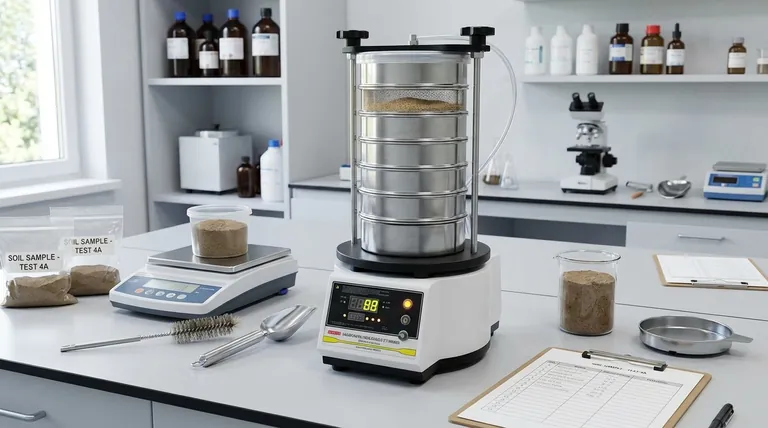
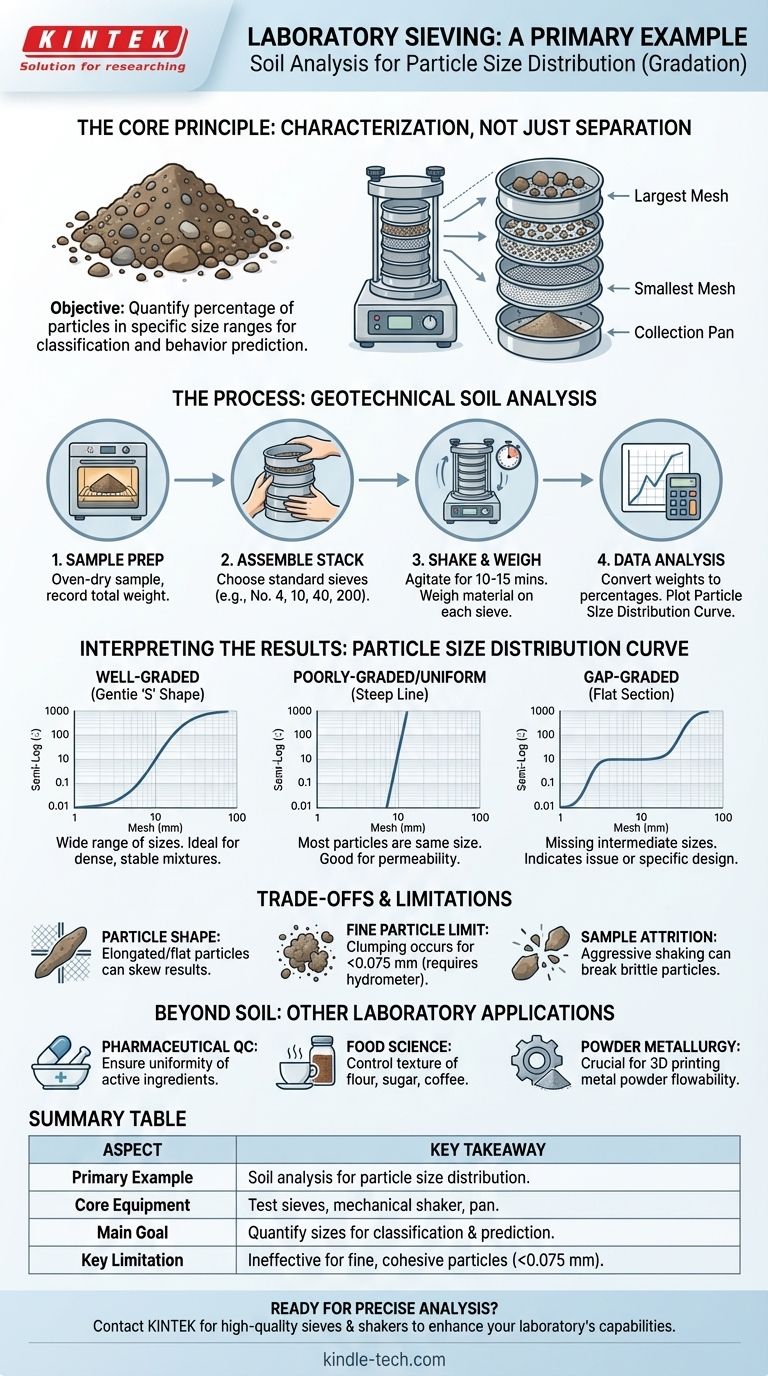
In a laboratory setting, a primary example of sieving is the analysis of a soil or sediment sample to determine its particle size distribution. This process, known as a sieve analysis, involves passing a known weight of dry material through a series of nested sieves with progressively smaller mesh openings. The result is not just separation, but a quantitative breakdown of the material into different size fractions, which is fundamental for classification and engineering purposes.
Sieving is more than just separating big particles from small ones; it's a foundational analytical technique for characterizing a material's physical makeup. Understanding a material's particle size distribution is critical for predicting its behavior, ensuring quality control, and meeting industry or scientific standards.

