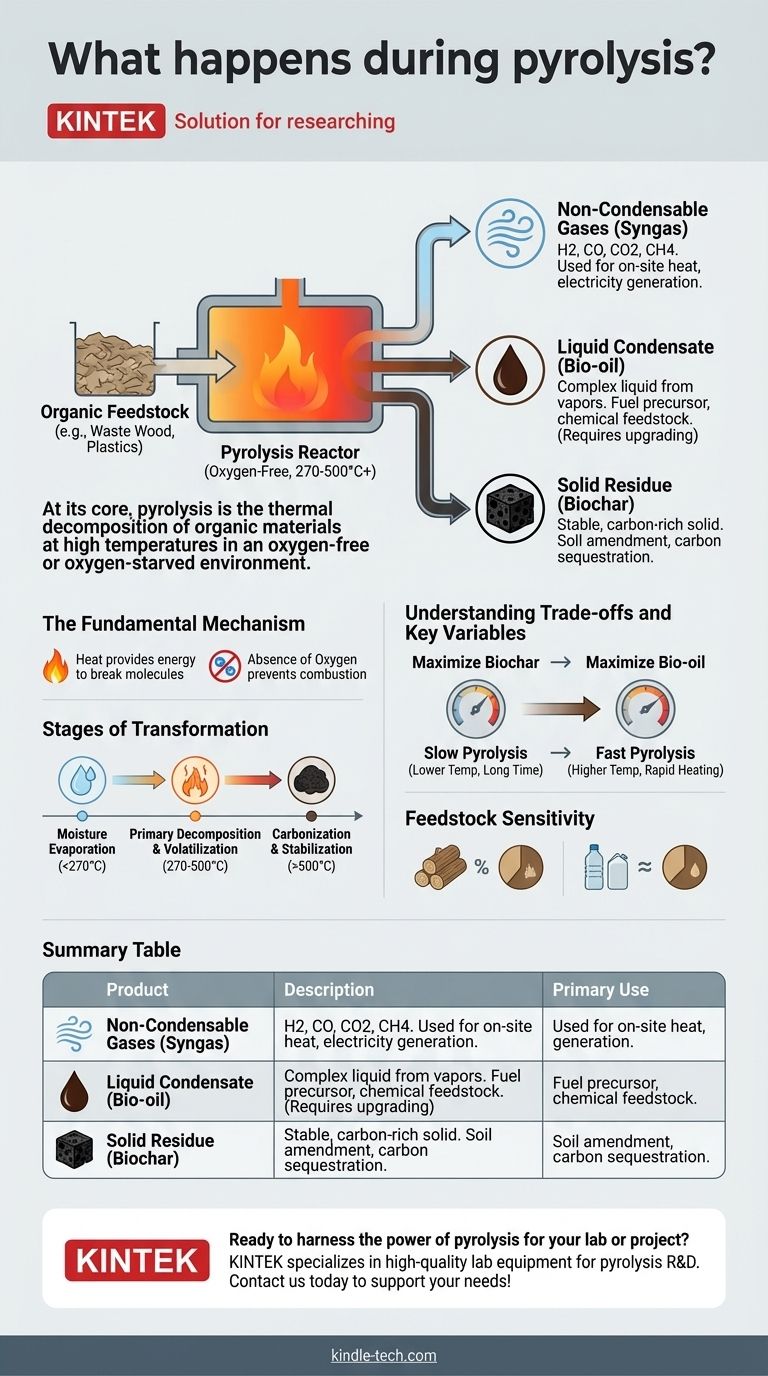
At its core, pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of organic materials at high temperatures in an oxygen-free or oxygen-starved environment. Instead of combusting (burning) and turning to ash, the intense heat breaks down the material's chemical structure, transforming it into a mixture of solid, liquid, and gaseous products. This process effectively unlocks the chemical energy and constituent parts of the original substance.
Pyrolysis should not be viewed as simple disposal, but as a chemical conversion platform. It transforms low-value organic matter—like waste wood, agricultural residue, or plastics—into valuable, stable outputs by rearranging its molecular structure without burning it.

The Fundamental Mechanism: How Decomposition Occurs
Pyrolysis is a carefully controlled process driven by heat in a specific atmosphere. Understanding the interplay of these factors is key to understanding its power.
