In short, a crucible is a high-temperature container used to melt materials like metals, alloys, and glass. It is specifically designed to withstand extreme heat without melting, breaking, or reacting with the substance it holds. The crucible is the core component inside a crucible furnace, which provides the necessary heat.
The central purpose of a crucible is to act as a clean, stable, and heat-resistant vessel. It allows you to safely transform a solid material into a liquid state at very high temperatures, so it can then be poured and cast into a new shape.

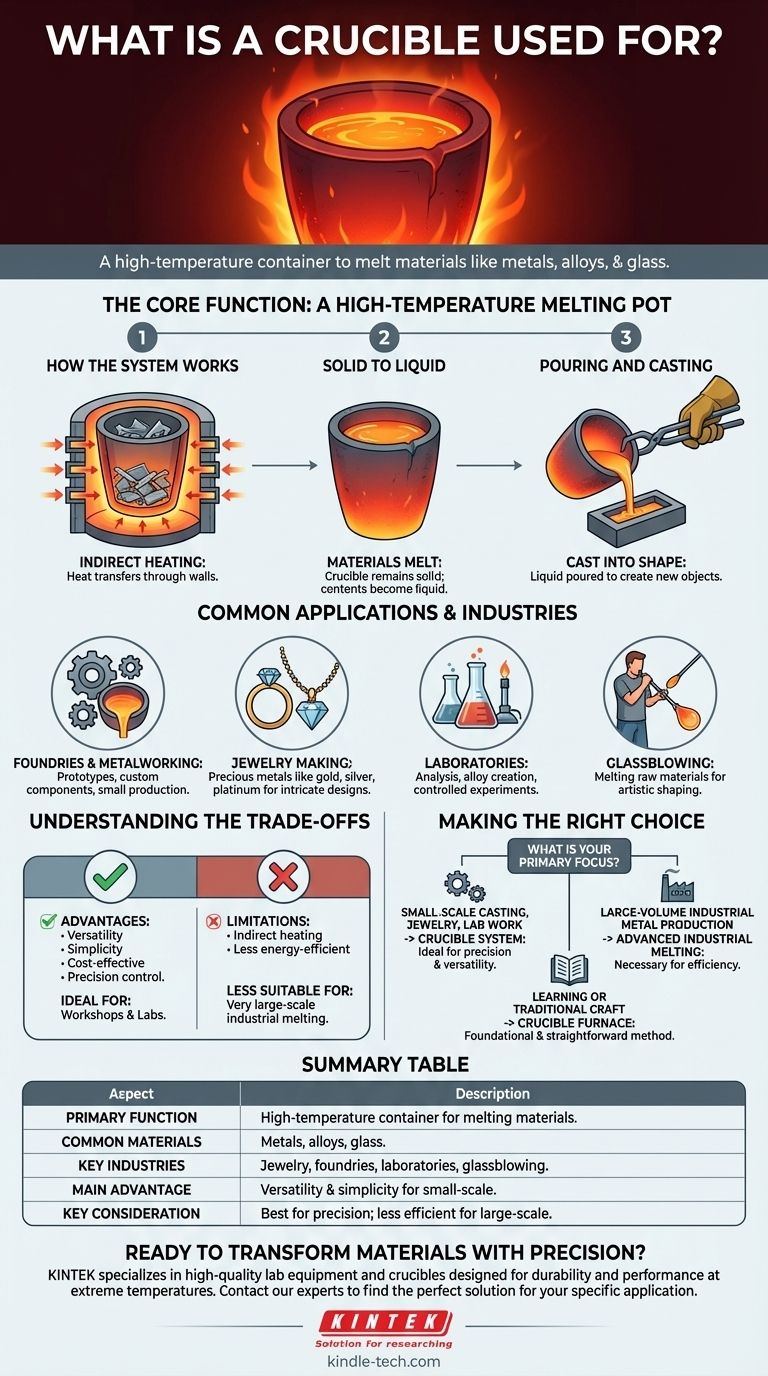
The Core Function: A High-Temperature Melting Pot
A crucible does not generate heat itself. It serves as the container for the material you intend to melt, which is then placed inside a furnace for heating.
