In the simplest terms, a laboratory furnace is a high-temperature oven used to fundamentally alter the physical or chemical properties of a material. Its applications range from simple drying and baking to complex processes like sintering ceramics, heat-treating metals, and preparing samples for chemical analysis.
A laboratory furnace is not merely a heater; it is a precision instrument designed for controlled material transformation. It enables scientists and engineers to create new materials, improve the properties of existing ones, and isolate components for analysis under precise high-temperature conditions.

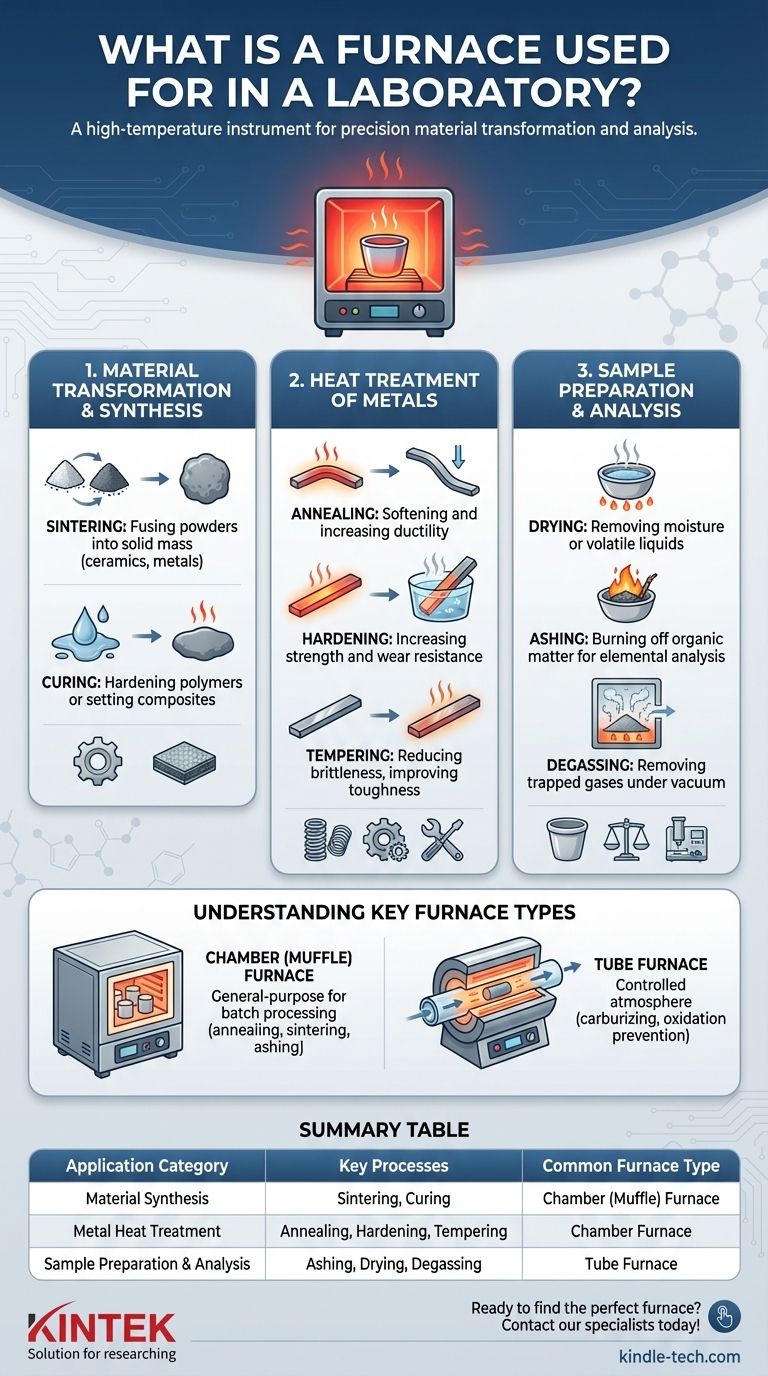
Core Functions of a Laboratory Furnace
A furnace's primary role is to apply a specific amount of heat for a specific amount of time, often within a controlled atmosphere, to achieve a desired change in a sample. These functions can be grouped into three main categories.
