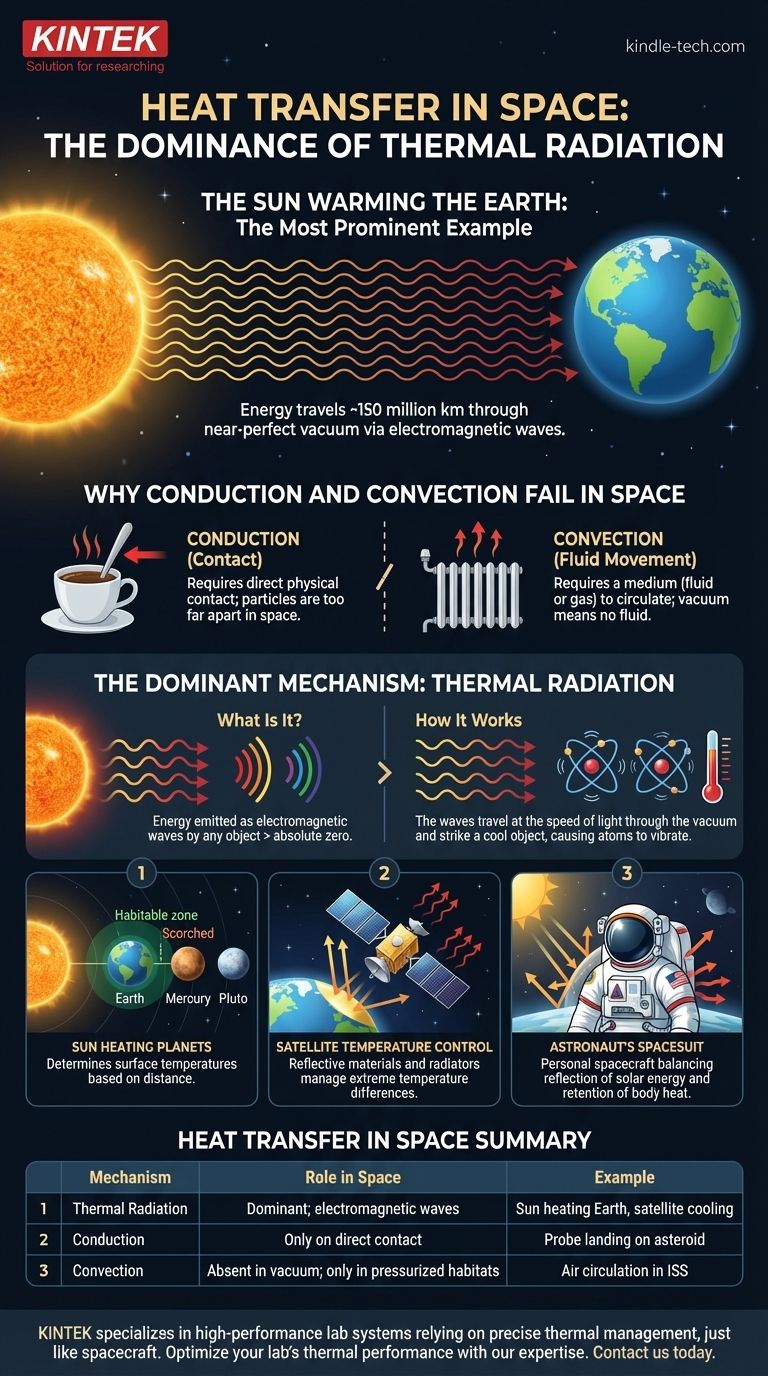
The most prominent example of heat transfer in space is the Sun warming the Earth. Despite being separated by approximately 150 million kilometers of near-perfect vacuum, the Sun's immense energy travels across this void, is absorbed by our planet, and makes life possible. This process occurs without any physical medium connecting the two bodies.
Unlike on Earth where heat can transfer through touch (conduction) or fluid currents (convection), space is a near-perfect vacuum. Therefore, heat transfer between distant objects in space occurs almost exclusively through a single, powerful mechanism: thermal radiation.

The Dominant Mechanism: Thermal Radiation
To understand heat in space, you must first understand that it doesn't "travel" in the way we typically imagine. Instead, energy is emitted from one object and absorbed by another.
