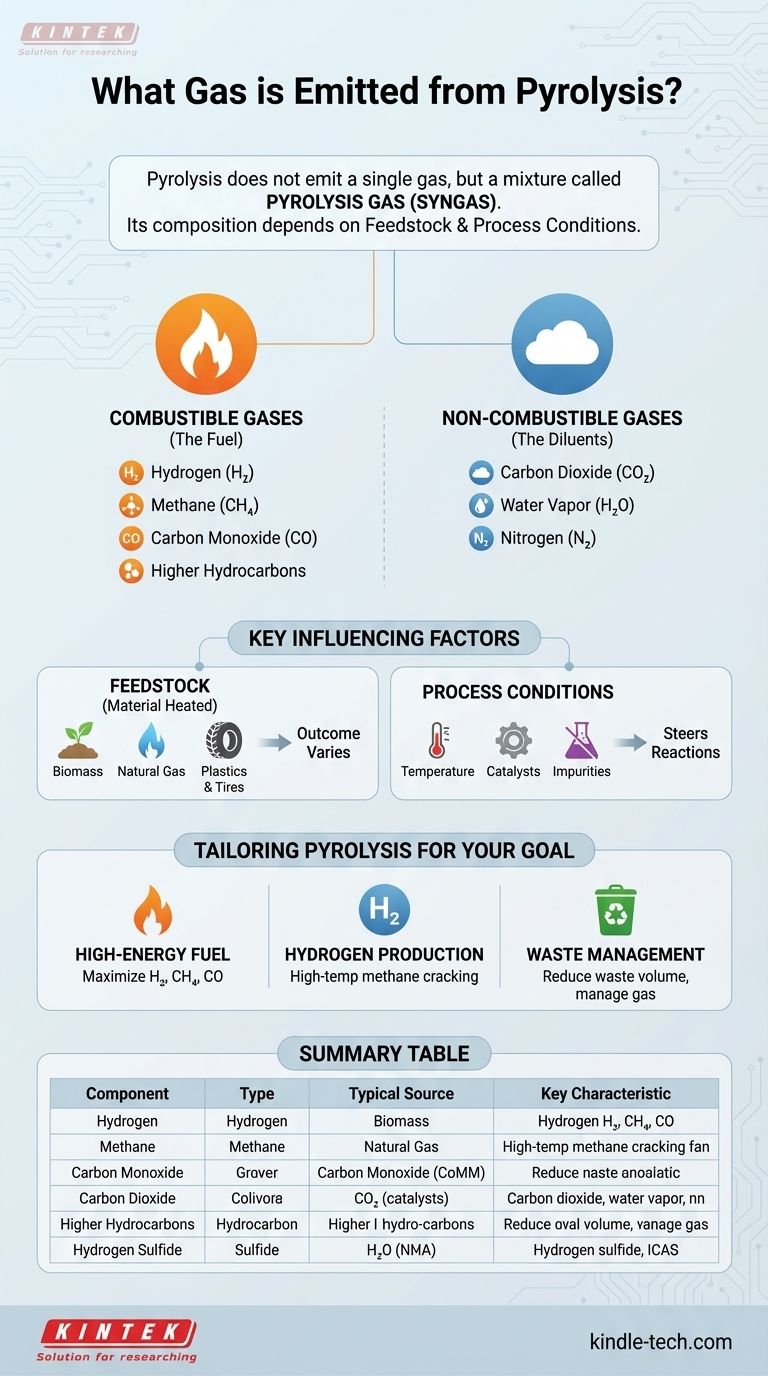
In short, pyrolysis does not emit a single gas but rather a mixture of gases, often called pyrolysis gas or syngas. The primary components are typically hydrogen (H₂), methane (CH₄), carbon monoxide (CO), and carbon dioxide (CO₂), along with other hydrocarbons and trace compounds.
The specific composition of the gas produced by pyrolysis is not fixed. It is entirely dependent on two critical factors: the material being heated (the feedstock) and the precise process conditions, such as temperature and pressure.

The Core Components of Pyrolysis Gas
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an inert atmosphere. The process breaks down complex organic matter into solid char, liquid bio-oil, and a gas mixture. This gas can be broadly divided into combustible and non-combustible components.
The Combustible Gases (The Fuel)
The value of pyrolysis gas comes from its combustible components, which store chemical energy. The main ones include:
- Hydrogen (H₂): A very clean-burning, high-energy fuel.
- Methane (CH₄): The primary component of natural gas.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): Can be combusted to release energy.
- Higher Hydrocarbons: Ethane, propane, and others may be present in smaller amounts.
The Non-Combustible Gases (The Diluents)
These gases are also produced but do not contribute to the fuel value of the syngas. Their presence can dilute the energy content of the mixture.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): A common byproduct of the decomposition of organic matter.
- Water Vapor (H₂O): Released from moisture in the feedstock.