The Core Principle: What is Sieve Analysis?
Sieve analysis is a methodical process used to assess the grain size distribution (gradation) of a granular material.
The Goal: Characterization, Not Just Separation
The primary objective is to quantify the percentage of particles within specific size ranges. This data allows a scientist or engineer to classify the material (e.g., as well-graded gravel, poorly-graded sand) and predict its physical properties like strength, permeability, and compaction.
The Equipment: A Stack of Test Sieves
The core apparatus is a stack of test sieves—wire mesh screens held in a rigid frame. These are stacked in order of decreasing mesh size, with the largest openings at the top and the smallest at the bottom. A solid collection pan is placed at the very bottom, and a lid covers the top sieve.
The Process: Agitation and Segregation
For consistent and repeatable results, the sieve stack is typically placed in a mechanical sieve shaker. The shaker agitates the stack for a set period, causing particles to move and find their way down through the sieves until they are retained by a mesh they cannot pass.
A Practical Example: Geotechnical Soil Analysis
Let's walk through the most common laboratory application: analyzing a soil sample.
Step 1: Sample Preparation
A representative sample of soil is first oven-dried to remove all moisture. The total dry weight of the sample is carefully recorded before the analysis begins.
Step 2: Assembling the Sieve Stack
A standard set of sieves is chosen based on the expected material. For soils, this might include U.S. Standard Sieves like the No. 4 (4.75 mm), No. 10 (2.00 mm), No. 40 (0.425 mm), and No. 200 (0.075 mm). These specific sizes are boundaries between gravel, sand, and fine-grained soils (silts and clays).
Step 3: Shaking and Weighing
The prepared soil sample is poured into the top sieve, the lid is secured, and the stack is agitated in a mechanical shaker for 10-15 minutes. After shaking, the material retained on each individual sieve and in the collection pan is carefully removed and weighed.
Step 4: Data Analysis and Interpretation
The weight of material on each sieve is converted into a percentage of the total initial sample weight. This data is often plotted on a semi-log graph to create a particle size distribution curve. This curve provides a powerful visual summary of the soil's gradation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, sieving is not a perfect method. Understanding its limitations is crucial for accurate interpretation.
The Challenge of Particle Shape
Sieve analysis inherently assumes particles are roughly spherical. Elongated or flat particles can skew results by passing through mesh openings sideways, making them appear smaller than they actually are.
The Fine Particle Limit
Dry sieving becomes ineffective for very fine particles, such as silts and clays (typically smaller than 0.075 mm). These particles tend to clump together due to electrostatic forces and cohesion, preventing them from passing through the fine mesh. For these materials, a wet method like hydrometer analysis is required.
The Risk of Sample Attrition
Aggressive or prolonged shaking can cause brittle or friable particles (like shale or some minerals) to break apart. This attrition creates more fine material than was originally present, altering the true distribution.
Beyond Soil: Other Laboratory Applications
The principle of sieving is applied across many scientific and industrial fields.
Pharmaceutical Quality Control
Sieving is used to ensure the uniformity of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients. Particle size directly impacts dissolution rates and bioavailability, making it a critical quality attribute.
Food Science and Production
The texture and consistency of products like flour, sugar, coffee grounds, and spices are controlled through sieving. It ensures a consistent final product for the consumer.
Powder Metallurgy and Additive Manufacturing
In processes like 3D printing with metal, the particle size distribution of the metal powder is crucial. It dictates the powder's flowability and the final density and structural integrity of the printed part.
How to Interpret Sieve Analysis Results
The shape of the particle size distribution curve tells a story about the material.
- If your curve is well-graded (a gentle 'S' shape): This indicates a wide range of particle sizes is present, which is often desirable for creating dense, stable mixtures like concrete or structural fill.
- If your curve is poorly-graded or uniform (a steep, almost vertical line): This means most particles are roughly the same size, which is important for applications requiring high porosity and good drainage, like filter media.
- If your curve is gap-graded (has a flat section): This signifies that one or more intermediate particle sizes are missing, which can be an intentional design choice or an indicator of a processing or sourcing issue.
Ultimately, sieving provides a simple yet powerful window into a material's physical structure, enabling precise control and prediction of its real-world performance.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Example | Soil analysis to determine particle size distribution (gradation). |
| Core Equipment | Stack of test sieves, mechanical sieve shaker, collection pan. |
| Main Goal | Quantify particle sizes for material classification and behavior prediction. |
| Common Applications | Geotechnical engineering, pharmaceutical QC, food science, powder metallurgy. |
| Key Limitation | Ineffective for fine, cohesive particles (< 0.075 mm) without wet methods. |
Ready to achieve precise and reliable particle size analysis in your lab? The right equipment is fundamental to accurate results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality test sieves, mechanical sieve shakers, and consumables designed for consistent performance in geotechnical, pharmaceutical, and industrial applications. Let our experts help you select the perfect sieving solution for your specific needs. Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why is a standardized sieving system necessary for elephant grass research? Ensure Reliable Sample Consistency
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment
- What is the significance of using a fine sieving system for catalyst particles? Optimize Size for Maximum Reactivity
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution



