What Is Thermal Radiation?
Every object with a temperature above absolute zero (−273.15°C) emits energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. Hotter objects emit more energy and at a higher frequency.
Think of a hot electric stove burner. First, you feel its warmth from a distance (infrared radiation), and as it gets hotter, it begins to glow red (visible light radiation). The Sun is an unimaginably large and hot object doing the same thing, emitting energy across the entire electromagnetic spectrum.
How It Works in Space
These electromagnetic waves, or photons, do not require any medium to travel. They move freely through the vacuum of space at the speed of light.
When this radiation strikes an object—like a planet, an asteroid, or a spacecraft—the energy is absorbed. This absorption causes the atoms and molecules within the object to vibrate more rapidly, which we perceive and measure as an increase in temperature, or heat.
Everyday Examples in the Cosmos
This principle governs the temperature of everything in the universe, from planets to the equipment we send into orbit.
The Sun Heating Planets
The Sun constantly radiates thermal energy in all directions. The Earth, Mars, and every other body in our solar system intercepts a tiny fraction of this energy, which determines their surface temperatures. This is why Mercury is scorched and Pluto is frozen; it is a direct result of their distance from the Sun's radiation.
A Satellite's Temperature Control
Engineers designing satellites face a major challenge with thermal radiation. The side of a satellite facing the Sun can become dangerously hot, while the side facing deep space can become intensely cold.
To manage this, satellites are often covered in reflective materials, like gold or silver foil, to reflect unwanted solar radiation. They also use devices called radiators to shed excess heat from internal electronics as thermal radiation back into space.
An Astronaut's Spacesuit
A spacesuit is essentially a personal spacecraft designed to manage radiation. The outer layers are highly reflective to protect the astronaut from the Sun's direct energy. At the same time, the suit's insulation is critical for preventing the astronaut's own body heat from radiating away too quickly into the cold void of space.
Why Conduction and Convection Fail in Space
Your intuition about heat transfer is likely based on your experience on Earth, where conduction and convection are common. In the vacuum of space, these methods are almost entirely absent between distant objects.
The Problem with Conduction
Conduction is heat transfer through direct physical contact. It's why a metal spoon gets hot when you leave it in a cup of coffee.
Because the particles in space are, on average, millions of kilometers apart, there is no medium to conduct heat between the Sun and the Earth. Conduction only becomes relevant when two objects physically touch, such as when a probe lands on a moon.
The Problem with Convection
Convection is heat transfer through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases). It's how a radiator heats a room, by warming the air which then circulates.
Since space is a vacuum, there is no air, water, or other fluid to create convection currents. Convection is, however, a critical factor for transferring heat inside the pressurized, air-filled environment of the International Space Station.
Applying This Principle to Your Thinking
To correctly analyze heat transfer in any space scenario, you must first identify the environment. The distinction between heat transfer in a vacuum versus inside a pressurized habitat is critical.
- If your primary focus is how a star heats a planet: The mechanism is thermal radiation traveling through the vacuum.
- If you are considering how a docked spacecraft cools: It radiates its own heat away into deep space via thermal radiation.
- If you are analyzing heat from a computer inside the International Space Station: The primary mechanism is convection, as fans circulate air to carry the heat away to cooling systems.
Understanding that radiation governs heat transfer between objects in space is the key to grasping cosmic and spacecraft thermodynamics.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | Role in Space | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Radiation | Dominant method; transfers energy via electromagnetic waves | Sun heating Earth, satellite cooling |
| Conduction | Only occurs on direct contact (e.g., a lander touching a moon) | Probe landing on an asteroid |
| Convection | Absent in vacuum; relevant only inside pressurized habitats | Air circulation inside the International Space Station |
Need precise thermal management for your lab equipment? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab systems that rely on controlled heat transfer principles—just like spacecraft in orbit. Whether you require uniform heating, exact temperature control, or efficient cooling for your laboratory processes, our expertise ensures reliability and accuracy. Contact our experts today to optimize your lab's thermal performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- Why is environmental control within a vacuum furnace important for diffusion bonding? Master Titanium Alloy Laminates
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment
- What is the maximum temperature in a vacuum furnace? It Depends on Your Materials and Process Needs
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost


