- Nitrogen (N₂): Often present if the feedstock contains nitrogen or if the process is not perfectly air-free.
Why Feedstock Determines the Outcome
The most significant factor influencing the output gas is the chemical makeup of the starting material. Different feedstocks will invariably produce different gas mixtures, even under identical conditions.
Pyrolysis of Biomass
When pyrolyzing organic matter like wood, agricultural waste, or manure, the gas composition varies widely. The specific type of biomass and the process conditions are adjusted to achieve a desired outcome, such as a gas with high heating value or one with low pollutant precursors like sulfur oxides (SOx).
Pyrolysis of Natural Gas
Even within a single feedstock category, small differences matter. For example, pyrolyzing pure methane is a controlled process aimed at producing hydrogen gas and solid carbon. However, pyrolyzing natural gas is more complex because it contains impurities like CO₂, water, and sulfur compounds. These impurities react during pyrolysis and alter the final gas composition, conversion rates, and even the lifespan of the equipment.
Pyrolysis of Plastics and Tires
Pyrolyzing plastics or tires will yield a completely different gas profile rich in complex hydrocarbons derived from the polymer chains. The goal here is often to recover valuable chemical building blocks or produce a fuel oil, with the gas being a secondary product.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Process Conditions
Beyond the feedstock, engineers manipulate process conditions to "steer" the chemical reactions toward a desired output. This is where pyrolysis moves from a simple process to a highly technical one.
The Critical Role of Temperature
Temperature is the primary lever for controlling the gas mixture. Lower temperatures (400-600°C) tend to favor the production of liquid bio-oil and char, while higher temperatures (>700°C) "crack" the larger molecules into smaller, simpler gas molecules like hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
The Impact of Catalysts
Catalysts can be introduced into the reactor to promote specific chemical reactions. This enhances the selectivity of the process, meaning it can be guided to produce more of a specific desired gas (like hydrogen) while minimizing others.
The Problem of Impurities
As noted with natural gas, impurities are not passive. They actively participate in reactions. Sulfur in the feedstock can lead to hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) in the output gas, a corrosive and toxic compound. These undesirable reactions can foul equipment and deactivate expensive catalysts, making feedstock purity a major operational concern.
Tailoring Pyrolysis for Your Goal
The gas emitted from pyrolysis is a direct result of deliberate choices about feedstock and process design. Understanding your primary objective is key to interpreting the results.
- If your primary focus is high-energy fuel production: Your goal is to maximize combustible gases (H₂, CH₄, CO) by selecting a suitable feedstock and optimizing temperature to favor gas formation over liquids or solids.
- If your primary focus is hydrogen production: You would likely use methane pyrolysis at very high temperatures, a process specifically designed to split methane into pure hydrogen gas and solid carbon.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Your main goal is reducing the volume of waste (like plastics or tires), and the gas produced is a co-product that must be managed, cleaned, and ideally used to power the process itself.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is a versatile chemical conversion tool, and the resulting gas is a direct reflection of the specific problem it has been engineered to solve.
Summary Table:
| Component | Type | Typical Source | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H₂) | Combustible | High-temp pyrolysis, methane cracking | Clean-burning, high-energy fuel |
| Methane (CH₄) | Combustible | Decomposition of organic matter | Primary component of natural gas |
| Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Combustible | Incomplete combustion of carbon | Can be combusted for energy |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) | Non-combustible | Complete oxidation, feedstock impurity | Dilutes energy content |
| Higher Hydrocarbons | Combustible | Pyrolysis of plastics, tires | Ethane, propane, etc. |
| Hydrogen Sulfide (H₂S) | Impurity | Feedstock containing sulfur | Corrosive, toxic, requires removal |
Ready to Optimize Your Pyrolysis Process?
Whether your goal is maximizing fuel gas production, generating high-purity hydrogen, or managing waste streams, the right laboratory equipment is critical for research and quality control. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab reactors, furnaces, and analytical equipment tailored for pyrolysis research and development.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve precise control over your process conditions and analyze your syngas output effectively.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Desktop Fast High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 16L 24L for Lab Use
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Spacer Cam Profile and Various Spacer Types
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Beaker and Lids
- Lab Sterile Slapping Type Homogenizer for Tissue Mashing and Dispersing
People Also Ask
- What is the water content of pyrolysis oil? A Key Factor in Bio-Oil Quality and Use
- What is the main difference between gasification and pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Biomass Conversion Process
- What is the pyrolysis method for plastic waste? Convert Non-Recyclable Plastics into Fuel
- In which furnace is calcination and roasting done? A Guide to Selecting the Right Thermal Processing Equipment
- What is the purpose of plastic pyrolysis? Convert Waste Plastic into Valuable Resources
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- How is biomass converted into biofuels? Unlock the Path from Plant Matter to Renewable Fuel
- What is the mechanism of pyrolysis decomposition? A Guide to Converting Waste into Valuable Products



















