At its core, a PVD device is a sophisticated machine that performs Physical Vapor Deposition. This is a high-tech coating process conducted inside a vacuum chamber where a solid material is vaporized, transported, and then deposited as a thin, high-performance film onto the surface of a component.
A PVD device isn't just a machine; it's a tool for fundamentally re-engineering the surface properties of an object. It allows you to make a base material harder, more wear-resistant, or give it a premium decorative finish without altering its underlying structure.
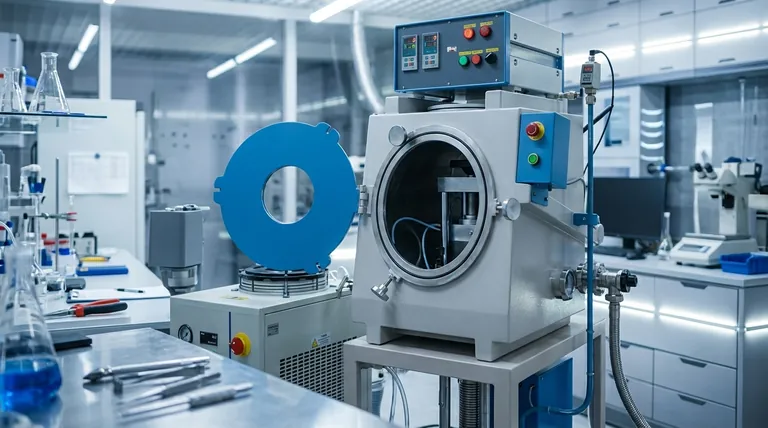

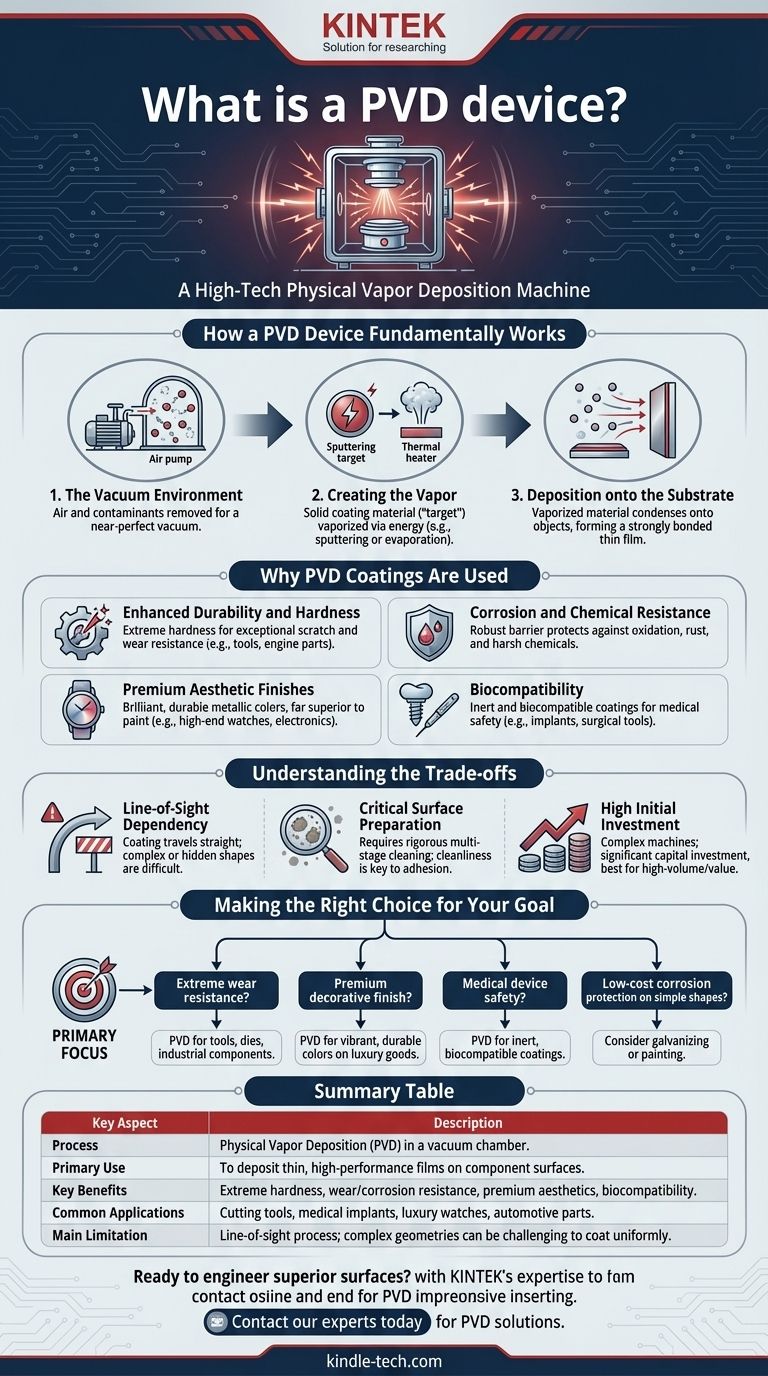
How a PVD Device Fundamentally Works
The name "Physical Vapor Deposition" perfectly describes the three essential stages of the process, all of which occur within the PVD device.
