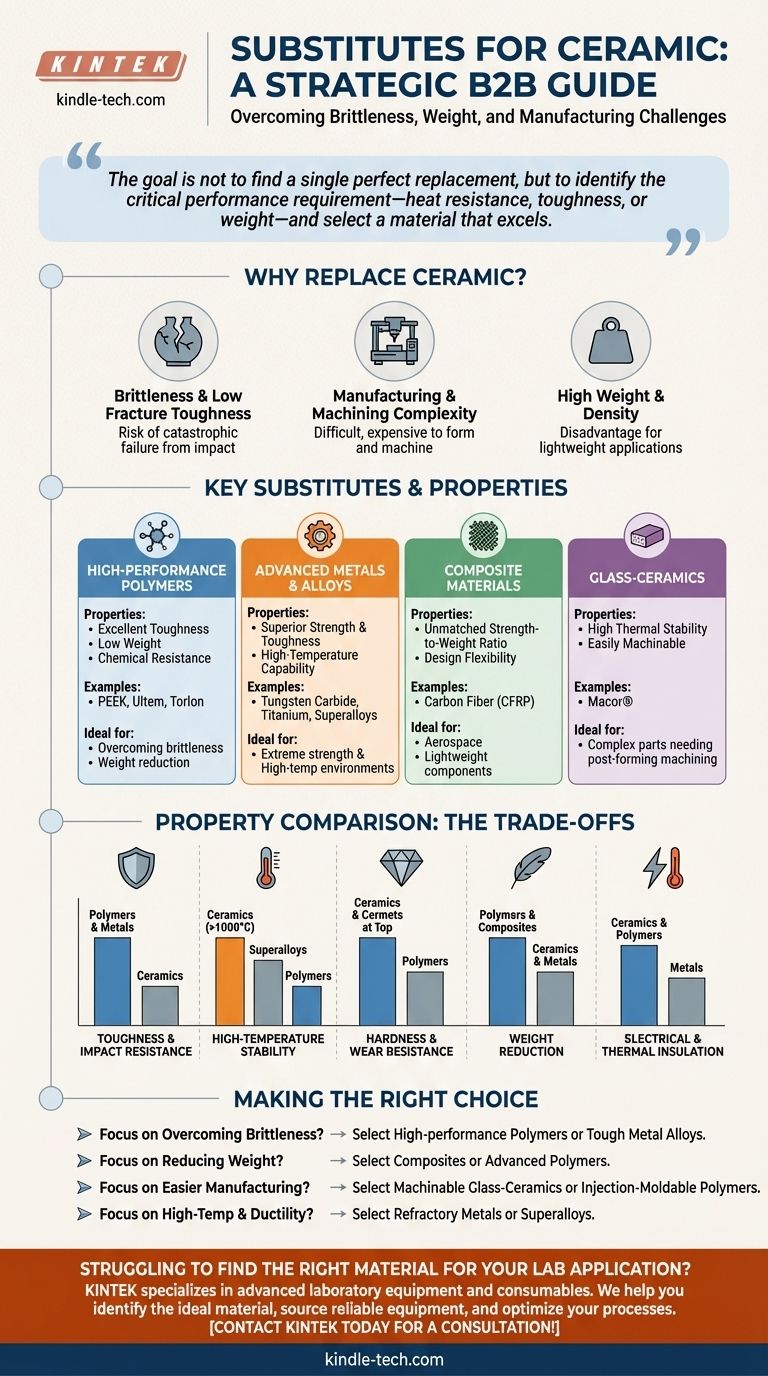
The primary substitutes for ceramic are high-performance polymers, advanced metal alloys, and composite materials. Each class of material offers a different profile of properties, allowing you to overcome common ceramic limitations like brittleness, weight, or manufacturing difficulty. The ideal choice depends entirely on which specific characteristic of ceramic you need to replace or improve upon for your application.
The search for a ceramic substitute is not about finding a single material that does everything a ceramic can do. It is about identifying the critical performance requirement for your specific application—be it heat resistance, toughness, or weight—and selecting an alternative material that excels in that area while accepting a series of calculated trade-offs.
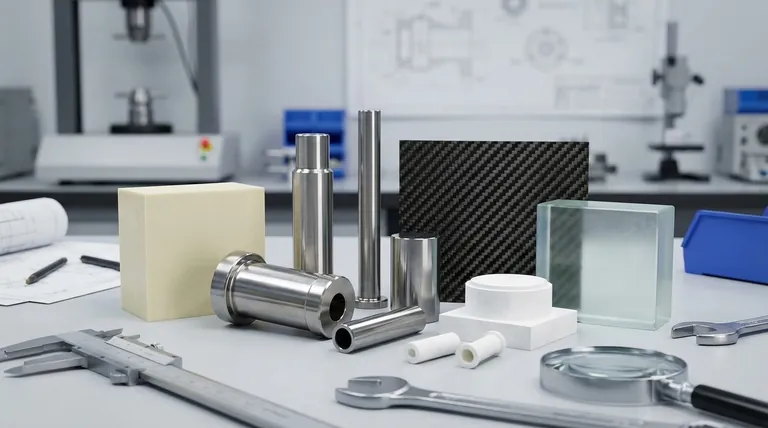

Why Replace Ceramic in the First Place?
While invaluable for their hardness and thermal stability, traditional ceramics present engineering challenges that often prompt the search for alternatives. Understanding these drawbacks is the first step in finding the right substitute.
The Brittleness Problem
The most significant limitation of many technical ceramics is their low fracture toughness, or brittleness. They are incredibly strong under compression but can fail suddenly and catastrophically when subjected to impact, tensile stress, or thermal shock.
