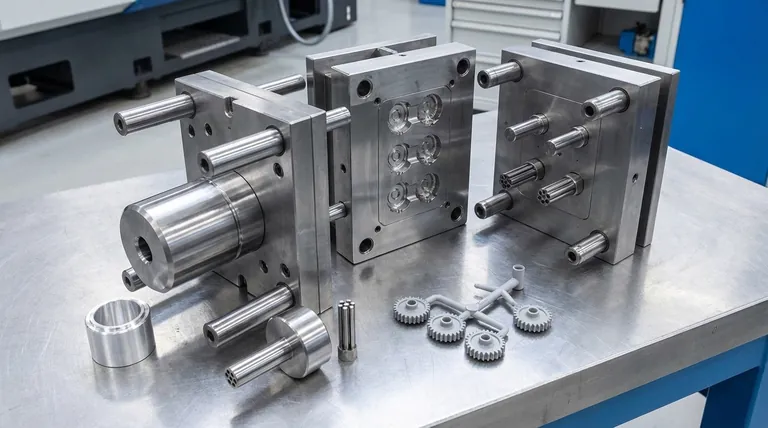
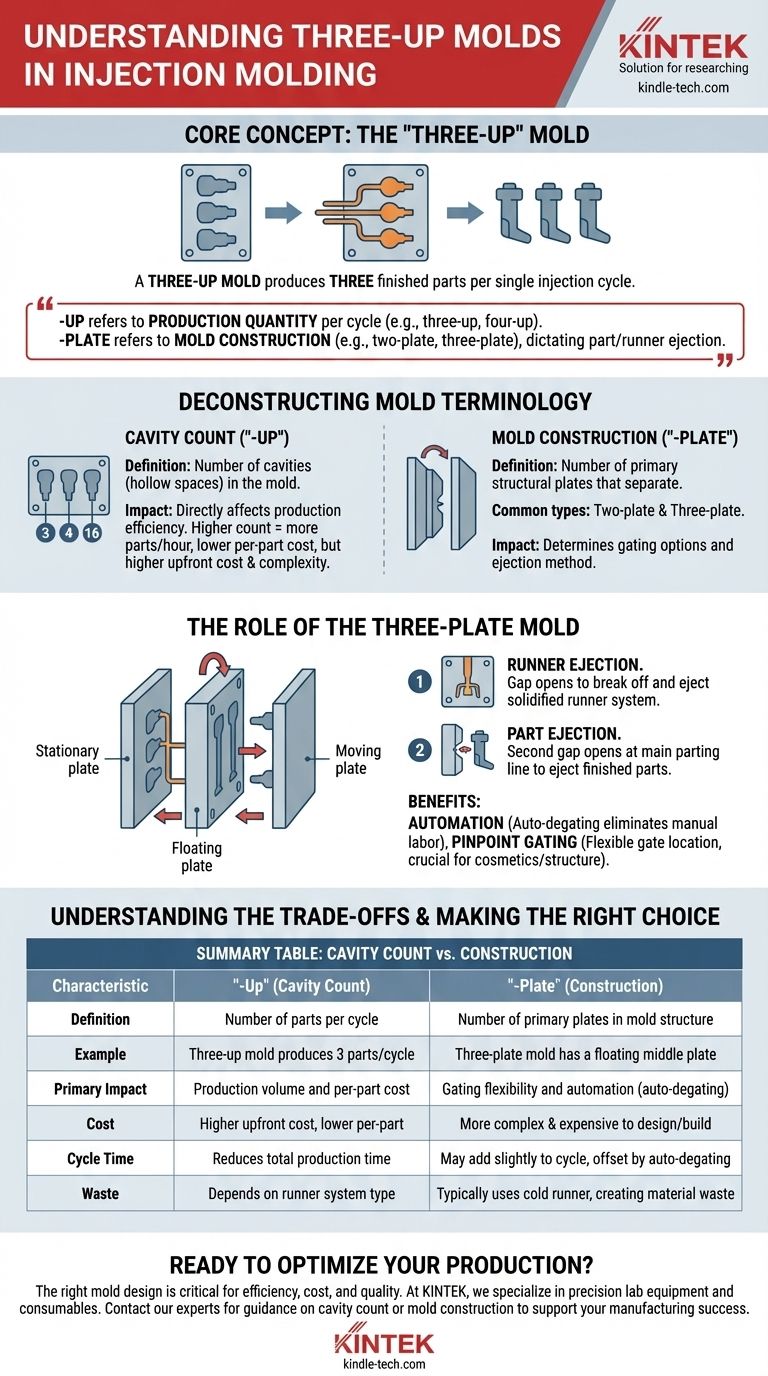
In injection molding, the term "three-up" refers to the number of cavities in the mold. A three-up mold is a tool designed to produce three finished parts with every single injection cycle. This terminology is distinct from a "three-plate" mold, which describes the mechanical construction of the tool itself, not the quantity of parts it produces.
