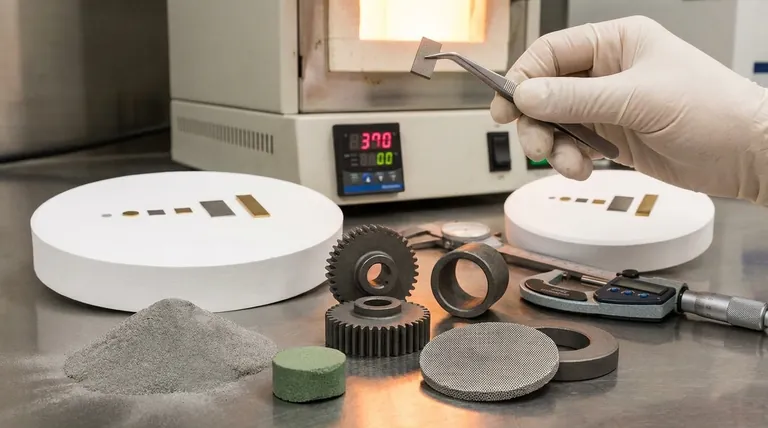
In essence, a sintered metal is a solid component created by compacting metal powder and heating it to just below its melting point. This process, known as sintering, fuses the individual particles together through atomic diffusion, resulting in a strong, precise, and often complex part without ever melting the material into a liquid state.
Sintering is a manufacturing method that transforms metal powder into a solid object. It is chosen for its unique ability to create intricate, net-shape parts at scale, offering a powerful alternative to traditional machining or casting for specific applications.

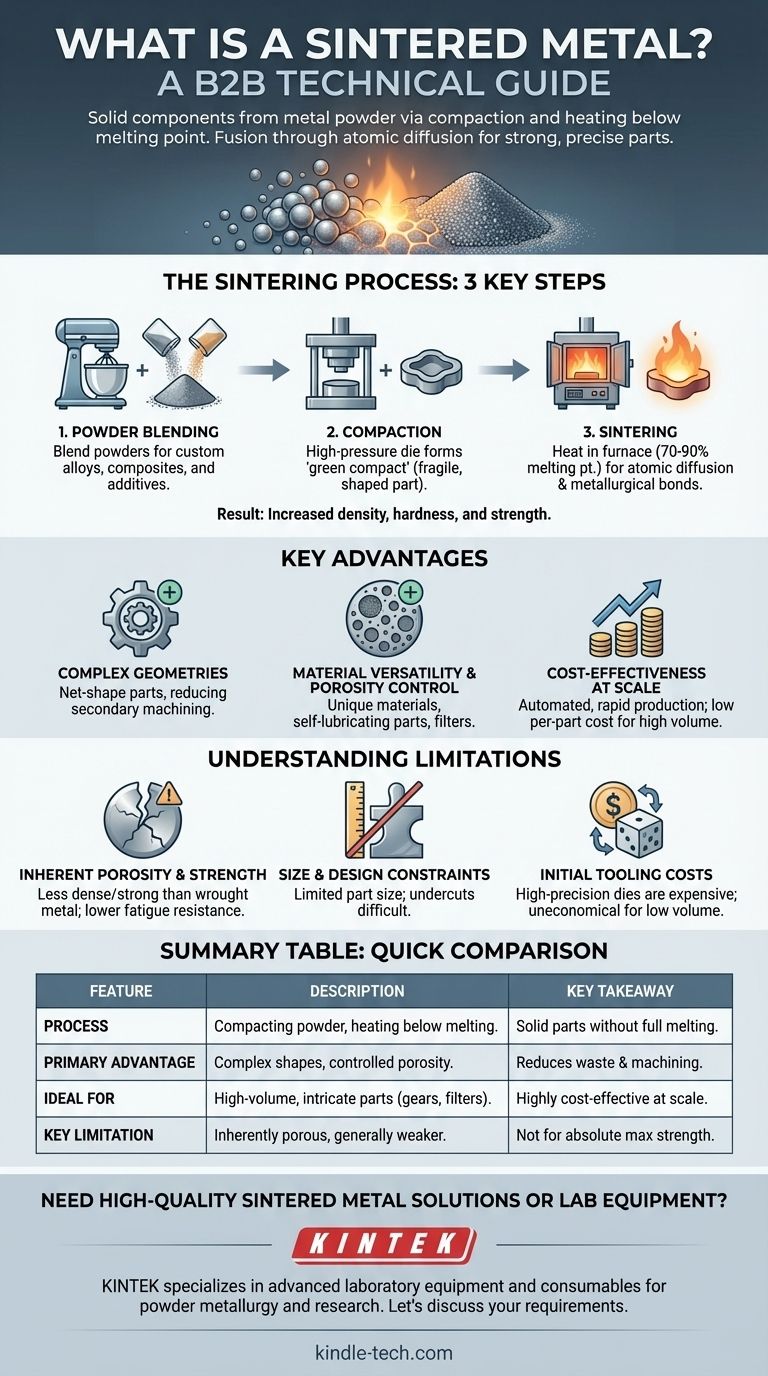
The Sintering Process: From Powder to Solid Part
Sintering is the final and most critical stage of a broader manufacturing discipline called powder metallurgy. The entire process consists of three primary steps.