Manufacturing and Machining Complexity
Ceramics are typically formed into their final shape before a high-temperature firing process called sintering. Once fired, their extreme hardness makes them very difficult and expensive to machine, often requiring diamond grinding tools and long processing times.
Weight and Density
For applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in aerospace or automotive components, the relatively high density of many ceramics can be a disadvantage compared to lighter alternatives.
Key Substitutes and Their Properties
The best substitute depends entirely on the application's demands. Below are the primary categories of materials used to replace ceramics, each with a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages.
High-Performance Polymers
These advanced plastics offer a compelling combination of chemical resistance, low weight, and manufacturability. They are often the first choice when the primary goal is to improve toughness and reduce weight.
Examples include PEEK (Polyetheretherketone), Ultem (PEI), and Torlon (PAI). They provide excellent strength, wear resistance, and maintain their properties at continuously elevated temperatures (typically 150°C to over 250°C), though not as high as ceramics.
Advanced Metals & Alloys
When extreme strength and toughness are non-negotiable, metals are a clear alternative. They are fully dense, handle impact exceptionally well, and can operate at very high temperatures.
Tungsten Carbide, often called a cermet (ceramic-metal), offers hardness approaching that of ceramic but with significantly better toughness. Titanium alloys provide an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, while superalloys like Inconel are designed for extreme-temperature environments where ceramics might otherwise be used.
Composite Materials
Composites, such as carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP), offer an unparalleled strength-to-weight ratio. They provide a unique ability to tailor material properties by controlling fiber orientation and resin choice.
This design flexibility allows for the creation of lightweight components that are incredibly stiff and strong in specific directions. Their primary limitations are often higher material costs and complex manufacturing processes.
Glass-Ceramics
This unique subclass of materials, like Macor®, begins as glass and is converted into a crystalline ceramic. This process results in a material that has many of the benefits of a technical ceramic—high service temperature, thermal insulation, and no porosity—but with one critical advantage: it is easily machinable with standard metalworking tools.
Understanding the Trade-offs: A Property Comparison
Selecting a material requires a clear-eyed view of its compromises. No substitute is perfect; each excels in different areas.
For Toughness and Impact Resistance
This is the biggest weakness of ceramics. High-performance polymers and metal alloys are vastly superior, absorbing energy and deforming before they fracture. This makes them ideal for components that will experience vibration or impact.
For High-Temperature Stability
Ceramics remain the champions of extreme-heat applications (often >1000°C). Superalloys are the next best choice, while the operating ceiling for even the most advanced polymers is significantly lower.
For Hardness and Wear Resistance
Technical ceramics and cermets like tungsten carbide are at the top for hardness and resistance to abrasive wear. While some polymers have excellent wear properties, they cannot match the surface hardness of a true ceramic.
For Weight Reduction
This is a clear win for polymers and composites. They offer substantial weight savings over both ceramics and metals, making them essential for aerospace, transportation, and medical applications.
For Electrical and Thermal Insulation
Both ceramics and polymers are excellent electrical insulators, a key reason they are used in electronic components. Metals, by contrast, are conductors. For thermal insulation, ceramics and polymers again perform well, while metals conduct heat readily.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To move forward, shift your focus from finding a direct replacement to solving your specific engineering problem.
- If your primary focus is overcoming brittleness and impact failure: High-performance polymers (like PEEK) or tough metal alloys (like titanium) are your best candidates.
- If your primary focus is reducing component weight: Carbon fiber composites and advanced polymers offer the most significant weight savings.
- If your primary focus is easier and faster manufacturing: Machinable glass-ceramics (like Macor) or injection-moldable polymers provide a direct path to lower production costs.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance with better ductility: Refractory metals or nickel-based superalloys are the logical choice.
By analyzing your application's specific property requirements, you can confidently select a material that provides the optimal balance of performance, manufacturability, and cost.
Summary Table:
| Material Substitute | Key Advantages | Common Trade-offs | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Performance Polymers | Excellent toughness, lightweight, chemical resistance | Lower temperature resistance than ceramics | Overcoming brittleness, weight reduction |
| Advanced Metal Alloys | Superior strength & toughness, high-temperature capability | Higher density, electrically conductive | Extreme strength & high-temp environments |
| Composite Materials | Unmatched strength-to-weight ratio, design flexibility | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | Aerospace, lightweight components |
| Glass-Ceramics | High thermal stability, easily machinable | Lower fracture toughness than some ceramics | Complex parts requiring post-forming machining |
Struggling to find the right material for your specific lab application?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced laboratory equipment and consumables tailored to your research and production needs. Whether you're working with high-performance polymers, advanced alloys, or composite materials, our expertise can help you select the perfect solution to overcome the limitations of traditional ceramics.
We help you:
- Identify the ideal material based on your specific requirements for toughness, temperature resistance, weight, and manufacturability.
- Source reliable equipment for processing and testing these advanced materials.
- Optimize your processes to ensure performance and cost-efficiency.
Let our experts guide you to a material solution that enhances your project's success. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Does higher heat capacity mean higher melting point? Unraveling the Critical Difference
- What are 4 disadvantages of brazing? Understanding the Critical Limitations of This Joining Method
- What are the disadvantages of brazing? Understanding the key limitations and trade-offs.
- Why is Boron Nitride utilized as a coating for graphite molds? Protect Your Mo-Na Powder During Sintering
- What is the function of a BN inner liner in a graphite mold during Flash Sintering? Master Precise Current Control



