The Critical Role of Heat and Oxygen Deprivation
Heat provides the energy required to shatter the complex, long-chain molecules (polymers) that make up organic materials like wood or plastic.
The crucial element is the absence of oxygen. If oxygen were present, the material would simply burn, a process called combustion, releasing its energy as heat and light and leaving behind mostly ash.
By removing oxygen, we prevent combustion and force the material to decompose into a range of new, often smaller and more stable molecules.
The Stages of Transformation
The process generally unfolds in predictable stages.
First, any residual moisture within the feedstock is boiled off at relatively low temperatures.
As the temperature climbs, typically above 270-300°C (518-572°F), the primary chemical bonds within the material begin to break. This is the main pyrolysis reaction, where volatile compounds are released as gases and the solid structure begins to carbonize.
The Three Primary Products of Pyrolysis
The output of pyrolysis is not a single substance but a portfolio of products. The exact ratio depends heavily on the input material and process conditions.
Solid Residue (Biochar)
This is the stable, carbon-rich solid that remains after the volatile components have been driven off. When derived from biomass like wood, it is called charcoal or biochar.
Biochar is highly porous and resistant to decomposition, making it valuable for carbon sequestration and as a soil amendment to improve water retention and nutrient availability.
Liquid Condensate (Bio-oil)
The hot gases and vapors released during decomposition can be rapidly cooled and condensed into a dark, viscous liquid known as pyrolysis oil or bio-oil.
This liquid is a complex blend of water, organic acids, alcohols, and other compounds. It can be a source for specialty chemicals or, with significant upgrading, a precursor to renewable liquid fuels.
Non-Condensable Gases (Syngas)
Not all of the gaseous products will condense into a liquid. The remaining gases are collectively known as syngas (synthesis gas).
Syngas is a combustible mixture primarily composed of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and methane. It can be burned on-site to provide the heat needed to sustain the pyrolysis reaction or to generate electricity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Variables
Achieving a desired outcome with pyrolysis requires precise control over its core variables. The process is not a one-size-fits-all solution.
The Influence of Temperature and Speed
The final product yields are highly sensitive to temperature and heating rate.
Slow pyrolysis involves lower temperatures (around 400°C) and long residence times. This process maximizes the production of solid biochar.
Fast pyrolysis uses higher temperatures (around 500°C) and extremely rapid heating. This method is optimized to break down the material quickly and maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil.
Feedstock Sensitivity
The composition of the input material, or feedstock, has a profound impact on the results.
Woody biomass, rich in cellulose and lignin, produces a balanced mix of the three products. Plastics, on the other hand, can yield high quantities of oil and syngas. The characteristics of the products are directly tied to the chemistry of the feedstock.
The Challenge of Bio-oil Upgrading
While promising, raw bio-oil is not a drop-in replacement for petroleum fuels. It is typically acidic, corrosive, and chemically unstable.
Significant and often costly post-processing, known as upgrading, is required to improve its properties for use in conventional engines or refineries. This remains a major area of research and development.
How to Apply This to Your Project
The optimal pyrolysis strategy is dictated entirely by your end goal. The process can be tuned to favor one output over another.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration or soil improvement: Slow, lower-temperature pyrolysis is the correct path to maximize the yield of stable, high-carbon biochar.
- If your primary focus is producing advanced biofuels: Fast pyrolysis at controlled, high temperatures is necessary to maximize the generation of liquid bio-oil for subsequent upgrading.
- If your primary focus is waste-to-energy: A simpler pyrolysis system designed to combust the resulting syngas and bio-oil can effectively convert waste streams into valuable heat and power.
By understanding these fundamentals, you can move from simply managing a material to strategically creating value from it.
Summary Table:
| Product | Description | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar (Solid) | Stable, carbon-rich solid residue | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration |
| Bio-oil (Liquid) | Condensed liquid from vapors | Fuel precursor, chemical feedstock |
| Syngas (Gas) | Non-condensable combustible gases | On-site heat, electricity generation |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis for your lab or project? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're optimizing biochar production, analyzing bio-oil, or scaling up syngas applications, our solutions ensure precision and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory needs and help you create value from organic materials!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success



