Material Transformation and Synthesis
This is where furnaces are used to create or fundamentally change materials.
Sintering is a key process that uses heat to fuse particles of powder together, forming a solid mass without melting it. This is essential for producing technical ceramics and in powder metallurgy.
Curing involves heating to induce a physical or chemical change, such as hardening a polymer or setting a composite material.
Heat Treatment of Metals
Furnaces are critical in metallurgy for enhancing the properties of metals and alloys.
Annealing is a process of heating and slow cooling to make a metal softer and more ductile, which makes it easier to work with.
Hardening involves heating a metal and then cooling it rapidly (quenching) to increase its strength and wear resistance.
Tempering is a subsequent, lower-temperature heating process used after hardening to reduce brittleness and improve toughness.
Sample Preparation and Analysis
In analytical chemistry, furnaces prepare samples for further testing.
Drying simply removes moisture or other volatile liquids from a sample by heating it.
Ashing or combustion is the process of burning off all organic matter in a sample at a high temperature. This leaves behind only the inorganic residue (ash), which can then be analyzed for its elemental composition.
Degassing uses heat, often under a vacuum, to remove trapped gases from a material, which is crucial for high-purity applications.
Understanding Key Furnace Types
While all furnaces heat things, their design is tailored to specific applications. The two most common laboratory types are chamber and tube furnaces.
Chamber Furnaces
Also known as muffle furnaces, these are general-purpose units with a box-like insulated chamber. They are ideal for processing batches of samples, such as annealing metal parts, sintering ceramic tiles, or ashing multiple samples at once.
Tube Furnaces
These furnaces feature a cylindrical chamber (a tube, often made of ceramic or quartz) through which samples are passed or placed. Their primary advantage is the ability to maintain a highly controlled or modified atmosphere by flowing specific gases (like nitrogen or argon) through the tube. This is critical for processes like carburizing (adding carbon to steel) or preventing oxidation during high-temperature treatments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your objective determines which furnace process you will use.
- If your primary focus is improving metal properties: You will use heat treatments like annealing to soften it, quenching to harden it, or tempering to toughen it.
- If your primary focus is creating a solid object from a powder: You will use sintering for ceramics or metals to fuse the particles together into a dense part.
- If your primary focus is preparing a sample for chemical analysis: You will use ashing to burn away organic material or drying to remove moisture before weighing or testing.
Ultimately, the laboratory furnace is an indispensable tool that enables precise control over the building blocks of matter.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Processes | Common Furnace Type |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis | Sintering, Curing | Chamber (Muffle) Furnace |
| Metal Heat Treatment | Annealing, Hardening, Tempering | Chamber Furnace |
| Sample Preparation & Analysis | Ashing, Drying, Degassing | Tube Furnace (for atmosphere control) |
Ready to find the perfect furnace for your lab's needs?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory furnaces and consumables, designed for precision sintering, heat treatment, and sample preparation. Whether you need a robust chamber furnace for batch processing or a versatile tube furnace for controlled atmosphere work, our experts can help you select the ideal equipment to enhance your research and development.
Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation and unlock the full potential of your materials!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role do muffle or tube furnaces play in Ni-Mn-Sn-In alloy processing? Achieve Precise Material Transformation
- How does a muffle furnace affect hematite nanoparticles? Control Morphology and Crystallinity During Calcination
- Where is a muffle furnace used? Essential for Clean, High-Temperature Processing
- What is a muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Controlled High-Temperature Heating
- How is a muffle furnace used for sample digestion? A Guide to Dry Ashing for Accurate Analysis
- What would a high ash content indicates? A Key Indicator of Material Composition and Quality
- What is the core role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in PEO-PTFE coatings? Master Sintering & Pore Infiltration
- What is the primary purpose of a muffle furnace in formaldehyde sensor prep? Engineering Metal Oxide Nanostructures



















