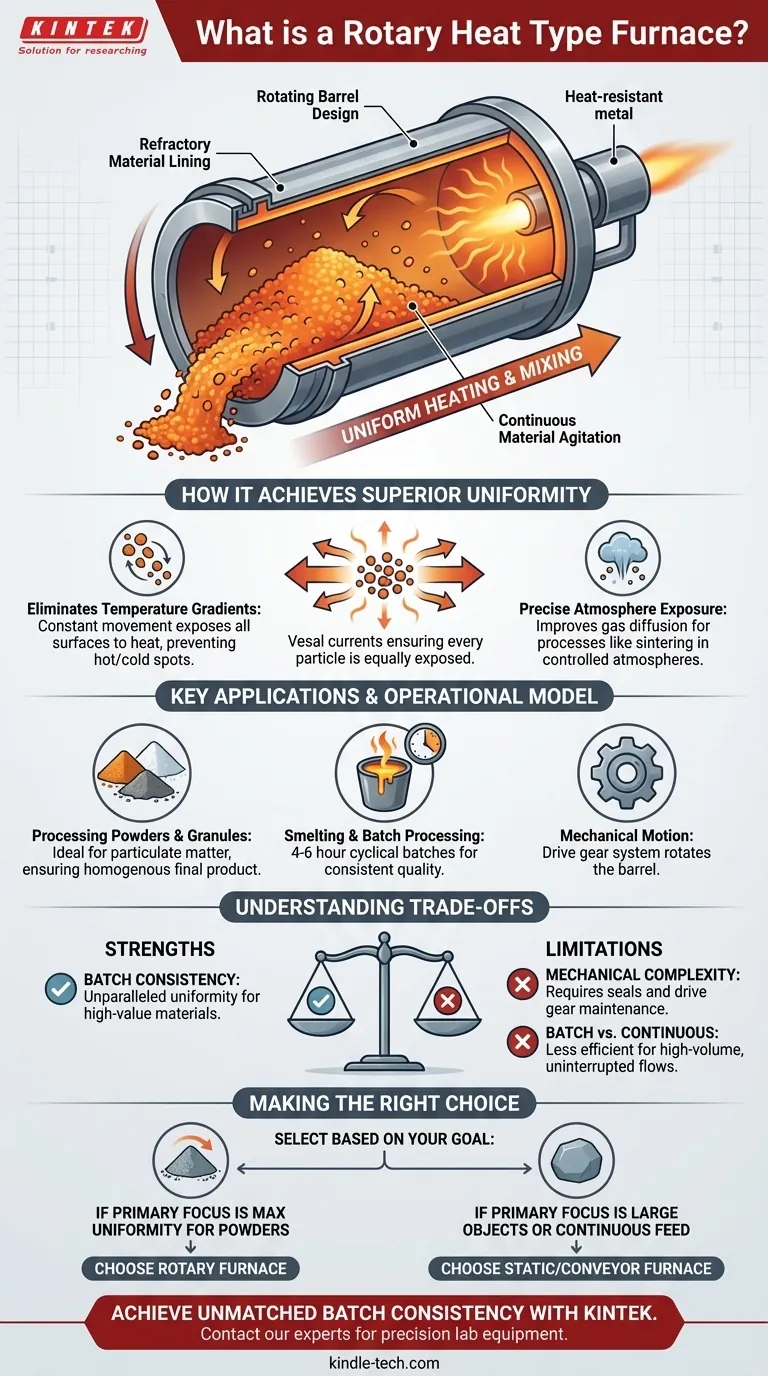
At its core, a rotary furnace is a cylindrical industrial furnace that rotates along its horizontal axis to simultaneously heat and mix the material inside. Unlike a static furnace where the material remains stationary, a rotary furnace's defining characteristic is its constant tumbling action, which ensures every particle is uniformly exposed to heat and the internal atmosphere.
The fundamental advantage of a rotary furnace is its ability to solve the problem of uneven heating. By continuously agitating the material, it eliminates hot and cold spots, leading to exceptionally consistent product quality, especially for powders, granules, and other particulate matter.