How the System Works
A crucible is part of a simple but effective system. The material, such as metal scrap, is placed inside the crucible. The crucible is then set inside a furnace, and heat is applied to the exterior of the crucible wall from burners or electric heating elements.
The Goal: From Solid to Liquid
Heat transfers through the crucible’s walls, raising the temperature of the contents until they reach their melting point. Because the crucible is made from materials like graphite, clay, or silicon carbide, it remains solid long after its contents have turned to liquid.
The Final Step: Pouring and Casting
Once the material is fully molten, the crucible is removed from the furnace. The liquid material is then carefully poured into a mold, a process known as casting, to create the desired object, whether it's a piece of jewelry or an industrial part.
Common Applications and Industries
The simplicity and versatility of crucibles make them essential tools across several fields, particularly for smaller-scale operations.
Foundries and Metalworking
Crucible furnaces are a staple in small foundries for casting metal parts. They are ideal for creating prototypes, custom components, and small production runs.
Jewelry Making
Artisans use crucibles to melt precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum. This allows them to cast intricate designs for rings, pendants, and other custom pieces.
Laboratories
In scientific and material research labs, crucibles are used to melt substances for analysis, create new alloys, or conduct experiments that require extreme heat in a controlled environment.
Glassblowing
Crucibles are also used in glassblowing studios to melt the raw materials—sand, soda ash, and limestone—that form molten glass, which is then shaped by the artist.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the crucible system has clear advantages and limitations that define its best use cases.
Key Advantage: Versatility and Simplicity
Crucible furnaces are relatively cost-effective, easy to operate, and compact. Their main strength is the ability to melt a wide variety of different materials with precise temperature control, making them perfect for workshops and labs.
Key Limitation: Indirect Heating and Scale
Because heat is applied from the outside, the process can be less energy-efficient than other furnace types where the heat is generated within the material itself. This makes crucible furnaces less suitable for very large-scale industrial melting, where efficiency is paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the role of a crucible helps you determine if it's the right tool for your specific high-temperature task.
- If your primary focus is small-scale casting, jewelry making, or lab work: The precision, versatility, and cost-effectiveness of a crucible and furnace system make it the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is large-volume industrial metal production: The indirect heating of a crucible furnace is likely too inefficient, and more advanced industrial melting technologies are necessary.
- If your primary focus is learning or traditional craft: The crucible furnace is the oldest type of melting furnace, offering a foundational and straightforward method for working with molten materials.
Ultimately, the crucible is the fundamental tool that enables the controlled transformation of solid materials through the power of intense heat.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | High-temperature container for melting materials. |
| Common Materials Melted | Metals, alloys, glass. |
| Key Industries | Jewelry making, foundries, laboratories, glassblowing. |
| Main Advantage | Versatility and simplicity for small-scale operations. |
| Key Consideration | Best for precision tasks; less efficient for large-scale industrial use. |
Ready to transform materials with precision? Whether you're in a lab, a jewelry studio, or a small foundry, having the right crucible is crucial for successful melting and casting. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including crucibles designed for durability and performance at extreme temperatures. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your specific application and ensure superior results in your high-temperature processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
People Also Ask
- What role does an Alumina Crucible play in the high-temperature solid-state synthesis of Na3OBr? Ensure Sample Purity
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for LATP? Preserve Purity and Conductivity in Sintering
- Why is a high-purity alumina crucible preferred for high-temperature oxidation? Ensure Unmatched Data Integrity
- What are the advantages of selecting an alumina crucible for TGA? Ensure High-Precision Thermal Analysis Data
- What are the functional advantages of using high-purity alumina crucibles? Achieve Precise Oxidation Data



