The Vacuum Environment
The entire process must happen in a near-perfect vacuum. This is critical for removing air and other contaminants that could react with the coating material or interfere with its path.
Creating the Vapor
A solid, high-purity coating material (known as the "target") is loaded into the device. Energy is then applied to this target to convert it into a vapor. This is typically done through processes like sputtering (bombarding the target with ions) or thermal evaporation (heating it until it vaporizes).
Deposition onto the Substrate
The vaporized material travels through the vacuum chamber and condenses onto the objects being coated (known as "substrates"). This forms an extremely thin, strongly bonded, and uniform film atom by atom.
Why PVD Coatings Are Used
The purpose of a PVD device is to impart beneficial properties to a substrate's surface that the base material lacks on its own.
Enhanced Durability and Hardness
PVD coatings can be extremely hard, often significantly harder than the underlying material. This provides exceptional resistance to scratches and wear, which is why it's used on cutting tools, engine components, and firearms.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
The deposited film acts as a robust barrier between the substrate and the environment. This protects the component from oxidation, rust, and damage from harsh chemicals.
Premium Aesthetic Finishes
PVD allows for the deposition of a wide array of brilliant, metallic colors that are far more durable than paint or powder coating. This is common on high-end watches, faucets, and consumer electronics.
Biocompatibility
Certain PVD coatings are inert and biocompatible, meaning they don't react with the human body. This makes them essential for coating medical implants and surgical tools to ensure patient safety.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the PVD process is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Line-of-Sight Dependency
The vaporized coating material travels in a straight line. This means that coating the inside of complex shapes or deep, hidden crevices can be extremely difficult or impossible without specialized fixtures.
Critical Surface Preparation
The success of PVD coating is highly dependent on the cleanliness of the substrate. Any oil, dust, or microscopic contaminant on the surface will prevent proper adhesion, leading to coating failure. This requires a rigorous multi-stage cleaning process.
High Initial Investment
PVD devices are complex, high-precision industrial machines that represent a significant capital investment. This generally makes the process more suitable for high-volume or high-value applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a coating process depends entirely on the desired outcome for your component.
- If your primary focus is extreme wear resistance: PVD is a leading choice for creating ultra-hard surfaces on tools, dies, and industrial components.
- If your primary focus is a premium decorative finish: The process offers a wide range of vibrant, durable colors ideal for luxury goods and architectural hardware.
- If your primary focus is medical device safety: PVD provides the inert, biocompatible coatings essential for implants and surgical instruments.
- If your primary focus is low-cost corrosion protection on simple shapes: A simpler process like galvanizing or painting might be a more cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, a PVD device provides a powerful method to engineer the surface of a material, fundamentally enhancing its performance, appearance, and value.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) in a vacuum chamber. |
| Primary Use | To deposit thin, high-performance films on component surfaces. |
| Key Benefits | Extreme hardness, wear/corrosion resistance, premium aesthetics, biocompatibility. |
| Common Applications | Cutting tools, medical implants, luxury watches, automotive parts. |
| Main Limitation | Line-of-sight process; complex geometries can be challenging to coat uniformly. |
Ready to engineer superior surfaces?
Whether your goal is extreme wear resistance for industrial tools, a brilliant decorative finish for consumer goods, or a biocompatible coating for medical devices, KINTEK's PVD expertise can help. We specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed to achieve precise, high-performance coatings.
Contact our experts today to discuss how PVD technology can enhance your products' performance, durability, and value.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is hot press lamination? The Ultimate Guide to Strong, Durable Material Bonding
- What is the advantage by using hot press forming? Achieve Stronger, More Complex Parts
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot pressing? Choose the Right Powder Metallurgy Process
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot stamping? Unlock Ultra-High Strength for Automotive Parts
- What is hot press moulding? Achieve Superior Density and Complex Shapes with Heat and Pressure



