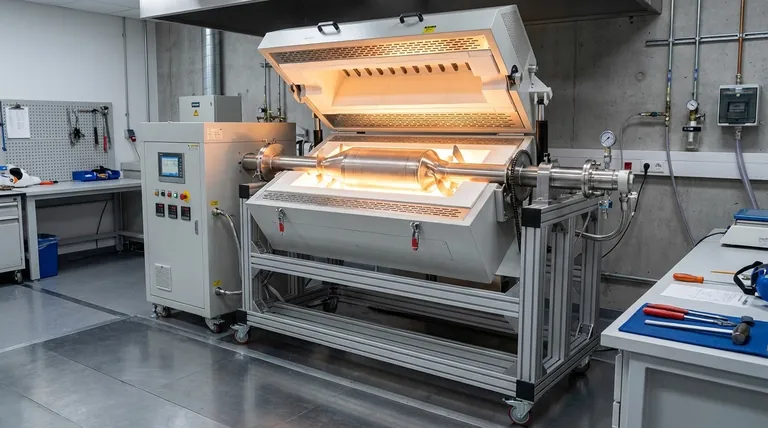

How a Rotary Furnace Achieves Superior Uniformity
The unique design of a rotary furnace is purpose-built to deliver highly uniform processing conditions. This is achieved through a combination of mechanical motion and precise environmental control.
The Rotating Barrel Design
A rotary furnace consists of a metal barrel, often installed at a slight angle, which is lined with a heat-resistant refractory material. This entire barrel is rotated by a drive gear system, causing the material, or "charge," loaded inside to tumble continuously.
Continuous Material Agitation
This tumbling motion is the key to the furnace's effectiveness. As the material cascades inside the rotating barrel, new surfaces are constantly exposed to the internal heat source. This eliminates temperature gradients that can form in static systems where the outer layers of a material can insulate the core.
Precise Atmosphere and Heat Exposure
The continuous movement also ensures the entire surface area of the charge is exposed to the furnace's atmosphere. This is critical for processes like high-temperature sintering in a reducing atmosphere, as it improves gas diffusion, reduces overall gas consumption, and increases the efficiency of the heat treatment. Heat is typically supplied by burners or nozzles that inject fuel directly into the furnace.
Key Applications and Operational Model
Rotary furnaces are versatile and are chosen for specific processes where their unique capabilities provide a distinct advantage.
Processing Powders and Granules
Their ability to mix and heat simultaneously makes them ideal for processing any kind of particulate matter. This ensures that every granule or powder particle undergoes the exact same thermal cycle, resulting in a homogenous final product.
Smelting and Batch Processing
Operation is typically done in batches. A worker charges the furnace with material, allows it to smelt or process for a set time period (often 4–6 hours), and then taps the furnace to remove the finished product and byproducts. This straightforward, cyclical process can often be managed by relatively unskilled operators.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary furnace design comes with specific trade-offs that make it more suitable for some applications than others. Understanding these is crucial for making an informed decision.
Strength: Batch Consistency
The primary strength is unparalleled consistency within a single batch. For high-value materials where every particle must be treated identically, the rotary furnace is often the superior choice.
Limitation: Mechanical Complexity
The rotation mechanism, including the drive gear and the seals required for atmosphere control, adds mechanical complexity compared to a simple static box furnace. This introduces additional points of maintenance over the furnace's lifetime.
Limitation: Batch vs. Continuous Flow
The standard operational model is batch-based. This is perfect for many applications but may be less efficient than a continuous conveyor-style furnace for certain high-volume, uninterrupted production lines.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace requires matching the technology to your material and processing objectives.
- If your primary focus is processing powders or granules with maximum uniformity: A rotary furnace is the ideal solution because its continuous mixing action eliminates temperature inconsistencies.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature treatment in a controlled atmosphere: The design's ability to expose all material surfaces to the gas makes it highly efficient and effective for sintering or reduction reactions.
- If your primary focus is processing a single large object or you require a continuous-feed operation: A static furnace or a conveyor-belt furnace may be a more appropriate choice for your specific workflow.
Ultimately, choosing a rotary furnace is a decision to prioritize product homogeneity and processing consistency above all else.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Rotating Barrel Design | Continuous mixing and agitation | Powders, granules, particulate matter |
| Uniform Heating | Eliminates hot/cold spots | High-temperature sintering, smelting |
| Batch Processing | Consistent product quality within a batch | Applications requiring precise homogeneity |
| Atmosphere Control | Efficient gas diffusion and consumption | Processes in reducing or controlled atmospheres |
Achieve Unmatched Batch Consistency with KINTEK
Does your process demand perfect uniformity for powders, granules, or other particulate materials? The continuous mixing action of a rotary furnace is the key to eliminating temperature gradients and ensuring every particle receives identical heat treatment.
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment, including rotary furnaces designed for superior performance in controlled atmosphere processing, sintering, and more. Our solutions help you achieve homogenous results and improve your process efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK rotary furnace can meet your specific laboratory needs and enhance your product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- What is a rotary retort furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- At what temperature does wood pyrolysis begin? Control the Process for Biochar, Bio-Oil, or Syngas



















