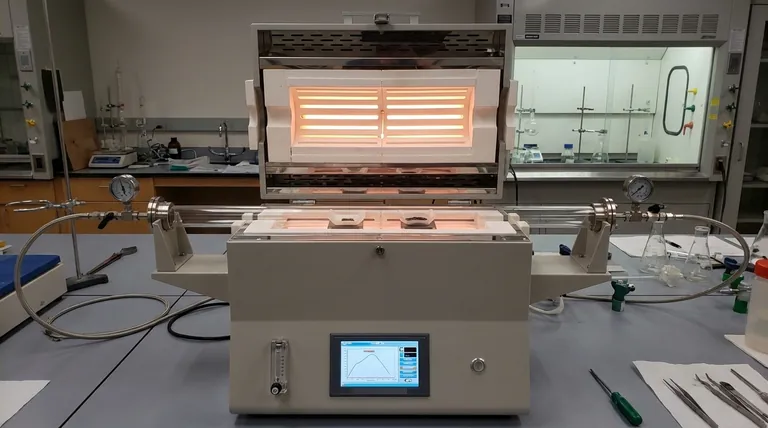
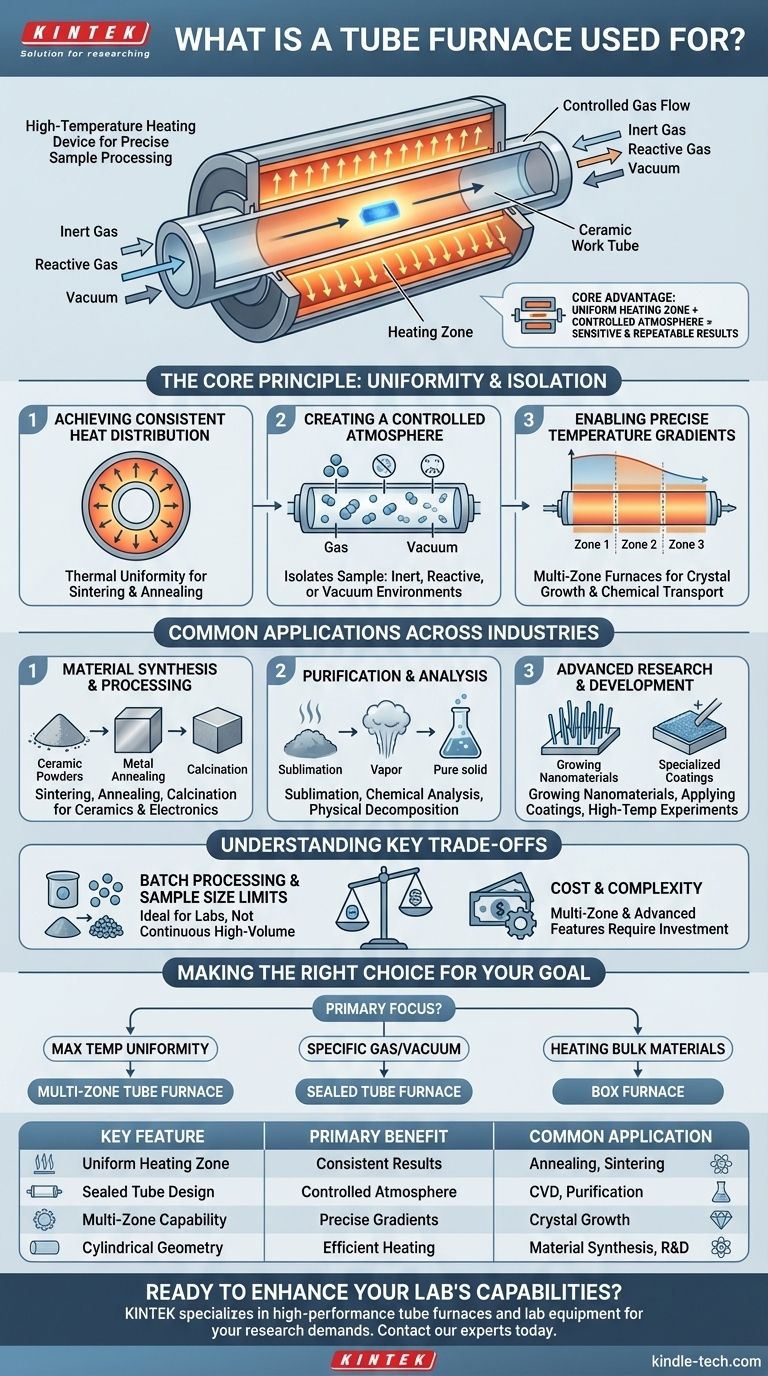
At its core, a tube furnace is a high-temperature heating device used for processing small samples with exceptional precision. It is widely employed in scientific research and industrial settings for a vast range of thermal processes, including annealing, sintering, purification, chemical analysis, and the synthesis of new materials within a highly controlled environment.