Step 1: Powder Blending
Before any shaping occurs, raw metal powders are precisely blended. This allows for the creation of custom alloys or composites that would be difficult or impossible to produce through melting. Other additives, such as lubricants, can also be mixed in to aid in the next step.
Step 2: Compaction
The blended powder is poured into a high-precision die and compacted under immense pressure, typically at room temperature. This action forces the powder into the desired shape, creating a fragile, weakly bonded object known as a "green compact." This part has the shape of the final product but none of its strength.
Step 3: Sintering
The green compact is placed in a controlled-atmosphere furnace and heated to a high temperature, usually around 70-90% of the metal's absolute melting point. At this temperature, the particles fuse together at their contact points. Atomic diffusion across the particle boundaries creates strong metallurgical bonds, significantly increasing the part's density, hardness, and strength.
Why Choose Sintered Metals? Key Advantages
Sintering is not a universal solution, but it offers distinct advantages that make it the ideal choice for certain engineering challenges.
Creating Complex Geometries
Sintering excels at producing parts with complex shapes, internal voids, or specific density requirements directly from the die. This is a "net-shape" or "near-net-shape" process, meaning it drastically reduces or eliminates the need for secondary machining, saving time and material waste.
Material Versatility and Porosity Control
The process allows for the production of unique materials, including metal-matrix composites and alloys with very high melting points. Crucially, sintering enables precise control over the final part's porosity. This is leveraged to create self-lubricating bearings (where pores hold oil) or filters.
Cost-Effectiveness at Scale
While the initial cost for tooling and dies can be high, the process is highly automated and rapid. For high-volume production runs, the per-part cost becomes extremely low compared to machining each component individually.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
To use sintering effectively, you must understand its inherent compromises. Not all parts are suitable for this manufacturing method.
Inherent Porosity and Strength
Unless secondary operations are performed, sintered parts almost always retain some level of porosity. This means they are typically less dense and have lower tensile strength and fatigue resistance compared to parts forged or machined from solid metal bar stock.
Size and Design Constraints
The need to compact powder in a die places limitations on part size and geometry. Very large parts are difficult to produce, and certain features like undercuts or threads perpendicular to the pressing direction cannot be formed directly.
Initial Tooling Costs
The high-precision dies required for compaction are expensive to design and manufacture. This makes powder metallurgy uneconomical for low-volume production or one-off prototypes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a manufacturing process requires aligning its capabilities with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of small, complex parts: Sintering offers an unmatched combination of cost-effectiveness and repeatable dimensional accuracy.
- If your primary focus is creating a self-lubricating or porous component: Sintering is the ideal and often only method to precisely control porosity for applications like filters or oil-impregnated bearings.
- If your primary focus is absolute maximum strength and impact resistance: A part forged or fully machined from a solid billet is a more appropriate choice.
By understanding its unique process and trade-offs, you can leverage sintering as a powerful and economical solution for the right engineering problem.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Compacting metal powder and heating it below its melting point. | Creates solid parts without full melting. |
| Primary Advantage | Excellent for complex, net-shape parts and controlled porosity. | Reduces waste and secondary machining. |
| Ideal For | High-volume production of small, intricate components like gears, filters, and bearings. | Highly cost-effective at scale. |
| Key Limitation | Parts are inherently porous, generally weaker than wrought metals. | Not ideal for applications requiring absolute maximum strength. |
Need High-Quality Sintered Metal Parts or Lab Equipment?
Sintering is a powerful solution for creating complex, cost-effective metal components. KINTEK specializes in supplying the advanced laboratory equipment and consumables essential for research, development, and quality control in powder metallurgy and materials science.
Whether you are developing new sintered materials or need reliable tools for your lab, we provide the precision and support you need to succeed.
Let's discuss your specific requirements. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory or manufacturing challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Gold Platinum Copper Iron Metal Sheets
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Acid and Alkali Resistant Chemical Powder Material Scoops
- Custom Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Cleaning Racks
People Also Ask
- What materials are sintered steel? Unlock the Secrets of Powder-Based Steel Manufacturing
- What are the benefits of staying updated with the latest ULT freezer technologies? Save Costs & Boost Sustainability
- What are the safety procedures for a water bath? A Guide to Preventing Electrical, Thermal, and Contamination Risks
- Why is a high-power ultrasonic homogenizer essential for cellulose-graphene hybrids? Unlock Superior Material Uniformity
- What is the function of a forced air drying oven in Ni/CN catalyst recovery? Maximize Reuse Efficiency
- What is the HIP process of metal? Achieve Perfect Density for Critical Components
- What is the primary function of an ultrasonic cleaner or homogenizer? Ensure Optimal TiO2 Gold Loading
- What is a laboratory heater? A Guide to Precision, Safety, and Choosing the Right Type



