The core distinction is simple: "-up" refers to production quantity per cycle (e.g., three-up, four-up), while "-plate" refers to the mold's physical construction (e.g., two-plate, three-plate), which dictates how parts and plastic runners are ejected.

Deconstructing Mold Terminology
To make informed decisions in manufacturing, it's critical to understand the precise language used to describe tooling. The terms "-up" and "-plate" define two separate, fundamental characteristics of an injection mold.
The Cavity Count ("-Up")
A cavity is the hollow space in the mold that forms the shape of the final part.
The term "-up" is industry shorthand for how many cavities a mold contains. A three-up mold has three cavities. A sixteen-up mold has sixteen cavities.
This number directly impacts production efficiency. A higher cavity count produces more parts per hour, reducing the per-part cost, but it also increases the upfront cost and complexity of the mold.
The Mold Construction ("-Plate")
The term "-plate" describes the primary plates that make up the mold's structure and separate when it opens. The most common types are two-plate and three-plate designs.
A three-plate mold is a more complex design used to solve specific manufacturing challenges. It consists of a stationary side, a floating plate in the middle, and the moving side.
The Role of the Three-Plate Mold
The reference material you provided describes a three-plate mold, which is an excellent example of how mold construction impacts the manufacturing process.
The Two-Plane Runner System
A three-plate mold uses a runner system—the channels that guide molten plastic to the cavities—that exists on a different plane from the parts themselves.
This separation is the defining feature of the design. It allows for greater flexibility in where the plastic enters the part.
The Sequential Opening Action
When a three-plate mold opens, it does so in two distinct stages.
First, a gap opens to break off and eject the solidified runner system. Then, a second gap opens at the main parting line to eject the finished parts.
Why Choose a Three-Plate Design?
The primary advantage is automation. This design automatically separates, or "de-gates," the parts from their runners. This eliminates the need for a secondary manual or robotic operation, streamlining the production line.
It also allows for pin-point gating, meaning the plastic can be injected at nearly any point on the part's surface, which is crucial for cosmetic or structural reasons where edge gating is undesirable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single design is perfect for every application. Choosing between a simple two-plate mold and a more advanced three-plate design involves clear trade-offs.
Complexity and Cost
A three-plate mold is mechanically more complex than a standard two-plate mold. It requires more components, more precise engineering, and is therefore more expensive to design and build.
Cycle Time Considerations
The dual-opening motion of a three-plate mold can sometimes add slightly to the overall cycle time. However, this is often offset by the time saved from not needing a secondary de-gating process.
Runner Waste
Three-plate molds typically use a cold runner system, as described in the reference. This means the plastic in the runner cools and is ejected with every cycle, creating material waste that must be ground up and recycled or discarded.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your tooling decisions should be driven by the specific goals of your project, balancing part cost, tool cost, and quality requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximizing production volume: Increasing the cavity count (e.g., moving from a two-up to an eight-up mold) is your most direct path to higher output.
- If your primary focus is automation and gate location flexibility: A three-plate mold construction is an excellent choice, as it automatically separates parts from runners and allows for precise gating.
- If your primary focus is minimizing upfront tooling cost and complexity: A simple two-plate, single-cavity ("one-up") mold is the most straightforward and least expensive option.
Ultimately, understanding this terminology empowers you to specify the exact tool needed to achieve your manufacturing objectives.
Summary Table:
| Mold Characteristic | "-Up" (Cavity Count) | "-Plate" (Construction) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Number of parts produced per cycle | Number of primary plates in the mold structure |
| Example | Three-up mold produces 3 parts/cycle | Three-plate mold has a floating middle plate |
| Primary Impact | Production volume and per-part cost | Gating flexibility and automation (auto-degating) |
Ready to optimize your injection molding production? The right mold design is critical for efficiency, cost, and part quality. At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment and consumables, supporting manufacturing innovation. Whether you need guidance on cavity count or mold construction for your project, our experts are here to help. Contact us today to discuss your specific tooling requirements and discover how we can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
- Multi-Punch Rotary Tablet Press Mold Ring for Rotating Oval and Square Molds
- Round Bidirectional Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- How do ECAP molds and pressure equipment enhance FM steel? Master Microstructural Refinement & Grain Strength
- How to mold pottery clay? Master Wedging for Perfect, Air-Free Results
- How to compression mold? A Guide to Creating High-Strength, Large Parts
- What role do graphite molds serve during the vacuum hot pressing of titanium? Achieve Precision Densification
- What is the core function of a Graphite Mold in Ti-6Al-4V hot-pressing? Enhance Your Material Densification
- What are the advantages of two plate Mould? Simpler Design, Faster Production, Lower Cost
- How should KBr powder be pre-treated before it is used to make a pellet? Optimize Your FTIR Spectra Quality
- What are the primary functions of graphite molds in hot-pressing sintering? Achieve Precision in Silicon Nitride Ceramic



