The essential advantage of a tube furnace is not just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its capacity to create a highly uniform heating zone within a sealed, controlled atmosphere, which is critical for sensitive and repeatable results.

The Core Principle: Uniformity and Isolation
The unique cylindrical design of a tube furnace is what provides its primary benefits. Unlike a box furnace which heats a larger chamber, a tube furnace concentrates its energy on a sample held within a narrow tube.
Achieving Consistent Heat Distribution
The heating elements surround a cylindrical tube, typically made of ceramic, quartz, or a metal alloy. This geometry allows for incredibly even heat distribution around the circumference of the sample.
This thermal uniformity is crucial for processes like sintering or annealing, where even minor temperature variations across the sample can lead to defects or inconsistent material properties.
Creating a Controlled Atmosphere
The tube can be sealed at both ends, isolating the sample from the outside air. This allows operators to create a specific processing atmosphere.
You can introduce inert gases like argon to prevent oxidation, reactive gases for chemical vapor deposition (CVD), or create a vacuum for processes like degassing. This level of atmospheric control is impossible in a standard oven.
Enabling Precise Temperature Gradients
Advanced multi-zone tube furnaces have separate heating element sections along the length of the tube.
This allows for the creation of a stable, well-defined temperature gradient. This is essential for specialized processes like crystal growth or certain types of chemical transport reactions where temperature must change predictably over a distance.
Common Applications Across Industries
The combination of uniform heating and atmospheric control makes the tube furnace indispensable in numerous fields, from metallurgy and electronics to materials science and chemistry.
Material Synthesis and Processing
This is the most common category of use. Applications include sintering ceramic powders into a solid form, annealing metals to increase their ductility, and calcination to thermally decompose materials.
Industries like ceramics, electronics, and refractories rely on these furnaces for developing and treating specialized materials.
Purification and Analysis
Tube furnaces are ideal for purifying materials through processes like sublimation, where a solid is vaporized and then re-condensed in a purer form.
They are also used for chemical analysis and physical decomposition studies, where a sample's reaction to heat in a specific environment provides critical data.
Advanced Research and Development
In universities and R&D labs, tube furnaces are workhorses for creating novel materials. They are used for growing nanowires, applying specialized coatings to substrates, and performing high-temperature experiments under precisely controlled conditions.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
While powerful, a tube furnace is a specialized tool with inherent limitations that make it suitable for some tasks but not others.
Batch Processing vs. Continuous Flow
A tube furnace is fundamentally a batch processing instrument. Samples must be loaded, the process must be run, and then the samples must be cooled and unloaded. It is not designed for continuous, high-volume manufacturing.
Sample Size Limitations
The processing capacity is strictly limited by the diameter and length of the work tube. This makes them ideal for labs and small-scale production but impractical for processing very large parts or bulk materials.
Cost and Complexity
While simple single-zone furnaces are common, multi-zone furnaces that offer precise temperature gradients and advanced atmospheric controls represent a significant investment in both cost and operational complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing equipment depends entirely on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature uniformity for a small, sensitive sample: A multi-zone tube furnace is the superior choice for exacting control.
- If your primary focus is processing materials in a specific gas or vacuum: The sealed environment of a tube furnace makes it the only viable option.
- If your primary focus is simply heating bulk materials or large parts in air: A less complex and larger capacity box furnace is likely the more practical and cost-effective tool.
Ultimately, a tube furnace is the definitive instrument when your process demands precise, repeatable control over both temperature and atmosphere in a contained environment.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Primary Benefit | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Uniform Heating Zone | Consistent, repeatable results | Annealing, Sintering |
| Sealed Tube Design | Controlled atmosphere (Inert/Reactive/Vacuum) | CVD, Purification, Oxidation Prevention |
| Multi-Zone Capability | Precise temperature gradients | Crystal Growth, Chemical Transport Reactions |
| Cylindrical Geometry | Efficient heating of small samples | Material Synthesis, R&D |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precise thermal processing?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance tube furnaces and lab equipment, providing the exact control and reliability your research or production demands. Whether you need uniform heating for sintering, a controlled atmosphere for synthesis, or multi-zone gradients for advanced R&D, our solutions are designed for your success.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect tube furnace for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How is the temperature in a tube furnace measured and controlled? Master Precise Thermal Processing
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis



















